Animal Tissue : Complete Notes, Class 9 Science PDF Download
Tissue
Animal Tissues
Animal tissues are of four types, viz. epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue and nervous tissue.
Epithelial Tissue:
The epithelial tissue forms the covering or lining of most of the organs. The cells of epithelial tissue are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet. There is small amount of cementing materials between the cells and no intercellular space is present. Permeability of the epithelial tissue plays a great role in exchange of materials among various organs it also plays an important role in osmoregulation. All epithelial tissues are separated by the underlying tissue by an extracellular fibrous basement membrane. Epithelial tissues are of following types:


- Simple Epithelium: The simple epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells. This type of epithelial tissue forms the lining of blood vessels and alveoli. Thin layer of cells facilitates exchange of substances; in such cases.
- Cuboidal Epithelium:- The cells are cube-shaped in cuboidal epithelium. Linings of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands are composed of cuboidal epithelium. Cuboidal cells provide mechanical support. Cells of epithelium may play the role of secretion and then they are called glandular epithelium.
- Columnar Epithelium:- Cells are column-shaped in columnar epithelium. Columnar epithelium facilitates secretion and absorption. For example; the lining of intestine is composed of columnar epithelium. In some organs, columnar epithelium has cilia present on the outer surface. Cilia facilitate movements of certain substances. The ciliated epithelium in the respiratory tract pushes the mucus forward.
- Stratified Epithelium:- Cells of the stratified epithelium are in many layers. Skin is an example of stratified epithelium. Stratification of layers prevents wear and tear.
Connective Tissue:
The cells of a connective tissue are loosely scattered in a matrix. The matrix can be a fluid, jelly like, dense or rigid. The nature of matrix depends on the function a connective tissue serves. Following are the various connective tissues:
- Areolar Connective Tissue: Areolar tissue is found between skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in bone marrow. Areolar tissue fills the gap between tissues and provides support. It also helps in repair of tissues.
- Adipose Tissue: Adipose tissue is composed of fat globules. This tissue is found below the skin and beneath the organs. Adipose tissue provides insulation and works as a cushion.
- Bone: Bone is mainly composed of osteoblasts. Bone makes the skeletal system. Skeletal system is responsible for providing structural framework to the body. It provides protection to important organs and facilitates movements.
- Cartilage: Cartilage is mainly composed of chondrioblasts. Cartilage is present at the ends of articulatory bones. Cartilage is also present in external ear, bronchii, etc.
- Blood: Blood is composed of blood cells, platelets and plasma. Blood plays an important role in transportation of various substances in the body. It also helps in osmoregulation and temperature control.
Muscular Tissue:
Muscular tissue is composed of muscle cells. Muscle cells are specialized cells which have the capability to contract and expand. Due to contraction and expansion, muscles facilitate various kinds of movements in the body. Muscular tissues are of three types:



- Striated Muscles: The cells of striated muscles are in the form of long, unbranched fibres. Cells are multinucleate. Light and dark bands (striations) are present on muscle fibres; which gives the name striated muscles. Striated muscles are found in those organs where voluntary movement is possible, e.g. hands, legs, back, neck, etc.
- Smooth Muscles: The cells of smooth muscles are spindle shaped and each has one nucleus. Smooth muscle is found in those organs where involuntary movement is possible, e.g. alimentary canal.
- Cardiac Muscles: The cells of cardiac muscles are in the form of branched fibres. Striations are present and cells are uninucleate. These are found in the heart. Cardiac muscles are capable continuous contraction and relaxation throughout the life.
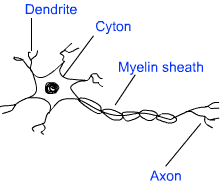
Nervous Tissue:
Nervous tissue makes the nervous system and is composed of specialized cells called neuron. A neuron can be divided into two distinct parts, viz. head and tail. The head is somewhat star-shaped and contains nucleus and some other cell organelles. This is called cyton. There are numerous hair-like outgrowths coming out of the cyton. These are called dendrites. The tail ends in axon terminals. Dendrites receive the nerve impulse, while axon relays the nerve signals.
FAQs on Animal Tissue : Complete Notes, Class 9 Science
| 1. What are animal tissues? |  |
| 2. What is the function of epithelial tissue in animals? |  |
| 3. How is connective tissue different from other animal tissues? |  |
| 4. What is the role of muscular tissue in animals? |  |
| 5. How does nervous tissue coordinate the functioning of different organ systems in animals? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















