Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Explain the effect of change in price of subs...
Start Learning for Free
Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.?
Verified Answer
Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary ...
Substitute Goods:
Substitute goods are those goods which can be used in place of one another for satisfaction of a particular want, like tea and coffee. Demand for a given commodity varies directly with the price of a substitute good. For example, if price of a substitute good (say, coffee) increases, then demand for given commodity (say, tea) will rise as tea will become relatively cheaper in comparison to coffee.
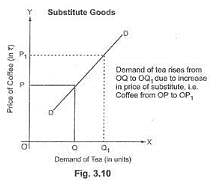
As seen in the given diagram, price of coffee (substitute good) is shown on the Y-axis and demand for tea (given commodity) on the X-axis. When price of coffee rises from OP to OP1, demand for tea also rises from OQ to OQ1.
Complementary Goods:
Complementary goods are those goods which are used together to satisfy a particular want. Demand for a given commodity varies inversely with the price of a complementary good. For example, if price of a complementary good (say, sugar) increases, then demand for given commodity (say, tea) will fall as it will be relatively costlier to use both the goods together.
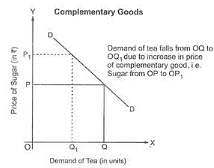
As seen in the given diagram, price of sugar (complementary good) is shown on the Y-axis and demand for tea (given commodity) on the X-axis. When the price of sugar rises from OP to OP1, demand for tea falls from OQ to OQ1.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary ...
Effect of Change in Price of Substitute and Complementary Goods
Substitute goods and complementary goods are important concepts in economics that impact the demand and pricing of products. A substitute good is one that can be used as an alternative to another good, while a complementary good is one that is consumed alongside another good. When the price of a substitute or complementary good changes, it can have both direct and indirect effects on the demand and pricing of the related goods. Let's analyze the effects using a table and diagram.
Effect of Change in Price of Substitute Goods:
A substitute good can be seen as a close competitor to another product. When the price of a substitute good changes, it affects the demand for the related product in the following ways:
1. Direct Effect:
- If the price of the substitute good increases, the demand for the related product will generally increase. Consumers will switch to the cheaper alternative, resulting in a higher demand for the related good.
- Conversely, if the price of the substitute good decreases, the demand for the related product will generally decrease. Consumers will prefer the cheaper alternative, leading to a lower demand for the related good.
2. Indirect Effect:
- The change in demand of the related good due to a change in price of the substitute good can also affect the price of the related good. If the demand for the related good increases, the price may also increase due to increased competition for the product.
- On the other hand, if the demand for the related good decreases, the price may decrease as producers try to attract consumers with lower prices.
Effect of Change in Price of Complementary Goods:
Complementary goods are products that are consumed together or enhance the use of each other. When the price of a complementary good changes, it can affect the demand for the related product in the following ways:
1. Direct Effect:
- If the price of the complementary good increases, the demand for the related product will generally decrease. Consumers may find it less affordable to consume both goods together, resulting in a lower demand for the related good.
- Conversely, if the price of the complementary good decreases, the demand for the related product will generally increase. Consumers may be more willing to purchase both goods together, leading to a higher demand for the related good.
2. Indirect Effect:
- The change in demand of the related good due to a change in price of the complementary good can also impact the price of the related good. If the demand for the related good decreases, the price may decrease as producers try to stimulate demand by offering lower prices.
- Conversely, if the demand for the related good increases, the price may increase as producers take advantage of the increased demand and consumers' willingness to pay.
Conclusion:
Understanding the effects of changes in the price of substitute and complementary goods is crucial for businesses and consumers alike. It helps businesses strategize their pricing and marketing decisions, while consumers can make informed choices based on price differentials. By analyzing the direct and indirect effects, stakeholders can navigate the market dynamics and make rational decisions.
Substitute goods and complementary goods are important concepts in economics that impact the demand and pricing of products. A substitute good is one that can be used as an alternative to another good, while a complementary good is one that is consumed alongside another good. When the price of a substitute or complementary good changes, it can have both direct and indirect effects on the demand and pricing of the related goods. Let's analyze the effects using a table and diagram.
Effect of Change in Price of Substitute Goods:
A substitute good can be seen as a close competitor to another product. When the price of a substitute good changes, it affects the demand for the related product in the following ways:
1. Direct Effect:
- If the price of the substitute good increases, the demand for the related product will generally increase. Consumers will switch to the cheaper alternative, resulting in a higher demand for the related good.
- Conversely, if the price of the substitute good decreases, the demand for the related product will generally decrease. Consumers will prefer the cheaper alternative, leading to a lower demand for the related good.
2. Indirect Effect:
- The change in demand of the related good due to a change in price of the substitute good can also affect the price of the related good. If the demand for the related good increases, the price may also increase due to increased competition for the product.
- On the other hand, if the demand for the related good decreases, the price may decrease as producers try to attract consumers with lower prices.
Effect of Change in Price of Complementary Goods:
Complementary goods are products that are consumed together or enhance the use of each other. When the price of a complementary good changes, it can affect the demand for the related product in the following ways:
1. Direct Effect:
- If the price of the complementary good increases, the demand for the related product will generally decrease. Consumers may find it less affordable to consume both goods together, resulting in a lower demand for the related good.
- Conversely, if the price of the complementary good decreases, the demand for the related product will generally increase. Consumers may be more willing to purchase both goods together, leading to a higher demand for the related good.
2. Indirect Effect:
- The change in demand of the related good due to a change in price of the complementary good can also impact the price of the related good. If the demand for the related good decreases, the price may decrease as producers try to stimulate demand by offering lower prices.
- Conversely, if the demand for the related good increases, the price may increase as producers take advantage of the increased demand and consumers' willingness to pay.
Conclusion:
Understanding the effects of changes in the price of substitute and complementary goods is crucial for businesses and consumers alike. It helps businesses strategize their pricing and marketing decisions, while consumers can make informed choices based on price differentials. By analyzing the direct and indirect effects, stakeholders can navigate the market dynamics and make rational decisions.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.?
Question Description
Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.?.
Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.?.
Solutions for Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.?, a detailed solution for Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? has been provided alongside types of Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain the effect of change in price of substitute and complimentary goods with the help of table and diagram.? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























