Class 9 NCERT - Solved Question Answers Documents
I. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Which parallel of latitude divides India into almost two equal parts?
(a) Tropic of Cancer
(b) Tropic of Capricorn
(c) Equator
(d) None of these
2. Where is Indira Point located?
(a) In Lakshadweep Islands
(b) In Andaman Islands
(c) In Nicobar Islands
(d) In Maldives
3. What is the total geographical area of the Indian landmass?
(a) 3.28 million square km
(b) 3.38 million square km
(c) 3.58 million square km
(d) 4.08 million square km
4. What is the percentage of India’s total area in relation to the total geographical area of the world?
(a) 2.4
(b) 2.6
(c) 3.4
(d) 3.9
5. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) India is the fifth largest country of the world.
(b) India is the sixth largest country of the world.
(c) India is the seventh largest country of the world.
(d) India is the smallest country of the world.
6. From which place in Uttar Pradesh does the Standard Meridian of India pass?
(a) Kanpur
(b) Mirzapur
(c) Allahabad
(d) Lucknow
7. What influences the duration of the day and night as one moves from south to north?
(a) Longitudinal extent
(b) Latitudinal extent
(c) Tropic of Cancer
(d) Tropic of Capricorn
8. In which year was the Suez Canal opened?
(a) 1769
(b) 1801
(c) 1850
(d) 1869
9. How many states are there in India?
(a) 25
(b) 28
(c) 29
(d) 31
10. What is the number of union territories of India?
(a) 7
(b) 8
(c) 9
(d) 10
11. With which country/countries does India share its land boundaries in the northwest?
(a) Pakistan and Tajikistan
(b) Afghanistan
(c) Afghanistan and China
(d) Pakistan and Afghanistan
12. Where are Maldives Islands situated?
(a) To the south of the Lakshadweep Islands
(b) To the north of the Lakshadweep Islands
(c) To the north of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(d) To the south of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
13. With which country/countries does India share its land boundaries in the east?
(a) Nepal and Bhutan
(b) Nepal and China
(c) Pakistan
(d) Myanmar and Bangladesh
14. Which sign signifies the state boundary of India?
(a) —— – ——
(b) ——x——
(c) – – – – – –
(d) - - - - - -
Ans. 1.(a) 2.(c) 3.(a) 4.(a) 5.(c) 6.(b) 7.(b) 8.(d) 9.(c) 10.(a) 11.(d) 12.(a) 13.(d) 14.(c)
II. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. In which Hemisphere does India lie?
Ans. India lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere.
Q2. What is India’s rank in the Northern Hemisphere?
Ans. In terms of size, India is the seventh largest country of the world.
Q3. Mention the land boundary of India.
Ans. India has a land boundary of about 15,200 km and the total length of the coastline of the mainland including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep is 7,516.6 km.
Q4. What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of the mainland of India?
Ans. The latitudinal and longitudinal extent of the mainland of India is 8°4' N and 37°6' N and 68°7' E and 97°25' E respectively.
Q5. Name the countries which are larger than India.
Ans. Russia, Canada, USA, China, Brazil and Australia.
Q6. What is the southernmost point of the Indian union called?
Ans. The southernmost point of the Indian union is called Indira Point.
Q7. What is the Standard Meridian of India?
Ans. The Standard Meridian of India is 82°30' E.
Q8. The Suez canal was opened in 1869. How has it helped India?
Ans. Since the opening of the Suez canal, India’s distance from Europe has been reduced by 7,000 km.
Q9. Name the countries with which India shares its land boundaries in the east.
Ans. Myanmar and Bangladesh.
Q10. Name the southern neighbours of India.
Ans. Sri Lanka and Maldives.
Q11. Which country is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar?
Ans. Sri Lanka.
Q12. Name the states through which passes the Tropic of Cancer.
Ans. Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattishgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura and Mizoram.
Q13. Which neighbouring country of India is an island?
Ans. Maldives is an island country which lies in the south of India.
Q14. Which Islands group lies in the south-west of India?
Ans. The Lakshadweep Islands group lies in the south-west of India.
III. Short Answer Type Questtions
Q1. Write about the size of India. Or
What is the length and breadth of India?
Ans.(i) The total geographical area of the landmass of India is 3.28 million square km. India’s total area accounts for about 2.42 per cent of the total geographical area of the world.
(ii) India is the seventh largest country of the world.
(iii) The country has a land boundary of about 15,200 km and the total length of the coastline of the mainland including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep is 7,516.6 km.
Q2. “India’s land routes have been important since ancient times.” Explain. [HOTS]
Ans.(i) India’s contacts with the world have continued through the ages, but her relationships through the land routes are much older than her maritime contacts. The various passes across the mountains in the north have provided passages to the ancient travellers.
(ii) These routes have contributed in the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times. The ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals and the decimal system thus could reach many parts of the world.
(iii) The spices, muslin and other merchandise were taken from India to different countries. On the other hand, the influence of Greek sculpture and the architectural styles of dome and minarets from West Asia can be seen in different parts of our country.
Q3. Why do we need a Standard Meridian for India?
Ans. India is a large country. It covers a long range of longitudes (67°E to 97°E). As we know that variation in time is caused by longitudinal difference, so the time difference between the westernmost and the easternmost longitudes of India should be very large. For example, the time of Arunachal Pradesh should be two hours ahead of Gujarat, but such a situation could cause inconvenience in the activities like transmission of information across different parts of the same country. To avoid this, we designate the 82°30′E longitude as Standard Meridian. The time at this longitude is accepted all across India as the Indian Standard Time.
Q4. What is the latitudinal extent of India? How does it influence our lives?
Ans. The latitudinal extent of India is 6°4′N to 37°6′N. It influences our lives in the following ways:
(i) The Tropic of Cancer divides the country into two equal parts. Thus, India is situated in tropical and temperate zones.
(ii) The northern part of India has high annual range of temperature whereas the southern part has low annual range of temperature.
(iii) The latitudinal extent influences the duration of the day and night as we move from south to north.
Q5. What is the ‘Prime Meridian’? What is the other name for it and why?
Ans. The Prime Meridian is the imaginary line used to indicate 0° longitude that passes through Greenwich. It is also known as Greenwich Meridian because it passes through the place called Greenwich in London.
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. Describe the location of India in the world map.
Ans. India lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. The mainland extends between latitudes 8°4′N and 37°6′N and longitudes 68°7′E and 97°25′E. The Tropic of Cancer (23°30′N) divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast of the mainland lies the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. To the southwest of the mainland lies the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea. The extent of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands is– Latitudinal extent : 6°45′N to 14°N Longitudinal extent : 92°E to 94°E
The extent of the Lakshadweep Islands is– Latitudinal extent : 8°N to 12°3′N Longitudinal extent : 71°E to 74′E
The southernmost point of the Indian union is Indira Point. But it is submerged in the ocean in 2004 in Tsunami.
Q2. What do you know about India and her neighbours? [HOTS]
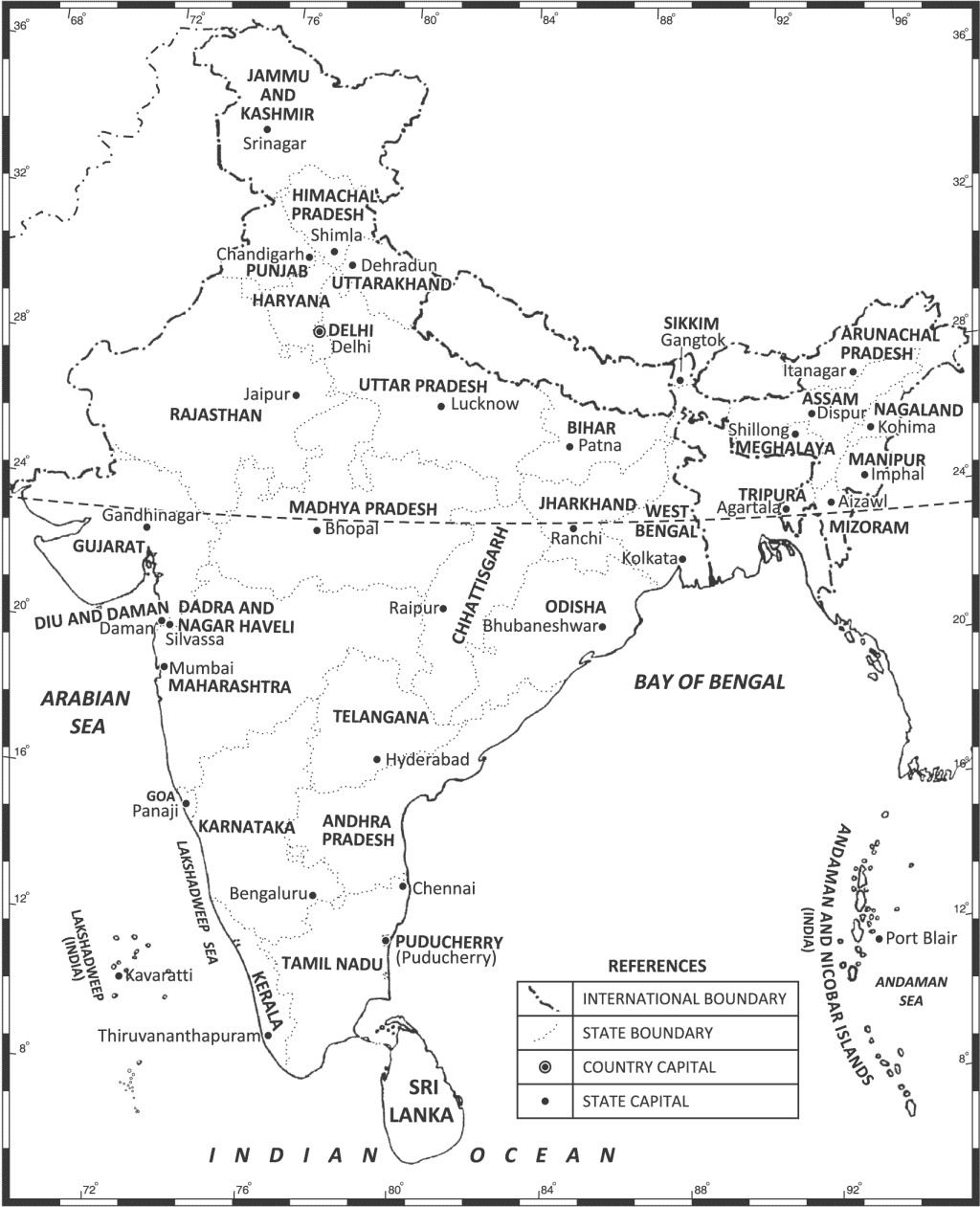
Ans.(i) India occupies an important strategic position in South Asia. India has 29 states and 7 Union Territories. (See the map of India on page 133)
(ii) India shares its land boundaries with Pakistan and Afghanistan in the northwest, China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan in the north and Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east. Our southern neighbours across the sea consist of the two island countries, namely Sri Lanka and Maldives.
(iii) Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea formed by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar while Maldives Islands are situated to the south of the Lakshadweep Islands.
India has had strong geographical and historical links with her neighbours.
Q3. India occupies an important strategic position in South Asia. Discuss. [HOTS]
Ans. (i) The Indian landmass has a central location between the East and the West Asia. India is a southward extension of the Asian Continent.
(ii) The trans-Indian Ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia provide a strategic central location to India.
(iii) The Indian landmass is centrally located between East and West Asia.
(iv) The part that is attached to the Asian continent connects India (through land routes and mountain passes) to the various countries lying to its north, west and east.
(v) The Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean, thus helping India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the western coast and with Southeast and East Asia from the eastern coast.
Q4. Why has 82°30' E been selected as the Standard Meridian of India? [HOTS]
Ans. 82°30' E has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India because it is situated in the centre of all longitudes and latitudes in which our country is located. It passes through Allahabad. Indian Standard Time (IST) is calculated on the basis of 82.5° E longitude, which is just west of the town of Mirzapur, near Allahabad in the state of Uttar Pradesh. To avoid confusion due to time differences and to have a standard time for reference, the time along the meridian (82°30' E) passing through Mirzapur (Uttar Pradesh) has been taken as the standard time for the entire country. This is why the watches show the same time.
Q5. Describe the location and size of India.
Ans. See Q.No. 1 (Long Answer Type Questions) and Q.No. 1 (Short Answer Type Questions).
V. Map Skills
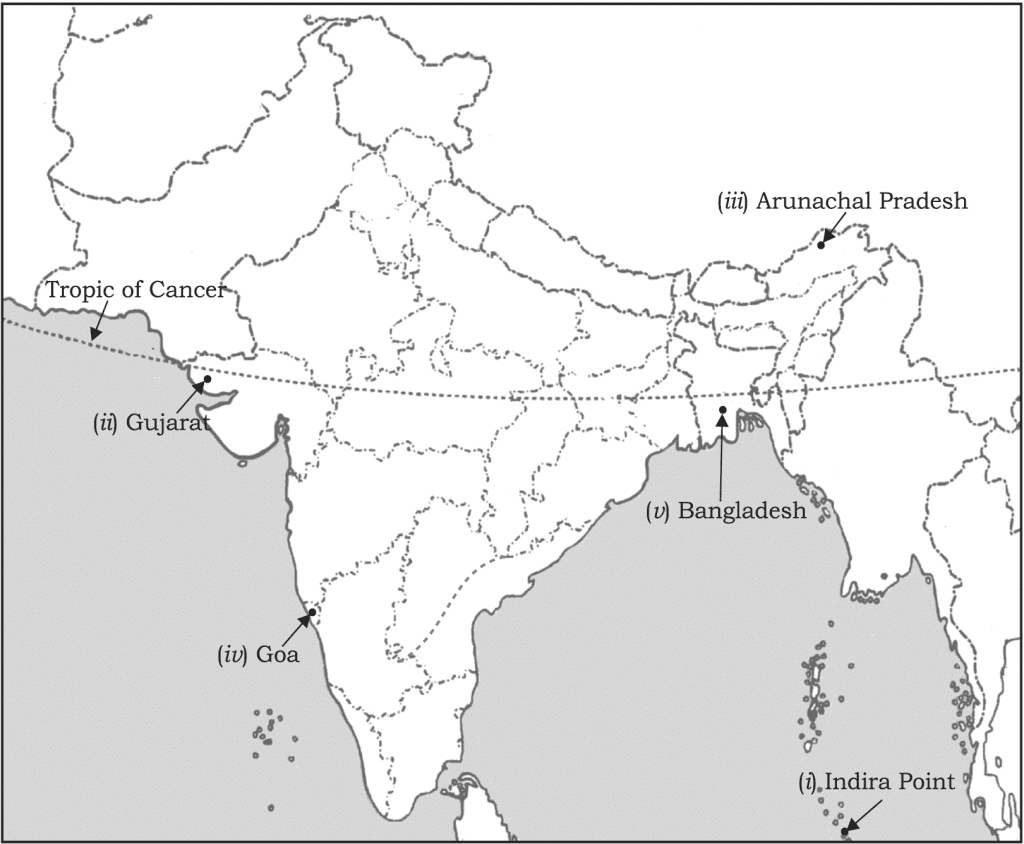
Q1. Locate and label the following on the political map of India:
(i) Southernmost point of the Indian Union
(ii) State situated on the extreme west
(iii) State situated on the extreme east
(iv) Smallest state of India
(v) A country lying east of India
Ans.
Q2. On an outline map of India, show all the Indian states and union territories.
(as per the CBSE Map List 2017-18)
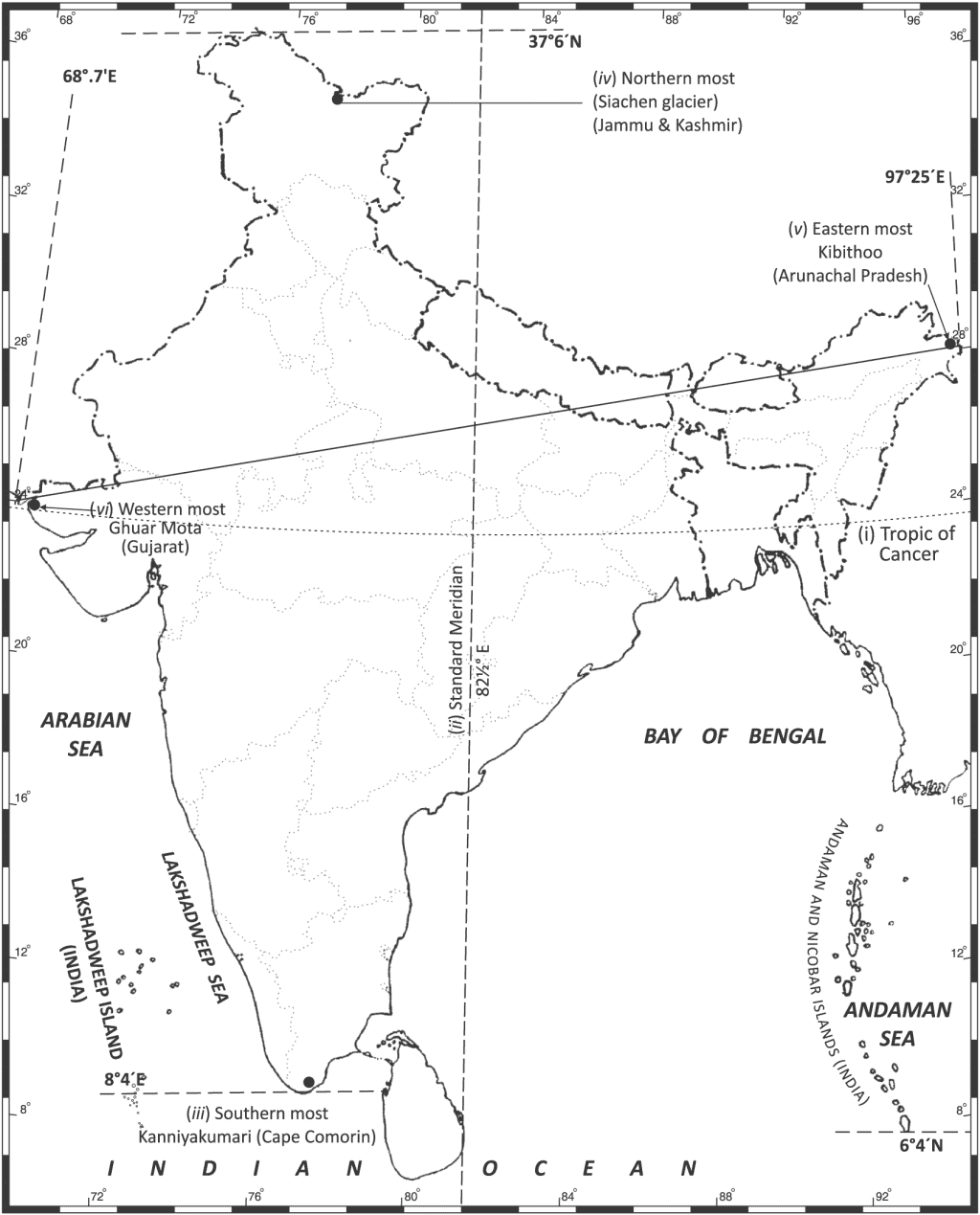
Q3. On an outline map of India, locate and label the following:
(i) Tropic of Cancer, (ii) Standard Meridian, (iii) Southern most, (iv) Northern most,
(v) Eastern most, (vi) Western most point of India.(as per CBSE Map List 2017-18)
Ans.
VI. Value-based Questions
Q1. How has India contributed significantly to the making of world history? Explain with three examples.
Ans.(i) India has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean. It is her eminent position in the Indian Ocean which justifies the naming of an ocean after it.
(ii) India’s contacts with the world have continued through the ages but her relationships through the land routes are much older than her maritime contact. The various passes across the mountains in the north have provided passages to the ancient travellers. These routes have contributed in the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times.
(iii) The ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals and the decimal system have reached many parts of the world.
Q2. Look at the map of India with her neighbouring countries. We know that India has had strong geographical and historical links with her neighbours.
Which values does India reflect while maintaining her relations with her neighbours?
Ans.(i) Tolerance and forbearance
(ii) Fraternity
(iii) Non-interference
(iv) Honesty
(v) Non-violence
(vi) Solidarity
Test Your Skills
1. How was the opening of Suez Canal important to India?
2. What is the length of India’s land boundary?
3. Before 1947, there were two types of states in India. Name them and give a brief account of them.
4. Name all the neighbouring countries of India.
|
1 videos|228 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 NCERT - Solved Question Answers Documents
| 1. What are the important topics to study for the Class 9 Additional Questions exam? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 9 Additional Questions exam? |  |
| 3. Are additional questions important for the Class 9 exam? |  |
| 4. Can I rely solely on the textbook for the Class 9 Additional Questions exam preparation? |  |
| 5. How can I manage my time effectively during the Class 9 Additional Questions exam? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|

















