Advanced Tactics and Checkmates in Chess - 1 | Chess Tutorial Course: Beginner to Advanced - Class 6 PDF Download
Chess is a game that combines strategic planning, tactical maneuvers, and the pursuit of checkmate. As a beginner, it is important to delve into advanced tactics and checkmate patterns to elevate your gameplay. In this article, we will explore several crucial concepts and provide easy-to-understand explanations along with multiple examples.
How to Understand Chess Combinations
Chess combinations involve a sequence of moves that exploit weaknesses in the opponent's position or create advantageous situations. Understanding combinations requires the ability to spot tactical opportunities, calculate variations, and visualize future positions. Let's examine a simple combination:

In this position, White can create a combination by playing 1.Nf6+ gxf6 2.Qg4+, winning Black's queen. The knight sacrifice on f6 opens up a discovered check from the queen on g4. By spotting this combination, White gains a significant advantage.
How to Understand Pawn Structure
Pawn structure refers to the arrangement of pawns on the chessboard. Understanding pawn structure is crucial as it determines the dynamics of the position and influences strategic plans. Here's an example:

In this position, both players have adopted different pawn structures. Black has a pawn chain on c7, d6, and e5, which provides a solid foundation and restricts White's pawn breaks. White, on the other hand, has a pawn majority on the kingside, which can be utilized to launch an attack or create weaknesses in Black's position. Understanding pawn structure helps players formulate appropriate plans and identify critical pawn breaks.
Capturing Pieces vs. Pursuing Checkmate
When evaluating moves, beginners often face a dilemma between capturing opponent's pieces or pursuing checkmate. It is important to strike a balance between material advantage and tactical opportunities. Sometimes, checkmate takes precedence over material gains. Consider the following position:
In this position, White has a chance to checkmate Black with 1.Rf7+. Instead of capturing the rook on f7 with their king, Black should focus on escaping the checkmate threat, as capturing the rook would lead to a forced checkmate in the next move. Pursuing checkmate takes precedence over material considerations.
Principles of Attacking & Defending
Understanding the principles of attacking and defending is crucial in chess. When attacking, players aim to create threats, exploit weaknesses, and generate pressure on the opponent's position. On the other hand, defending involves minimizing vulnerabilities, safeguarding key squares, and countering the opponent's threats. Let's consider an attacking scenario: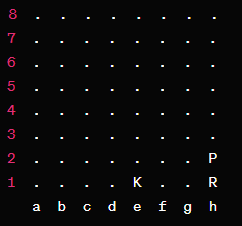
In this position, White can attack Black's king by playing 1.Rh8+. Black's defense involves responding with the only move available: 1...Kxh8. Understanding both attacking and defending principles allows players to assess the dynamics of the position accurately.
3 Basic Opening Strategy Principles
The opening phase of the game sets the tone for the subsequent middlegame and endgame. Here are three basic principles for the opening:
- Develop your pieces: Aim to bring your knights and bishops out from their initial positions to active squares. Develop your pieces efficiently to control the center and prepare for future maneuvers.
- Control the center: Occupying and exerting influence over the central squares (d4, d5, e4, e5) provides flexibility and greater mobility for your pieces. Focus on establishing a strong presence in the center during the opening.
- Castle for safety: Castling helps safeguard your king by moving it to a secure position behind a wall of pawns. Castling early allows you to activate your rook and connect the rooks, enhancing your position.
3 Things to Consider If You Get Stuck
It's common for beginners to feel stuck in a position where progress seems difficult. Here are three things to consider if you find yourself in such a situation:
- Reassess the position: Analyze the current position and look for hidden tactical opportunities or weaknesses in your opponent's position. Reassessing the position can help you find a breakthrough.
- Create imbalances: Look for ways to create imbalances in the position, such as sacrificing material for a positional advantage or opening lines for your pieces. Imbalances often lead to tactical chances.
- Plan ahead: Formulate a long-term plan by evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of both positions. Identify potential weaknesses in your opponent's camp and develop a plan to exploit them.
How to Achieve Checkmate in 2 Moves
There are a few checkmate patterns that can be achieved in just two moves. One such example is the Fool's Mate:
In this position, White can achieve checkmate with 1.f3 e5 2.g4 Qh4#. It is crucial to avoid falling into such quick checkmates by being mindful of the opening moves.
How to Achieve Checkmate in 3 Moves
Checkmate in three moves is possible through various checkmate patterns. One well-known example is the Scholar's Mate:

In this position, White can achieve checkmate with 1.e4 e5 2.Bc4 Bc5 3.Qh5 Nf6 4.Qxf7#. The Scholar's Mate is an example of a quick and effective checkmate pattern.
|
45 videos|14 docs|5 tests
|





















