Lexical Analysis | Compiler Design - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to Lexical Analysis |

|
| Token Definition |

|
| Lexical Analyzer in Action |

|
| Representation of Tokens |

|
Introduction to Lexical Analysis
- Lexical Analysis is the initial phase of the compiler, also known as a scanner.
- It converts high-level input programs into a sequence of Tokens.
- Implemented using Deterministic Finite Automata.
- The output is a sequence of tokens sent to the parser for syntax analysis.
Token Definition
A lexical token is a sequence of characters treated as a unit in the grammar of programming languages.
Tokens : It include type tokens (id, number, real), punctuation tokens (IF, void, return), alphabetic tokens (keywords like for, while, if), identifiers (variable name, function name), operators (+, ++, -), and separators (, ;).
Keywords; Examples-for, while, if etc.
Identifier; Examples-Variable name, function name etc.
Operators; Examples '+', '++', '-' etc.
Separators; Examples ',' ';' etc
Non-tokens: It include comments, preprocessor directives, macros, blanks, tabs, newline, etc.
Lexeme: A lexeme is the sequence of characters forming a token or a single token's input sequence (e.g., "float", "abs_zero_Kelvin", "=", "-", "273", ";").
- Input Preprocessing: Clean up input by removing comments, whitespace, and non-essential characters.
- Tokenization: Break input into tokens using patterns or regular expressions.
- Token Classification: Determine the type of each token (keywords, identifiers, operators).
- Token Validation: Check each token's validity according to language rules.
- Output Generation: Generate the final list of tokens for the next compilation or interpretation stage.
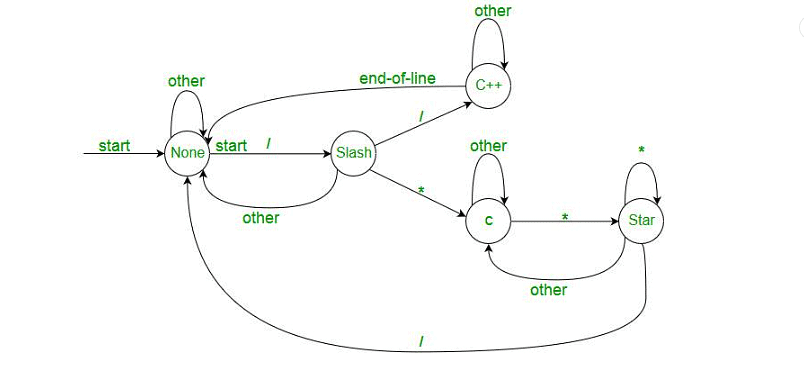
Lexical Analyzer in Action
- Identifies errors with the help of automation and language grammar, providing row and column numbers.
- Generates token sequences, e.g., for the statement "a = b + c;" it creates "id=id+id;" where each id refers to a variable in the symbol table.
For example, consider the program
int main()
{
// 2 variables
int a, b;
a = 10;
return 0;
}
All the valid tokens are:
'int' 'main' '(' ')' '{' '}' 'int' 'a' 'b' ';'
'a' '=' '10' ';' 'return' '0' ';' '}'- Above are the valid tokens.
- You can observe that we have omitted comments.
- As another example, consider below printf statement.
There are 5 valid token in this printf statement.
Exercise 1:
Count number of tokens :
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 20;
printf("sum is :%d",a+b);
return 0;
}
Answer: Total number of token: 27.
Exercise: Count number of tokens: int max(int i);
Answer: Lexical analyzer first read int and finds it to be valid and accepts as token.max is read by it and found to be a valid function name after reading (int is also a token , then again I as another token and finally.
Hence, Total number of tokens 7:
int, max, ( ,int, i, ), ;
Representation of Tokens
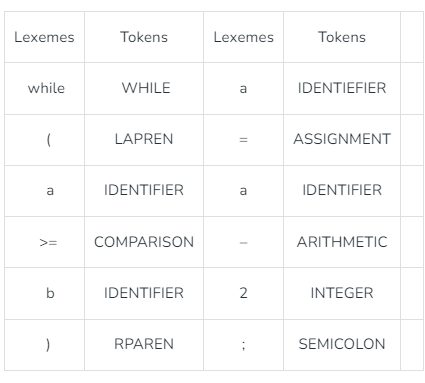
Advantages
- Efficiency: Improves parsing efficiency by breaking down input into smaller, manageable chunks.
- Flexibility: Allows the use of keywords and reserved words, aiding language creation and modification.
- Error Detection: Detects errors like misspellings, missing semicolons, and undefined variables.
- Code Optimization: Identifies patterns for code optimization, improving program performance.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Can be complex, requiring significant computational power, making it challenging to implement in some languages.
- Limited Error Detection: Does not detect all errors, such as logic errors or type errors.
- Increased Code Size: Addition of keywords and reserved words may increase code size, affecting readability.
- Reduced Flexibility: Use of keywords and reserved words may reduce language flexibility.
|
26 videos|90 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Lexical Analysis - Compiler Design - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is the main purpose of lexical analysis in computer science engineering? |  |
| 2. How does lexical analysis contribute to the overall compiler design process? |  |
| 3. What are some common challenges faced during lexical analysis? |  |
| 4. How does lexical analysis differ from syntax analysis in compiler design? |  |
| 5. Can lexical analysis be performed manually, or is it usually automated in modern compilers? |  |
















