Accounting Equation - Commerce PDF Download
Q.1. Prepare Accounting Equation from the following: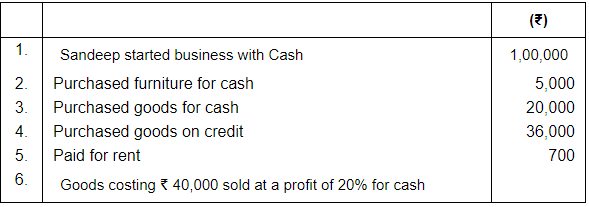 Ans.
Ans.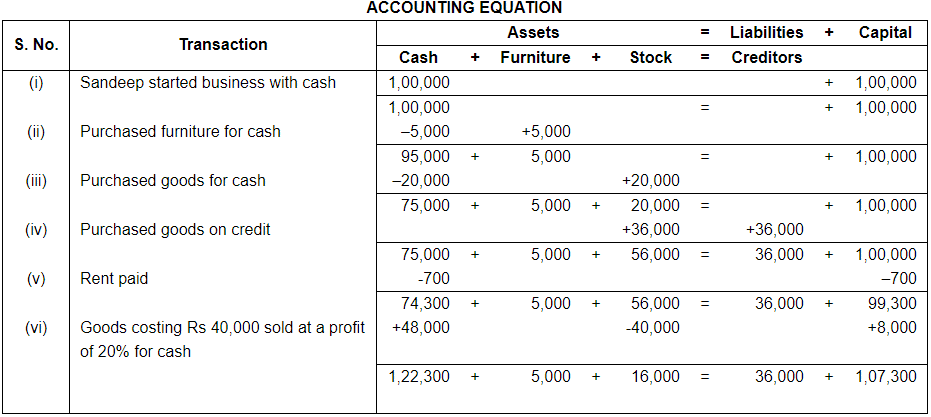
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 6 goods costing Rs. 40,000 sold on 20% profit (40,000 × 20%) = 40,000 × = Rs. 8,000.
Selling price of goods = 40,000 + 8,000 = Rs. 48,000.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Furniture + Stock
= 1,22,300 + 5,000 +16,000
= 1,43,300
Liabilities = Creditors
= 36,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 1,43,300 – 36,000
= 1,07,000
Point of Knowledge:
- Accounting equation is based on the dual concept of accounting, according to which, every transaction has two aspects namely Debit and Credit. It means that every transaction in accounting affects both Debit (Dr.) and Credit (Cr.)
Q.2. (A): Show the Accounting Equation on the basis of the following and present a balance sheet on the last new equation balances: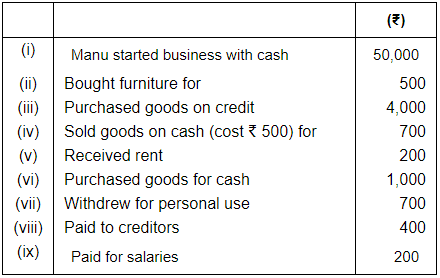 Ans.
Ans.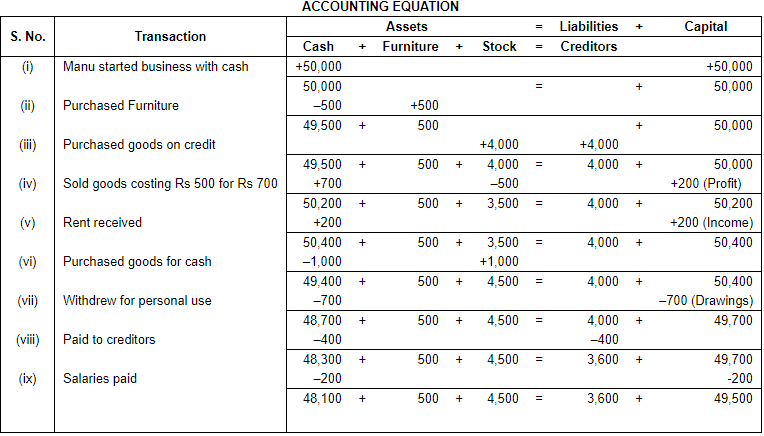
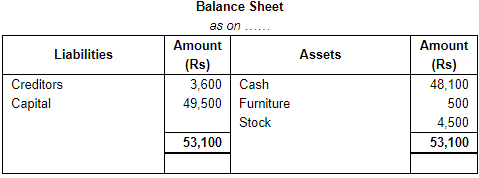
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 4 goods costing Rs. 500 sold at Rs. 700. So, the profit will be Rs. 700 - Rs. 500 = Rs. 200 it will rise our capital by Rs. 200.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Furniture + Stock
= 48,100 + 500 +4,500
= 53,100
Liabilities = Creditors
= 3,600
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 53,100 – 3,600
= 49,500
Point of Knowledge:
- Accounting equation thus refers to an equation in which total assets are always equal to the total Liabilities (i.e. Capital + Liabilities).
Q.2. (B): Prove that the Accounting Equation is satisfied in all the following transactions of Rajaram. Also prepare a Balance Sheet:−
(i) Started business with Cash ₹ 1,20,000.
(ii) Purchased a typewriter for Cash for ₹ 8,000 for office use.
(iii) Purchased goods for ₹ 50,000 for cash.
(iv) Purchased goods for ₹ 40,000 on credit.
(v) Goods costing ₹ 60,000 sold for ₹ 80,000 on credit.
(vi) Paid for Rent ₹ 1,500 and for salaries ₹ 2,000.
(vii) Received ₹ 800 for Commission.
(viii) Withdrew for private use ₹ 5,000 in cash.
Ans.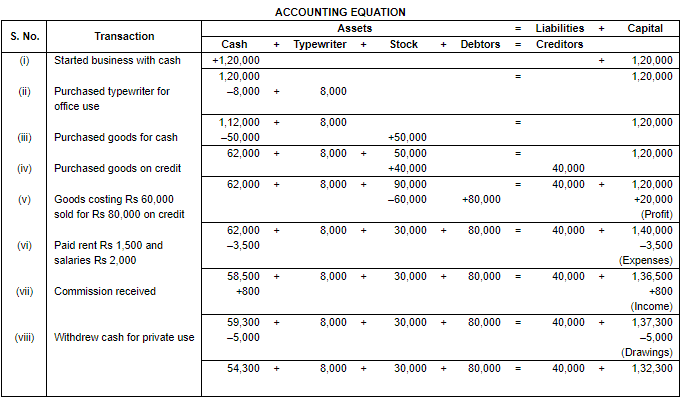
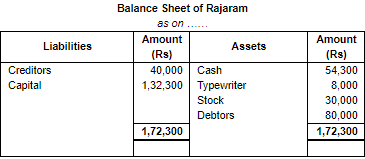 Working Note:
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 5 goods costing Rs. 60,000 sold at Rs. 80,000. So, the profit will be Rs. 80,000 - Rs. 60,000 = Rs. 20,000 it will rise our capital by Rs. 20,000.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash +Typewriter + Stock + Debtors
= 54,300 + 8,000 + 30,000 + 80,000
= 1,72,300
Liabilities = Creditors
= 40,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 1,72,300 – 40,000
= 1,32,300
Point of Knowledge:
- Accounting equation thus refers to an equation in which total assets are always equal to the total Liabilities (i.e. Capital + Liabilities).
Q.3. Prepare Accounting Equation from the following:
(a) Started business with Cash ₹ 2,00,000.
(b) Purchased goods for Cash ₹ 60,000 and on Credit ₹ 1,50,000.
(c) Sold goods for Cash costing ₹ 40,000 at a profit of 20% and on Credit costing ₹ 72,000 at a profit of 25%.
(d) Paid for Rent ₹ 5,000.
Ans.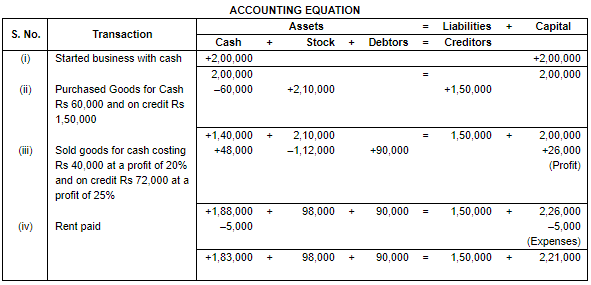
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 3 the Cost of goods sold is Rs. 40,000. Sold on cash 20% of profit Rs. 40,000 ×20/100 = Rs. 8,000.
Selling price = Rs. 40,000 + Rs. 8,000 = Rs. 48,000.
Cost of goods sold is Rs. 72,000. Sold on cash 20% of profit Rs. 72,000 ×25/100 = Rs. 18,000.
Selling price = Rs. 72,000 + Rs. 18,000 = Rs. 90,000.
Total cost of goods sold = Rs. 40,000 + 72,000 = 1,12,000.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Debtors
= 1,83,000 + 98,000 + 90,000
= 3,71,000
Liabilities = Creditors
= 1,50,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 3,71,000 – 1,50,000
= 2,21,000
Point of Knowledge:
- The accounting equation is always equal from both sides debit and credit. It shows the accuracy of recording of a financial transaction.
Q.4. Prepare Accounting Equation from the following: Ans.
Ans.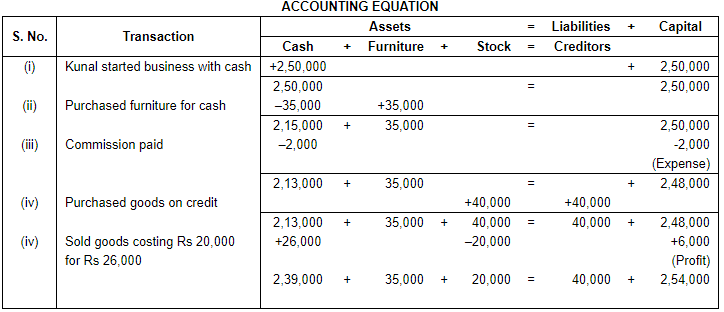
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 4 the cost of goods Rs. 20,000 sold at Rs. 26,000. So, the profit will be Rs. 26,000 - Rs. 20,000 = Rs. 6,000.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Furniture + Stock
= 2,39,000 + 35,000 + 20,000
= 2,94,000
Liabilities = Creditors
= 40,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 2,94,000 – 40,000
= 2,54,000
Point of Knowledge
- The accounting equation is always equal from both sides debit and credit. It shows the accuracy of recording of a financial transaction.
Q.5. Mohit has the following transactions, prepare Accounting Equation: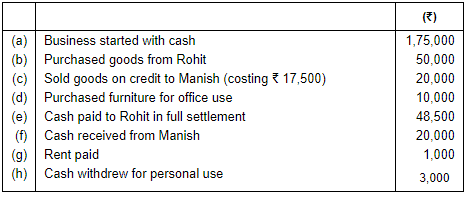 Ans.
Ans. 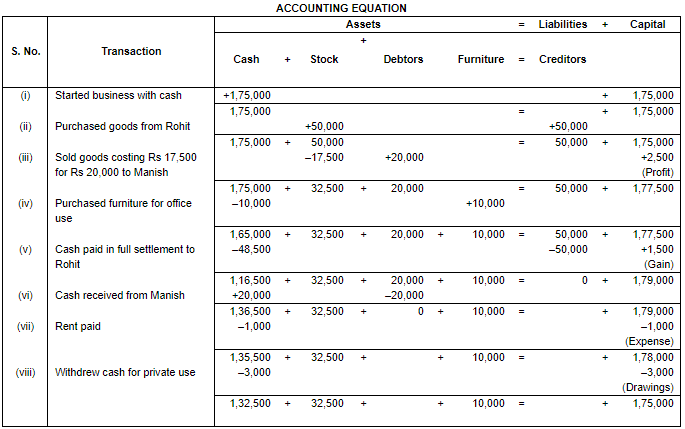
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 3 the cost of goods Rs. 17,500 sold at Rs. 20,000. So, the profit will be Rs. 17,500 - Rs. 20,000 = Rs. 2,500.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Debtors + Furniture
= 1,32,500 + 32,500 + 0 + 10,000
= 1,75,000
Liabilities = Creditors
= 0
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 1,75,000 – 0
= 1,75,000
Point of Knowledge:
- Every transaction has two aspects- debit and credit. It holds that for every debit there is a credit of equal amount and vice versa.
Q.6. What will be the effect of the following on the Accounting Equation?
(i) Harish started business with cash ₹ 1,80,000.
(ii) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 60,000 and on credit ₹ 30,000.
(iii) Sold goods for cash ₹ 40,000; costing ₹ 24,000.
(iv) Rent paid ₹ 5,000; and rent outstanding ₹ 2,000.
(v) Sold goods on credit ₹ 50,000 (costing ₹ 38,000).
(vi) Salary paid in advance ₹ 3,000.
Ans.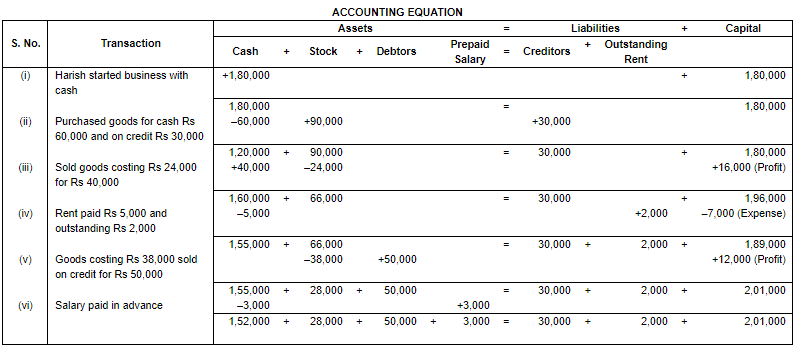
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 3 the cost of goods Rs. 24,000 sold at Rs. 40,000. So, the profit will be Rs. 17,500 - Rs. 20,000 = Rs. 16,000.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Debtors + Prepaid Salary
= 1,52,000 + 28,000 + 50,000 + 3,000
= 2,33,000
Liabilities = Creditors + Outstanding Rent
= 30,000 + 2,000
= 32,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 2,33,000 – 32,000
= 2,01,000
Point of Knowledge:
- Every transaction has two aspects- debit and credit. It holds that for every debit there is a credit of equal amount and vice versa.
Q.7. Use Accounting Equation to show the effect of the following transactions of M/s Royal Traders : Ans.
Ans.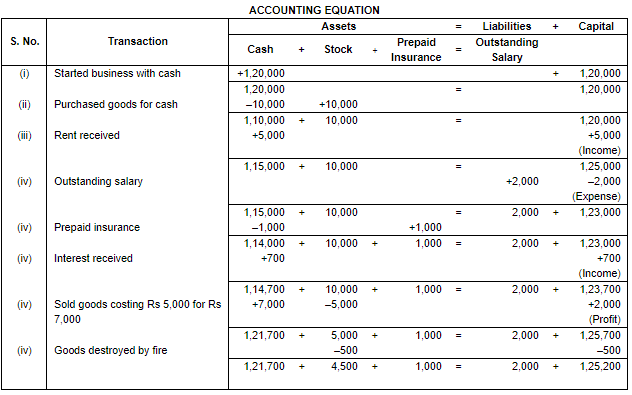
Working Note:
(i) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Prepaid Insurance
= 1,14,700 + 10,000 + 1,000 + 2,000
= 1,25,700
Liabilities = Outstanding Salary
= 2,000
= 2,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 1,25,700 – 2,000
= 1,23,700
Point of Knowledge:
- Outstanding transactions are the liability for the business firm and prepaid transaction are the assets for the business firm.
Q.8. (A) Prepare Accounting Equation from the following :−
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 75,000 and goods ₹ 25,000.
(ii) Paid for Rent ₹ 2,000.
(iii) Bought goods for cash ₹ 30,000 and on credit for ₹ 44,000.
(iv) Goods costing ₹ 50,000 sold at a profit of 25%, out of which ₹ 27,500 received in Cash.
(v) Purchased a Motor-cycle for personal use ₹ 20,000.
Ans.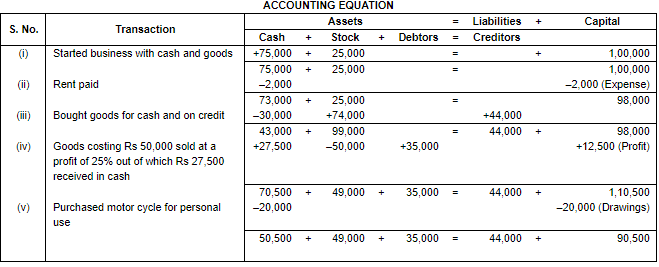
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 4 the cost of goods Rs. 50,000 sold at Rs. 25% of profit. So, the profit will be Rs. 50,000 × 25/100 = Rs. 12,500. Selling price = Rs. 50,000 + Rs. 12,500 = Rs. 62,500. In which Cash Sale = 27,500 and Credit Sale = Rs. 35,000.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Debtors
= 50,500 + 49,000 + 35,000
= 1,34,500
Liabilities = Creditors
= 44,000
= 44,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 1,34,500 – 44,000
= 90,500
Point of Knowledge:
- Every transaction has two aspects- debit and credit. It holds that for every debit there is a credit of equal amount and vice versa.
Q.8. (B) Prepare Accounting Equation from the following and also prepare a Balance Sheet:
(i) Raghu started business with Cash ₹1,50,000.
(ii) Bought goods for cash ₹80,000 and on credit for ₹40,000.
(iii) Goods costing ₹75,000 sold at a profit of 33 1/3%. Half the payment received in cash.
(iv) Goods costing ₹10,000 sold for ₹12,000 on credit.
(v) Paid for Rent ₹2,000 and for salaries ₹4,000.
(vi) Goods costing ₹20,000 sold for ₹18,500 for Cash.
Ans.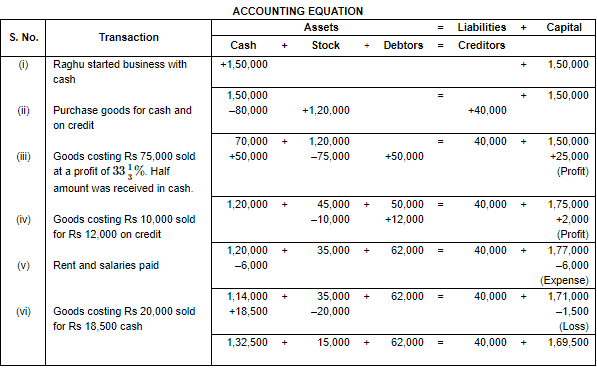
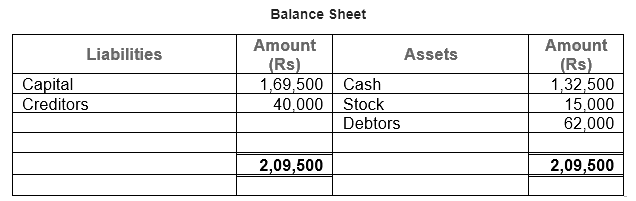
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 3 the cost of goods Rs. 75,000 sold at Rs. 100/3% of profit. So, the profit will be Rs. 75,000 × 100/3% = Rs. 25,000. Selling price = Rs. 75,000 + Rs. 25,000 = Rs. 1,00,000. In which Cash Sale = 50,000 and Credit Sale = Rs. 50,000.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Debtors
= 1,32,500 + 15,000 + 62,000
= 2,09,500
Liabilities = Creditors
= 40,000
= 40,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 2,09,500 – 40,000
= 1,69,500
Point of Knowledge:
- Every transaction has two aspects- debit and credit. It holds that for every debit there is a credit of equal amount and vice versa.
Q.9. If the Capital of a business is ₹ 1,20,000 and Outside liabilities are ₹ 20,000, calculate total assets of the business.
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
= 20,000 + 1,20,000
= Rs 1,40,000
Point of Knowledge:
The formulas using to calculate Assets, Liabilities and Capital are:
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
Liabilities = Assets – Capital
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Q.10. If total assets of a business are ₹ 1,30,000 and capital is ₹ 80,000, calculate creditors.
Ans. Assets = Rs. 1,30,000
Capital = Rs. 80,000
We know that
Liabilities = Assets – Capital
Liabilities = Rs. 1,30,000 – Rs. 80,000
Liabilities = Rs. 50,000
Point of Knowledge:
- The accounting equation is always equal from both sides debit and credit. It shows the accuracy of recording of a financial transaction.
Q.11. 'A' commenced his cloth business on 1st April, 2011 with a capital of ₹ 3,00,000. On 31st March, 2012 his assets were worth ₹ 5,00,000 and liabilities ₹ 1,00,000. Find out his closing capital and profits earned during the year.
Ans. Opening Capital = Rs. 3,00,000
Assets = Rs. 5,00,000
Liabilities = Rs. 1,00,000
Calculation of Closing Capital
Closing Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Closing Capital = Rs. 5,00,000 – Rs. 1,00,000
Closing Capital = Rs. 4,00,000
Calculation of Profit
Profit = Closing Capital – Opening Capital
Profit = Rs. 4,00,000 – Rs. 3,00,000
Profit = Rs. 1,00,000
Point of Knowledge:
- Closing Capital = Opening Capital + Additional Capital + Profit - Drawings
Q.12. (A): Yogesh commenced business on 1st April, 2011 with a Capital of ₹ 5,00,000 and a loan of ₹ 1,00,000 borrowed from Citi Bank. On 31st March, 2012, his assets were ₹ 8,00,000. Calculate his closing capital and profits earned during the year.
Ans. (A) Opening Capital = Rs. 5,00,000
Assets = Rs. 8,00,000
Liabilities (Loan) = Rs. 1,00,000
Calculation of Closing Capital
Closing Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Closing Capital = Rs. 8,00,000 – Rs. 1,00,000
Closing Capital = Rs. 7,00,000
Calculation of Profit
Profit = Closing Capital – Opening Capital
Profit = Rs. 7,00,000 – Rs. 5,00,000
Profit = Rs. 2,00,000
Working Capital:
(i) It is assumed that loan borrowed from Citi Bank has not been paid till the end of the accounting year.
Point of Knowledge:
- Closing Capital = Opening Capital + Additional Capital + Profit – Drawings
Q.12. (B) If in the above case, the proprietor had introduced fresh capital of ₹ 40,000 and had withdrawn ₹ 10,000 for personal purposes, calculate his profits.
Ans. (B) Opening Capital = Rs. 5,00,000
Assets = Rs. 8,00,000
Liabilities (Loan) = Rs. 1,00,000
Calculation of Closing Capital
Closing Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Closing Capital = Rs. 8,00,000 – Rs. 1,00,000
Closing Capital = Rs. 7,00,000
Calculation of Profit
Closing Capital = Opening Capital + Additional Capital + Profit – Drawings
Rs. 7,00,000 = Rs. 5,00,000 + Rs. 40,000 + Profit – Rs. 10,000
Rs. 7,00,000 = Rs. 5,30,000 + Profit
Rs. 7,00,000 - Rs. 5,30,000 = Profit
Profit = Rs. 7,00,000 - Rs. 5,30,000
Profit = Rs. 1,70,000
Point of Knowledge:
- Closing Capital = Opening Capital + Additional Capital + Profit – Drawings
Q.13. Give one example of each of the following transactions:
(i) Increase in an asset and a liability.
(ii) Decrease in an asset and a liability.
(iii) Increase in assets and capital.
(iv) Decrease in assets and capital.
Ans.
(i) Transaction: Increase in an asset and a liability.
- Example: Goods purchases on credit basis.
(ii) Transaction: Decrease in an asset and a liability.
- Example: Amount paid to creditors.
(iii) Transaction: Increase in assets and capital.
- Example: Additional capital introduce in the business.
(iv) Decrease in assets and capital.
- Example: Amount withdraw by proprietor.
Q.14. On which side the increase in the following accounts will be recorded? Also mention the nature of account:
1. Furniture
2. Rent Paid
3. Commission Received
4. Salary Paid
5. Proprietor's Account
6. Debtor
7. Creditor
Ans.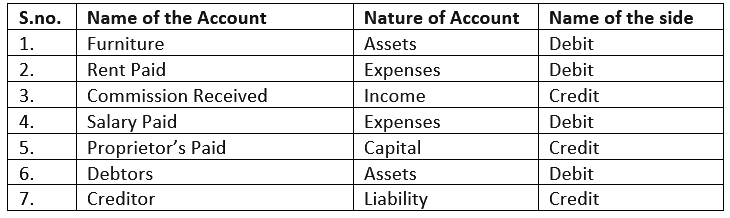
Ques 15: On which side the decrease in the following accounts will be recorded? Also mention the nature of account:−
1. Cash
2. Bank Overdraft
3. Rent Paid
4. Outstanding Rent
5. Prepaid Insurance
6. Manoj, Proprietor of the business
Ans.
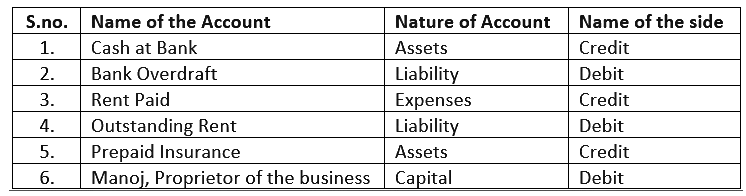
Q.16. From the following transactions, state the nature of accounts and state the accounts which will be debited and credited:
1. Ganesh started business with Cash ₹ 2,00,000.
2. Purchased goods for Cash ₹ 60,000.
3. Sold goods for cash ₹ 75,000.
4. Purchased goods from Nakul on Credit for ₹ 80,000.
5. Sold goods to Bhushan on Credit for ₹ 50,000.
6. Paid Cash to Nakul ₹ 20,000.
7. Received Cash from Bhushan ₹ 10,000.
8. Paid salary ₹ 20,000.
Ans.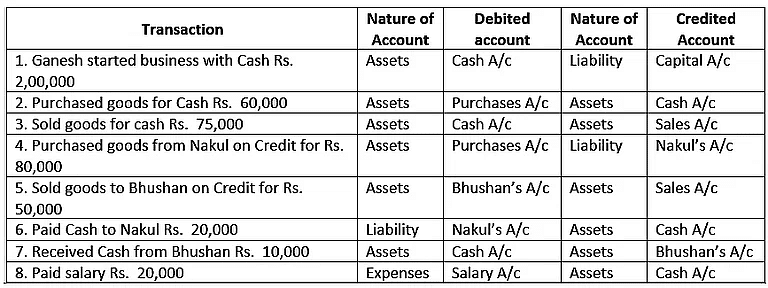
Ques 17: Open 'T' shape account for Machinery and write the following on the proper side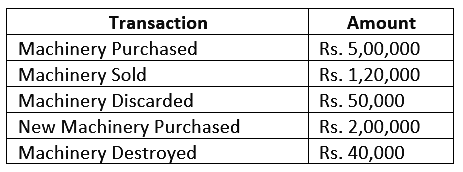 Ans.
Ans. 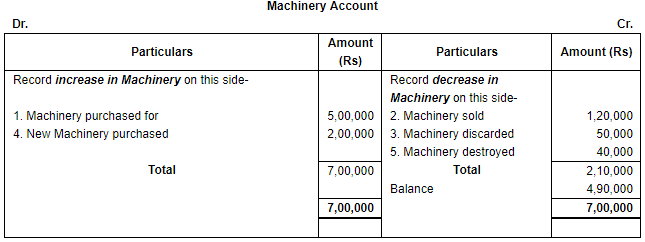
Working Note:
- Increase in assets will be debit and decrease In assets will be credited. Here Machinery is an asset.
Q.18. Open 'T' shape account of our creditor 'Raghubir' and write the following transactions on the proper side:
1. Purchased goods from Raghubir on credit for ₹ 50,000.
2. Returned goods to Raghubir for ₹ 5,000.
3. Paid to Raghubir ₹ 30,000.
4. Purchased goods from Raghubir on credit for ₹ 16,000.
5. Paid to Raghubir ₹ 20,000.
Ans. Raghubir is a creditor, which means, it is a liability for the business. As we know, increase in liability is recorded on the credit side while decrease in liability will be shown on the debit side of the concerned liability account.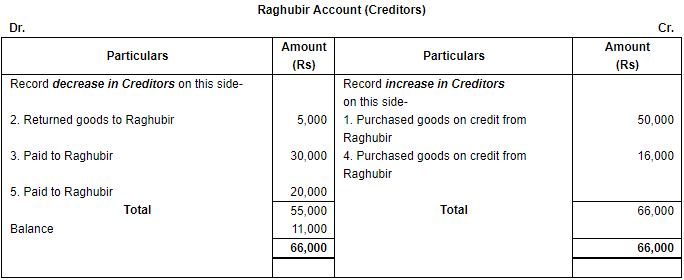
Working Note:
- Decrease in liabilities will be debit and increase in liabilities will be credited. Here Raghubir is a creditor (liability).
Q.19. Put the following on the proper side of Cash account, Debtor's account and Creditor's account:
(a) Sold goods for cash ₹ 60,000.
(b) Sold goods to Hari on credit ₹ 20,000.
(c) Purchased goods from Krishan on credit ₹ 36,000.
(d) Purchased goods from Krishan for cash ₹ 10,000.
(e) Cash received from Hari ₹ 15,000.
(f) Cash paid to Krishan ₹ 28,000.
Ans. Increase in Cash (being an asset) will be shown on the debit side and decrease in cash will be recorded on the credit side of the Cash Account.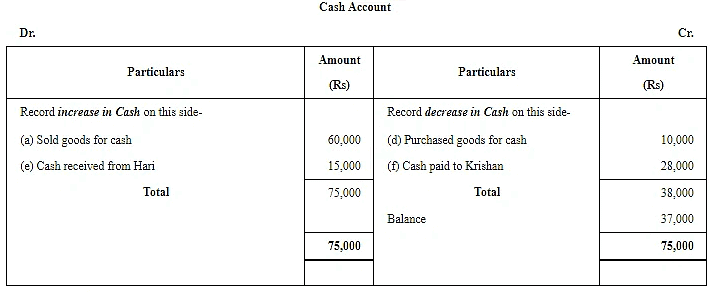
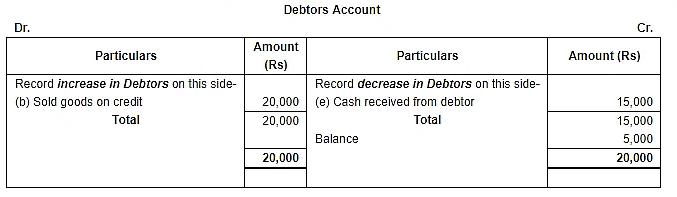
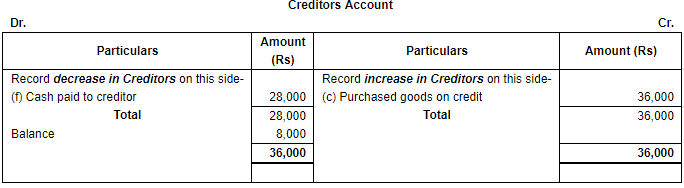
Point of Knowledge:
- Increase in asset will be debited and decrease will be credited.
- Increase in the liabilities will be credited and decrease will be debited.
- Increase in the capital will be credited and decrease will be debited.
- Increase in the revenue or income will be credited and decrease will be debited.
- Increase in expenses and losses will be debited and decrease will be credited.
Q.20. From the following transactions prepare the Proprietor's Account in 'T' shape:
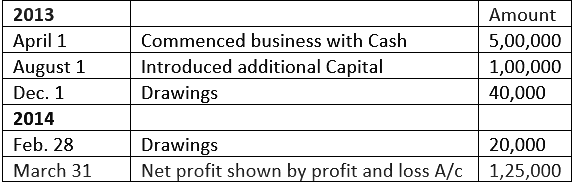 Ans.
Ans.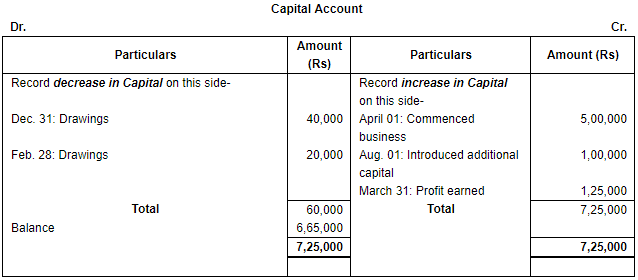
Point of Knowledge:
- Increase in asset will be debited and decrease will be credited.
- Increase in the liabilities will be credited and decrease will be debited.
- Increase in the capital will be credited and decrease will be debited.
- Increase in the revenue or income will be credited and decrease will be debited.
- Increase in expenses and losses will be debited and decrease will be credited.
Q.21. Prepare the Accounting Equation on the basis of the following:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 1,40,000 and Stock ₹ 2,50,000.
(ii) Sold goods (costing ₹ 50,000) at a profit of 25% on the cost.
(iii) Deposited into bank account ₹ 1,80,000.
(iv) Purchased goods from Mohan ₹ 80,000.
Ans.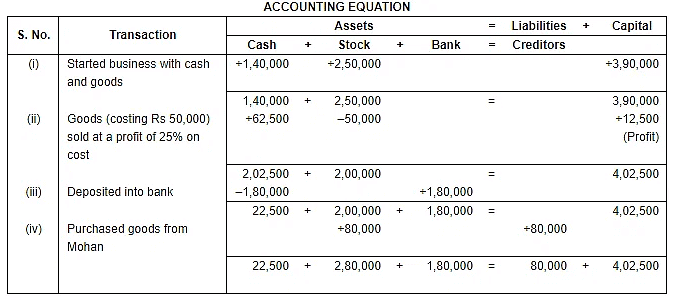
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 2 goods costing Rs. 50,000 sold at 25% profit on cost = Rs. 50,000 ×25/100 = 12,500.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Bank
= 22,500 + 2,80,000 + 1,80,000
= 4,82,500
Liabilities = Creditors
= 80,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 4,82,500 – 80,000
= 4,02,500
Point of Knowledge:
- Increase in asset will be debited and decrease will be credited.
- Increase in the liabilities will be credited and decrease will be debited.
Q.22. Prepare Accounting Equation on the basis of the following transactions:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 70,000.
(ii) Credit purchase of goods ₹ 18,000.
(iii) Payment made to creditors in full settlement ₹ 17,500.
(iv) Purchase of machinery for cash ₹ 20,000.
Ans.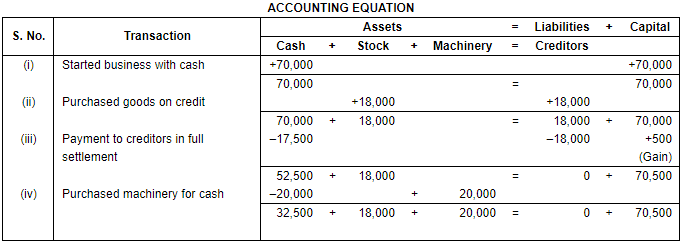
Working Note:
(i) Amount paid to creditor Rs. 17,500 in full settlement instant of Rs. 18,000. Here the gap of Rs. 500 treated as discount received.
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Machinery
= 32,500 + 18,000 + 20,000
= 70,500
Liabilities = Creditors
= 0
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= 70,500 – 0
= 70,500
Point of Knowledge:
- The rules of credit and debit same for both capital and liabilities because as per business entity concept the owner and business are the different entities. It is assumes that the owner of the business are creditors to the business firm and business firm is label to pay their owners.
Q.23. Prepare accounting equation from the following:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 50,000 and goods ₹ 30,000.
(ii) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 30,000 and on credit from Karan ₹ 20,000.
(iii) Goods costing ₹ 40,000 were sold for ₹ 55,000 for cash.
(iv) Withdrew cash for personal use ₹ 10,000.
(v) Rent outstanding ₹ 2,000.
Ans.
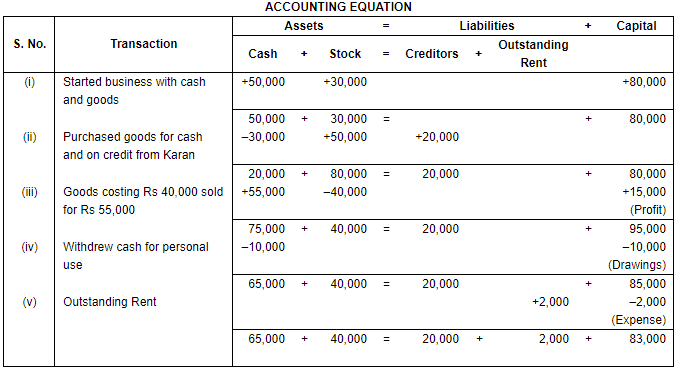
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 3 goods costing Rs. 40,000 sold at Rs. 55,000. Profit = Selling price – Cost Price
Profit = Rs. 55,000 – Rs. 40,000
Profit = Rs. 15,000
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock
= Rs. 65,000 + Rs. 40,000
= Rs. 1,05,000
Liabilities = Creditors + Outstanding Rent
= Rs. 20,000 + Rs. 2,000
= Rs. 22,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= Rs. 1,05,000 – Rs. 22,000
= Rs. 83,000
Point of Knowledge:
- In the accounting equation if the capital shows negative figure then it is drawings.
Q.24. Show the accounting equation on the basis of the following transactions and present a Balance Sheet of the last new equation balance: Ans.
Ans.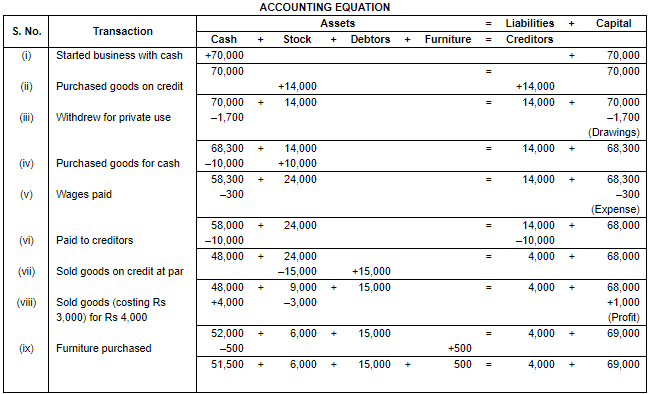
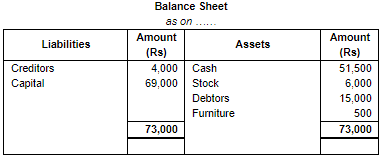
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 3 goods costing Rs. 3,000 sold at Rs. 4,000. Profit = Selling price – Cost Price
Profit = Rs. 4,000 – Rs. 3,000
Profit = Rs. 1,000
(ii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Debtors + Furniture
= Rs. 51,500 + Rs. 6,000 + Rs. 15,000 + Rs. 500
= Rs. 73,000
Liabilities = Creditors
= Rs. 4,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= Rs. 73,000 – Rs. 4,000
= Rs. 69,000
Point of Knowledge:
- Accounting equation thus refers to an equation in which total assets are always equal to the total Liabilities (i.e. Capital + Liabilities).
Q.25. Prove that the accounting equation is satisfied in the following transactions:− Ans.
Ans. 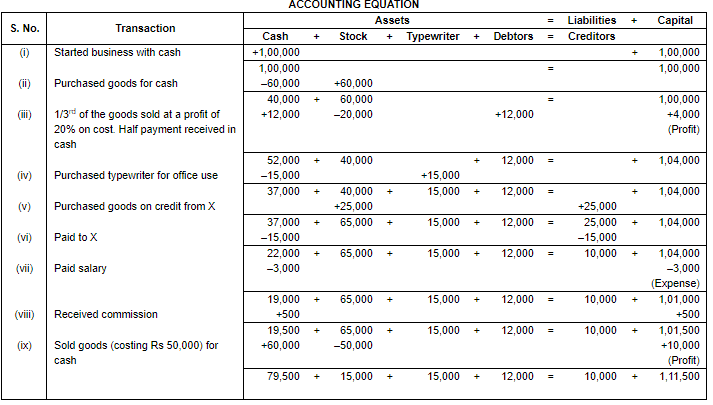
Working Note:
(i) In transaction 3 goods costing Rs. 50,000 sold at Rs. 60,000. Profit = Selling price – Cost Price
Profit = Rs. 60,000 – Rs. 50,000
Profit = Rs. 10,000
(ii) 1/3 part of total Goods = Rs. 60,000 ×1/3= Rs. 20,000
Rs. 60,000 × 1/3 = Rs. 20,000
Add: Profit (Rs. 20,000 ×20%) = Rs. 4,000
Selling price = Rs. 20,000 + Rs. 4,000 = Rs. 24,000
Cash Received = 24,000 × 50% = Rs. 12,000
Credit Sales = 24,000 × 50% = Rs. 12,000
(iii) Total Assets = Cash + Stock + Typewriter + Debtors
= Rs. 79,500 + Rs. 15,000 + Rs. 15,000 + Rs. 12,000
= Rs. 1,21,500
Liabilities = Creditors
= Rs. 10,000
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
= Rs. 1,21,500 – Rs. 10,000
= Rs. 1,11,500
Point of Knowledge:
Traditional or English rules of accounting:
- Personal Account: Debit the receiver and credit the giver.
- Real Account: Debit what comes in and credit what goes out.
- Nominal Account: Debit all expenses and losses credit all incomes and gains.
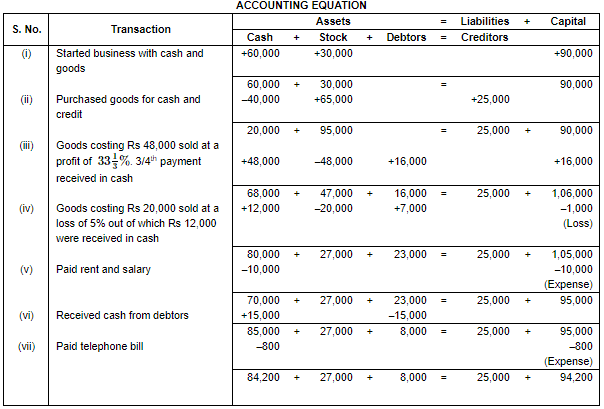
Q.26. Show the accounting equation on the basis of the following transactions and also show the Balance Sheet:
(i) Started business with Cash ₹ 60,000 and Goods ₹ 30,000.
(ii) Purchased goods for Cash ₹ 40,000 and on Credit ₹ 25,000.
(iii) Goods costing ₹ 48,000 sold at a profit of 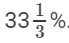 . Three-fourth payment received in Cash
. Three-fourth payment received in Cash
(iv) Goods costing ₹ 20,000 sold at a loss of 5%, out of which ₹ 12,000 received in Cash.
(v) Paid Rent ₹ 4,000 and Salary ₹ 6,000.
(vi) Received Cash from Debtors ₹ 15,000.
(vii) Paid telephone bill amounting to ₹ 800.
Ans.
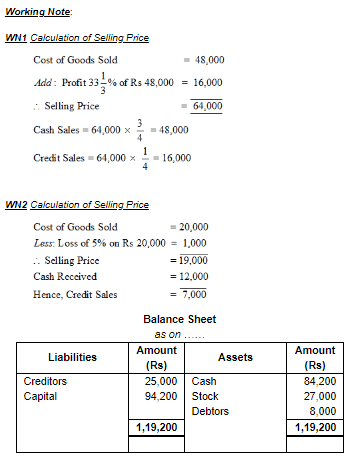
Q.27. Show the accounting equation on the basis of following transactions:
(i) Commenced business with Cash ₹ 20,000; Goods ₹ 50,000 and Furniture ₹ 30,000.
(ii) Purchased goods from Gopal on Credit ₹ 40,000.
(iii) Sold goods for Cash ₹ 40,000 (costing ₹ 30,000).
(iv) Sold goods to Ram on Credit ₹ 65,000 (costing ₹ 50,000).
(v) Withdrew for personal use goods costing ₹ 5,000.
(vi) Purchased typewriter for personal use of the proprietor ₹ 20,000.
(vii) Purchased chairs for office use for Cash ₹ 10,000.
(viii) Paid for printing ₹ 500 and received Commission ₹ 1,200.
(ix) Introduced fresh Capital ₹ 40,000.
(x) Paid to Gopal ₹ 30,000.
Ans.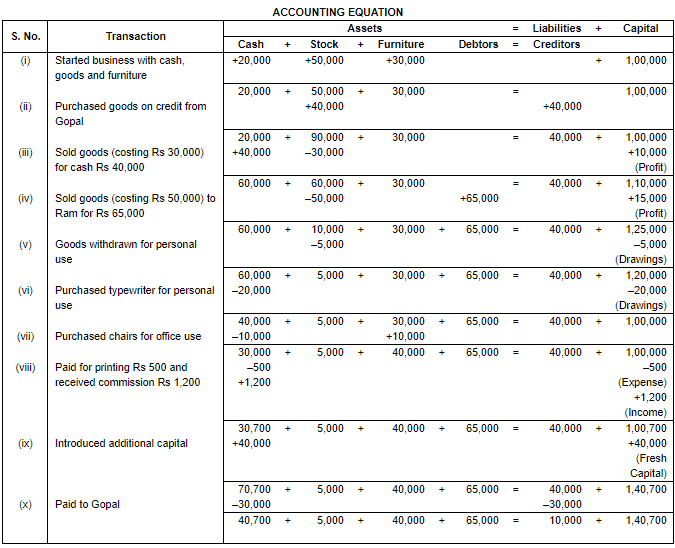
Q.28. X started a business on 1st April, 2013 with a Capital of ₹ 1,00,000 and a loan of ₹ 50,000 from the bank. On 31st March, 2014, his assets were ₹ 1,75,000. Find out his Capital as on 31st March, 2014 and profit earned during the year 2013-14.
Ans. Opening Capital (Capital as on 1st April, 2013) = Rs 1,00,000
Q.29. Y started a business on 1st April, 2013 with a Capital of ₹ 2,00,000 and a loan of ₹ 75,000 from the bank. During the year, he had introduced additional capital of ₹ 60,000 and had withdrawn ₹ 36,000 for personal purposes. On 31st March, 2014 his assets were ₹ 3,80,000. Find out his Capital as on 31st March, 2014 and profit earned during the year 2013-14.
Ans. Opening Capital (Capital as on 1st April, 2013) = Rs 2,00,000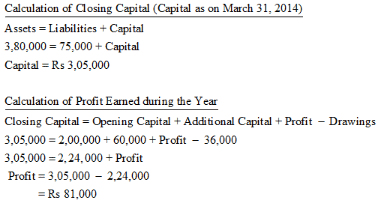
Q.30. On which side will the increase in the following accounts be recorded? Also mention the nature of account:
1. Furniture
2. Wages paid
3. Rent Received
4. Cash
5. Proprietor's Account
6. Debtor
7. Prepaid Insurance
8. Outstanding Salary
Ans.
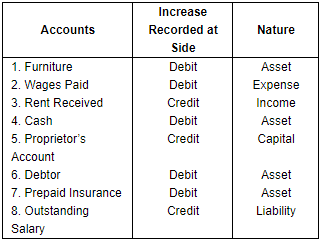
Q.31. Open 'T' shape account for Furniture and write the following on the proper side∶−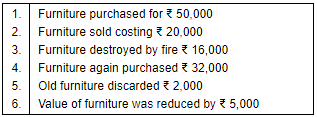 Ans. As we know, Furniture is an asset, so, increase in furniture will be recorded on the debit side while decrease in furniture will be recorded on the credit side of the Furniture Account.
Ans. As we know, Furniture is an asset, so, increase in furniture will be recorded on the debit side while decrease in furniture will be recorded on the credit side of the Furniture Account.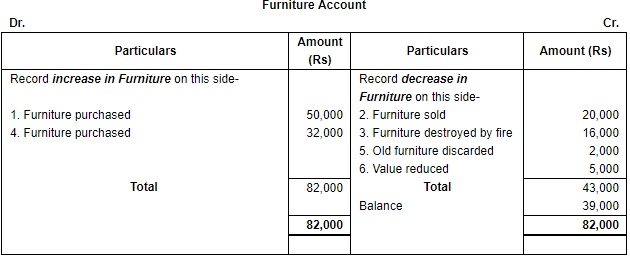
Q.32. Open 'T' shape account of our Creditor 'X' and write the following transactions on the proper side: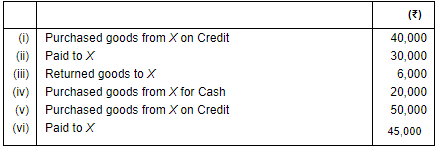 Ans. Increase in Creditors (being a liability) will be shown on the credit side and decrease in the creditors will be recorded on the debit side of the Creditors Account.
Ans. Increase in Creditors (being a liability) will be shown on the credit side and decrease in the creditors will be recorded on the debit side of the Creditors Account.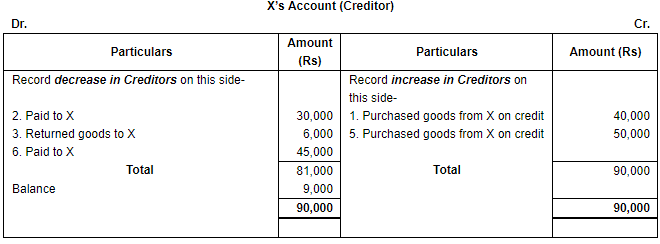 Note: Transaction Number (iv) will not be recorded in Creditors Account as goods are purchased for cash. Thus, there will be no impact on Creditors Account.
Note: Transaction Number (iv) will not be recorded in Creditors Account as goods are purchased for cash. Thus, there will be no impact on Creditors Account.
Q.33. Open 'T' shape account of our Debtor 'Ram' and write the following transactions on proper side: Ans. Increase in Debtors (being an asset) will be shown on the debit side and decrease in them will be recorded on the credit side of the Debtors Account.
Ans. Increase in Debtors (being an asset) will be shown on the debit side and decrease in them will be recorded on the credit side of the Debtors Account.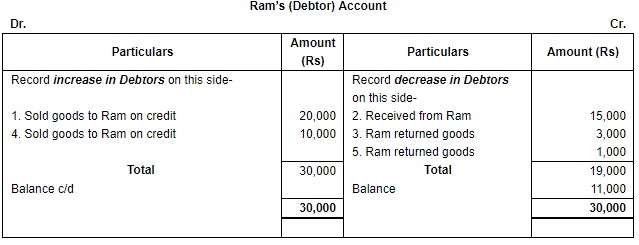
Q.34. Put the following on the proper side of Cash Account, Debtors's Account and Creditor's Account: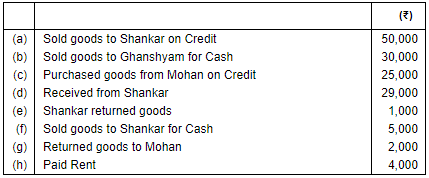 Ans. (i) Increase in Cash (being an asset) will be shown on the debit side and decrease in cash will be recorded on the credit side of the Cash Account.
Ans. (i) Increase in Cash (being an asset) will be shown on the debit side and decrease in cash will be recorded on the credit side of the Cash Account.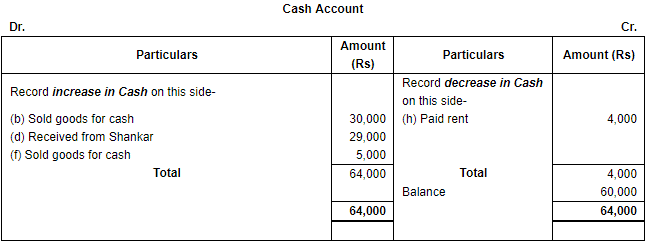 (ii) Increase in Debtors (being an asset) will be shown on the debit side and decrease in them will be recorded on the credit side of the Debtors Account.
(ii) Increase in Debtors (being an asset) will be shown on the debit side and decrease in them will be recorded on the credit side of the Debtors Account.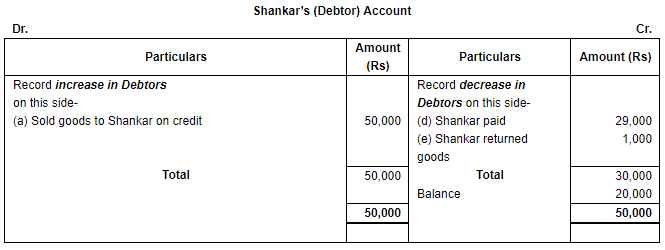 (iii) Increase in Creditors (being a liability) will be shown on the credit side and decrease in the creditors will be recorded on the debit side of the Creditors Account.
(iii) Increase in Creditors (being a liability) will be shown on the credit side and decrease in the creditors will be recorded on the debit side of the Creditors Account.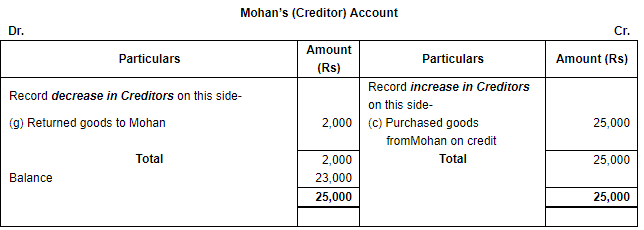
Q.35. Prove that accounting equation is satisfied in all the following cases:
(i) Commenced business with cash ₹ 50,000.
(ii) Paid rent ₹ 4,000 including ₹ 1,000 as advance.
(iii) Bought goods for cash ₹ 30,000 and on credit ₹ 20,000.
(iv) Sold the goods bought on credit for ₹ 25,000.
(v) Purchased furniture worth ₹ 10,000 for office use and for ₹ 5,000 for domestic use.
Ans. 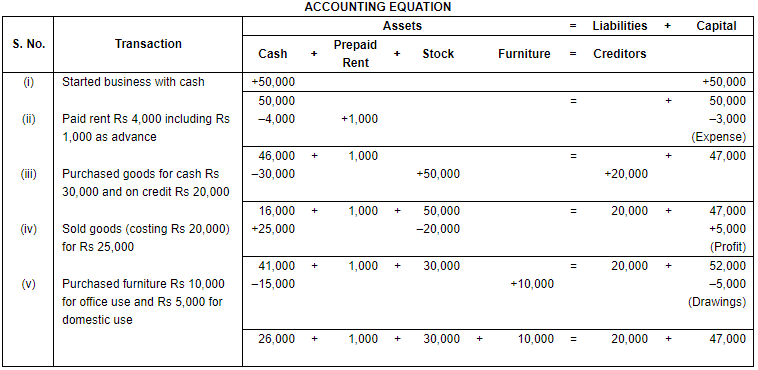
Q.36. Prepare accounting equation from the following:
(i) Started a business with cash ₹ 1,00,000 and goods worth ₹ 20,000.
(ii) Sold 50% of above goods at a profit of ₹ 2,000 on credit to Ram.
(iii) Rent paid ₹ 5,000.
(iv) Ram paid 50% of his balance in cash.
Ans.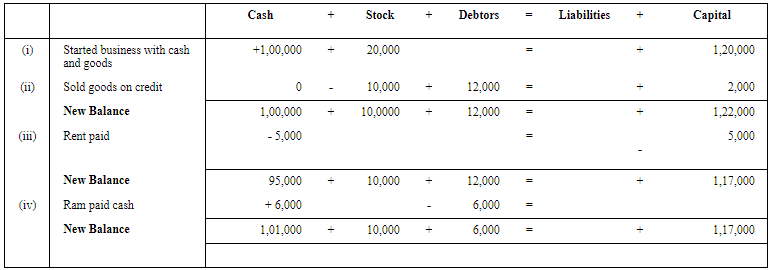
FAQs on Accounting Equation - Commerce
| 1. What is the accounting equation and how is it used in commerce? |  |
| 2. How does the accounting equation help businesses make financial decisions? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of transactions that affect the accounting equation? |  |
| 4. How can a company ensure that its financial statements are accurate and balanced using the accounting equation? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the accounting equation in financial analysis and reporting? |  |




















