Grade 11 Exam > Grade 11 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) > Alkenes
Alkenes | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) PDF Download
Catalytic Cracking
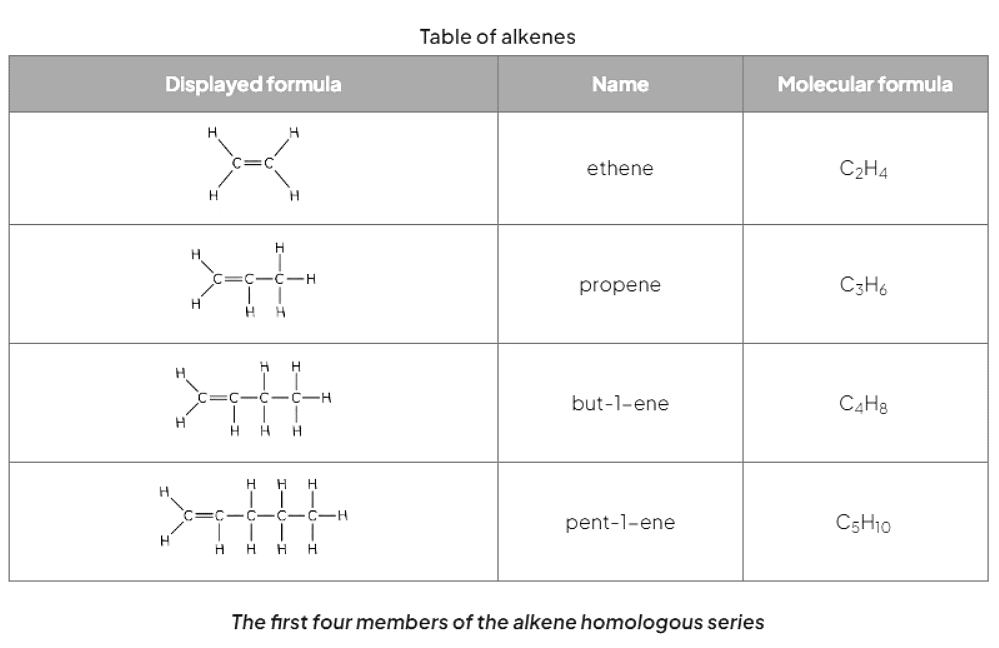
- Alkenes are a type of unsaturated hydrocarbons characterized by the presence of carbon-carbon double bonds (C=C).
- Their general formula is CnH2n, where "n" represents the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- Due to the presence of the double bond (C=C), alkenes can engage in additional bonding with other atoms. This occurs by breaking the double bond and allowing incoming atoms to form single bonds with each carbon atom of the functional group.
- Consequently, each carbon atom in the functional group forms four single bonds instead of one double bond and two single bonds.
- This increased bonding capability makes alkenes significantly more reactive compared to alkanes.
Manufacture of Alkenes
- Although each fraction obtained from the fractional distillation of crude oil serves a purpose, there's an excess production of longer-chain hydrocarbons.
- These longer-chain hydrocarbon molecules undergo further processing to create other products.
- Catalytic cracking is a method employed to convert longer-chain molecules into shorter-chain and more practical hydrocarbons.
- Longer-chain alkanes are cracked to produce shorter-chain alkanes, alkenes, and hydrogen.
- Alkenes find utility in polymer production, while hydrogen is used in ammonia synthesis.
- Kerosene and diesel oil are commonly subjected to cracking to yield petrol, additional alkenes, and hydrogen.
- Cracking entails heating hydrocarbon molecules to temperatures ranging from 600 to 700°C to vaporize them.
- The vapors then traverse over a hot powdered catalyst, typically alumina or silica.
- Through this process, covalent bonds within the molecules are disrupted upon contact with the catalyst surface, leading to thermal decomposition reactions.
- The breaking of molecules occurs randomly, generating a mixture of smaller alkanes and alkenes.
- Higher temperatures and pressures yield a higher proportion of hydrogen and alkenes.

Question for AlkenesTry yourself: What is the purpose of catalytic cracking in the manufacture of alkenes?View Solution
Distinguishing from Alkanes
Distinguishing Between Alkanes & Alkenes
- Alkanes and alkenes possess distinct molecular configurations.
- Alkanes are invariably saturated, while alkenes are unsaturated due to the presence of the C=C double bond.
- The existence of the C=C double bond enables alkenes to engage in reactions that are inaccessible to alkanes.
- A straightforward chemical examination utilizing bromine water facilitates the differentiation between alkanes and alkenes.

- Bromine water comprises an orange-tinted bromine solution.
- Interaction of bromine water with an alkane will sustain its orange hue since alkanes lack double carbon bonds (C=C), thereby retaining the bromine in solution.
- In contrast, when bromine water interacts with an alkene, it undergoes decolorization, turning colorless. This is because alkenes possess double carbon bonds (C=C), enabling bromine atoms to add across the C=C double bond, thus eliminating the orange coloration from the solution.
- This chemical process, where bromine adds across the double bond of alkenes, is termed an addition reaction.

Question for AlkenesTry yourself: How can alkanes and alkenes be distinguished using bromine water?View Solution
The document Alkenes | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) is a part of the Grade 11 Course Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE).
All you need of Grade 11 at this link: Grade 11
|
103 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Alkenes - Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE)
| 1. What is catalytic cracking and how is it related to the manufacture of alkenes? |  |
Ans. Catalytic cracking is a process used in the petroleum industry to break down large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones. This process helps in the production of alkenes, which are unsaturated hydrocarbons used in various industries.
| 2. How is the manufacture of alkenes different from alkanes? |  |
Ans. The manufacture of alkenes involves the production of unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one carbon-carbon double bond, while alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with only single bonds between carbon atoms.
| 3. What are the key differences between catalytic cracking and steam cracking in the production of alkenes? |  |
Ans. Catalytic cracking uses a catalyst to break down hydrocarbon molecules, while steam cracking uses high temperatures and steam to break them down. Both processes are used in the production of alkenes, but they differ in their mechanisms.
| 4. What are some common applications of alkenes in various industries? |  |
Ans. Alkenes are used in the production of plastics, synthetic rubber, detergents, and various chemicals. They are also used in the manufacture of solvents, adhesives, and coatings.
| 5. How does the catalytic cracking process help in the efficient production of alkenes compared to other methods? |  |
Ans. Catalytic cracking allows for the selective production of alkenes by breaking down larger hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones in the presence of a catalyst. This helps in maximizing the yield of alkenes and reducing the production of unwanted by-products.

|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















