Accounting Equation | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Q.1. What will be effect of the following on the Accounting Equation?
(i) Started business with cash Rs 45,000
(ii) Opened a Bank Account with a deposit of Rs 4,500
(iii) Bought goods from M\s. Sun & Co. for Rs11,200
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.


Points for Knowledge:
- In (iii) the name of the seller is given so it will be treated as credit sale. It will create effect on the liability side (creditors) also.
Q.2. Show the Accounting Equation for the following transactions:

Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.


Points for Knowledge:
- In (ii) transaction because the name of the seller is given so it will be treated as credit sale. It will create effect on liability side (creditors) also.
- In (iv) Gopinath who is the proprietor of the business takes out Rs.5, 000 from Business.
Q.3. Show the effect of the following transactions on the Accounting Equation:
(i) Started business with cash Rs 50,000.
(ii) Salaries paid Rs 2,000.
(iii) Wages Outstanding Rs 200.
(iv) Interest due but not paid Rs 100.
(v) Rent paid in advance Rs 150.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points for Knowledge:
- Outstanding expenses (iii) are always liability for a business.
- Rent paid in advance (v) is an asset as it is prepaid in Nature.
Q.4. What will be the effect of the following on the Accounting Equation?
(i) Harish started business with cash Rs 18,000
(ii) Purchased goods for Cash Rs 5,000 and on credit Rs 2,000
(iii) Sold goods for cash Rs 4,000 (costing Rs 2,400)
(iv) Rent paid Rs1,000 and Rent Outstanding Rs 200
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points for Knowledge:
- Total Stock Purchases (ii) by Harish is 5,000 (Cash) + 2,000 (Credit) i.e., 7,000 in total.
- Outstanding rent (iv), as outstanding in nature, so it is always liability for a business.
Q.5. Prepare Accounting Equation from the following:
(i) Started business with cash Rs 1,00,000 and Goods Rs 20,000.
(ii) Sold goods worth Rs 10,000 for cash Rs 12,000.
(iii) Purchased furniture on credit for Rs 30,000
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.


Q.6. Prepare an Accounting Equation and Balance Sheet on the following basis:
(i) Ajeet started business Rs 20,000.
(ii) He purchased furniture for Rs 2,000.
(iii) He paid rent of Rs 200.
(iv) He purchase goods on credit Rs 3,000.
(v) He sold goods (cost price Rs 2,000) for Rs 5,000 on cash.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.


Calculation of Assets and Liabilites
Points of Knowledge:
- If the question is silent, we assume that sales and purchases are made in cash mode.
Q.7. Prepare an Accounting Equation from the following:
(i) Started business with cash Rs 1,00,000.
(ii) Purchased goods for cash Rs 20,000 and on credit Rs 30,000.
(iii) Sold goods for cash costing Rs 10,000 and on credit costing Rs 15,000 both at a profit of 20%.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points of Knowledge:
- In (ii) Calculation of total goods purchased Rs. 20,000(cash) + Rs.30, 000 (credit) i.e, 50,000 in total.
Page No: 5.18
Q.8. Develop an Accounting Equation from the following transactions:

Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Page No: 5.19
Q.9. Prepare an Accounting Equation on the basis of the following transactions:
(i) Started business with Cash Rs 70,000
(ii) Credit purchase of goods Rs 18,000
(iii) Payment made to creditor Rs17,500 in full settlement
(iv) Purchase of Machinery for Cash Rs 20,000
(v) Depreciation on Machinery Rs 2,000
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points of Knowledge:
- In (ii) Rs. 17500, paid to creditor in full settlement.
So, Calculation of Discount Received = Creditors – Total amount paid
= 18000 – 17,500
= 500 (Discount Received)
Q.10. Prove that the Accounting Equation is satisfied in all the following transactions of Suresh. Also prepare a Balance Sheet.
(i) Commenced business with cash Rs 60,000.
(ii) Paid Rent in Advance Rs 500.
(iii) Purchased goods for Cash Rs 30,000 and Credit Rs 20,000.
(iv) Sold goods for Cash Rs 30,000 Costing Rs 20,000.
(v) Paid Salary Rs 500 and Salary Outstanding being Rs 100.
(vi) Bought motorcycle for personal use Rs5,000.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Calculation of Assets and Liabilites
Points of Knowledge:
- In (vi) motorcycle purchased for personal use so it is treated as drawing, it is subtracted from capital. Anything purchased for personal use should be treated as drawing.
Q.11. Show the effect of the following transactions on assets, liabilities and capital using the Accounting Equation. Also prepare a Balance Sheet.
(i) Started business with Cash Rs 60,000
(ii) Rent Received Rs 2,000
(iii) Accrued Interest Rs 500
(iv) Commission received in advance Rs 1,000
(v) Amount withdrawn Rs 5,000
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Calculation of Assets and Liabilites
Points of Knowledge:
- In (iii) accrued interest is an asset for business. Hence, shown on the asset side.
Q.12. Prove that the Accounting Equation is satisfied in all the following transactions of Sameer Goel:
(i) Started business with cash Rs 10,000.
(ii) Paid rent in Advance Rs 300.
(iii) Purchased goods for cash Rs 5,000 and credit Rs 2,000.
(iv) Sold goods for cash Rs 8,000 costing Rs 4,000.
(v) Paid salary Rs 450 and salary outstanding being Rs100.
(vi) Bought motorcycle for personal use Rs 3,000.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points of Knowledge:
- In (ii) Calculation of total goods purchased Rs. 5,000 (cash) + Rs.2, 000 (credit) i.e., 7,000 in total.
- In (vi) Here motorcycle purchased for personal use so it is treated as drawing , it is subtracted from capital.
Page No: 5.20
Q.13. Show the Accounting Equation on the basis of the following transactions and present a Balance Sheet on the last new equation balance:

Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Calculation of Assets and Liabilites
Q.14. Raghunath had the following transactions in an accounting year:
(i) Commenced business with cash Rs 50,000.
(ii) Paid in to bank Rs 10,000.
(iii) Purchased goods for Cash Rs 20,000 and Credit Rs 30,000.
(iv) Sold goods for Cash Rs 40,000 Costing Rs 30,000.
(v) Rent paid Rs 500.
(vi) Rent Outstanding Rs 100.
(vii) Bought furniture Rs 5,000 on credit.
(viii) Bought refrigerator for personal use Rs 5,000.
(ix) Purchased motorcycle for cash Rs 20,000.
Create an Accounting Equations to show the effect of the above transaction on his assets, liabilities and capital and also show his final Balance Sheet.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Calculation of Assets and Liabilites
Points of Knowledge:
- In (ii) Calculation of total goods purchased Rs. 20,000(cash) + Rs.30,000 (credit) i.e. 50,000 in total.
- In(vi) Here Refrigerator purchased by Raghunath for personal use so it is treated as drawing. It is subtracted from capital.
Q.15. Prepare an Accounting Equation from the following :
(i) Started business with cash Rs 50,000 and goods Rs 30,000.
(ii) Purchased goods for cash Rs 30,000 and on credit from Karan Rs 20,000.
(iii) Goods costing Rs 40,000 were Sold for Rs 55,000.
(iv) Withdrew cash for personal use Rs 10,000.
(v) Rent outstanding Rs 2,000.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Q.16. Show an Accounting Equation for the following transactions:
(i) D. Mahapatra commenced business with cash of Rs 50,000 and Rs 1,00,000 by cheque; goods Rs 60,000; machinery Rs 1,00,000 and furniture Rs 50,000.
(ii) 1/3rd of above goods sold at a profit of 10% on cost, and half of the payment is received in cash.
(iii) Depreciation on machinery provided @10%.
(iv) Cash withdrawn for personal use Rs 10,000.
(v) Interest on drawings charged @ 5%.
(vi) Goods Sold to Gupta for Rs 10,000 and received a Bill Receivable for the same amount for 3 months.
(vii) Received Rs 10,000 from Gupta against the Bill Receivable on its maturity.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.
Points of knowledge:
- Total Capital= Cash + Bank + Stock + Machinery + Furniture
50,000 + 1, 00,000 + 60,000 + 1,00,000 + 50,000 = 3,60,000
Total Value of stock = Rs. 60,000
Value of 1/3rd Stock = 60,000 ×
= Rs. 20,000 - Calculation of Profit = 20,000 × 10% = Rs. 2,000
Total Sales = Value of stock + Profit
20,000 + 2,000 = Rs. 22,000
Half of total sales value received in cash = 22000 × ½ = Rs. 11,000
Interest on drawings = 10,000 × 5% = Rs. 500
Page No: 5.21
Q.17. Prepare Accounting Equation from the following :
(a) Started business with cash Rs 1,00,000.
(b) Purchase goods for cash Rs 20,000 and on credit Rs 30,000.
(c) Sold goods for cash costing Rs 10,000 and on credit costing Rs 15,000 both at a profit of 20%.
(d) Paid salaries Rs 8,000.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points of Knowledge:
- Total goods purchases = Cash Purchases + Credit Purchases
= 20,000 + 30,000 = 50,000 - Calculation of profit on sale = Cash Sale × % of profit
10,000 × 20% = 2,000
= Credit Sale × % of Profit
15,000 × 20% = 3,000
Total Profit = 2,000 + 3,000
Q.18. Show the accounting equation on the basis of following transactions:
(a) Ram started business with Rs 25,000.
(b) Purchased goods from Shyam Rs 10,000.
(c) Sold goods to Sohan costing Rs 1,500 for Rs 1,800.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points for Knowledge:
- In (ii) The name of the seller is given so it will be treated as credit sale. It will create effect on liability side (creditors) also.
Q.19. If the capital of a business is Rs 3,00,000 and liabilities are Rs 50,000, loss Rs 70,000, calculate the total assets of the business.
Ans.

TOTAL ASSETS WILL BE RS. 2,80,000
Q.20. If total assets of a business are Rs 1,30,000 and Net worth is Rs 80,000, calculate the creditors .
Ans.

TOTAL CREDITORS WILL BE RS. 2,80,000
Q.21. A commenced his cloth business on 1st April, 2017 with a capital of Rs 30,000. On 31st March 2018, his assets were worth Rs 50,000 and liabilities of Rs10,000. Find out his closing capital and profits earned during the year.
Ans.


NET PROFIT WILL BE RS. 10,000.
Q.22. If capital of a business is Rs 1,40,000 and liabilities are of Rs 80,000, calculate the total assets of the business.
Ans.
TOTAL ASSESTS WILL BE RS. 2,20,000
Q.23. Calculate the total assets if:
(i) Capital is Rs 40,000.
(ii) Creditors are Rs 25,000.
(iii) Revenue during the period is Rs 50,000.
(iv) Expenses during the period are Rs 40,000.
Ans. Method 1:
Tabular form

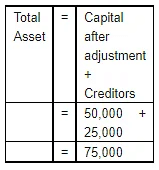
Method 2:
Total assets = Opening capital + Revenue during the year – Expenses during the year + creditors
= 40,000 + 50,000 – 40,000 + 25,000
= 75,000
Q.24. (a) A had a capital of Rs 75,000 on 1st April, 2017. He had also goods amounting to Rs 15,000 which he had purchased on credit and the payment had not been made. Find out the value of the total assets of the business.
(b) After a period of one month, he came to know that he had suffered a loss of Rs 1,700. He withdrew Rs 800 for his personal use. Find out his capital and assets of the business.
Ans.

Q.25. (a) Mohan started a business on 1st April, 2017 with a capital of Rs 10,000 and borrowed Rs 3,000 form a friend . He earned a profit of Rs 5,000 during the year ended 31st March, 2018 and withdrew cash Rs 4,000 for private use. What is his capital on 31st March, 2018?
(b) Mahesh started a business with a capital of Rs 15,000 on 1st April, 2017. During the year, he made a profit of Rs 3,000. He owes Rs 2,500 to suppliers of goods . What is the total of assets in his business on 31st March, 2018?
Ans.

Page No: 5.22
Q.26. Mohan started a business on 1st April, 2017 with a capital of Rs 25,000 and a loan of Rs 12,500 borrowed from Shyam. During 2017-18 he had introduced additional capital of 12,500 and had withdrawn Rs 7,500 for personal use. On 31st March, 2018 his assets were Rs 75,000. Find out his capital as on 31st March, 2018 and profit made or loss incurred during the year 2017-18.
Ans.

PROFIT DURING THE YEAR 2017-18 = 32,500
Q.27. On 31st March, 2018 , the total assets and external liabilities were Rs 2,00,000 and Rs 6,000 respectively . During the year, the proprietor had introduced capital of Rs 20,000 and withdrawn Rs 12,000 for personal use. He made a profit of Rs 20,000 during the year. Calculate the capital as on 1st April, 2017
Ans.

- CAPITAL AS ON MARCH 31, 2018 = 1,94,000
- CAPITAL ON APRIL 01, 2017 = 1,66,000
Q.28. Show an Accounting Equation on the basis of the following transactions:

Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points of knowledge:
- In (vi) cost of Building & Furniture is Rs. 1,00,000. Don’t Separate it
- In (xi) Investment in share market for personal use should be treated as drawings.
Q.29. Draw an Accounting Equation on the basis of the following transactions:
(i) Commenced business with cash Rs 50,000, cheque Rs 1,00,000, goods Rs 30,000 and furniture Rs 20,000.
(ii) Car, personal asset of the proprietor, was sold for Rs 1,00,000 against cheque which he deposited in his Savings Account.
(iii) An amount of Rs 50,000 was transferred from his Savings Account to the firm's Bank Account.
(iv) A new car was purchased for Rs 6,00,000 for office use. It was paid by taking loan from Bank of Rs 5,00,000 and balance by issue of cheque from firm's Bank Account .
(v) Sold goods to Ajay on credit costing Rs 4,000 for Rs 5,000.
(vi) Sold goods for cash costing Rs 12,000 for Rs 16,000
(vii) Purchased good for cash Rs 40,000
(viii) Purchased goods on credit for Rs 20,000.
(ix) Paid rent Rs 3,000 including Rs 2,000 in advance .
(x) Paid salaries Rs 2,000.
(xi) Sold goods costing Rs 8,000 for Rs 10,000.
(xii) Salaries outstanding Rs 1,000.
(xiii) Charge depreciation on furniture Rs500.
Ans. The Following table is Showing the Accounting Equation.

Points of Knowledge:
- In (ii) Car is a personal asset of the proprietor and amount also deposit in his personal accounts, So it Doesn’t show any impact on the Accounting Equation
|
64 videos|152 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Accounting Equation - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is the accounting equation in commerce? |  |
| 2. How is the accounting equation used in financial statements? |  |
| 3. Can the accounting equation be modified? |  |
| 4. How does the accounting equation impact decision-making in commerce? |  |
| 5. What happens if the accounting equation is not in balance? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|


















