Arithmetic Progression and Geometric Progression | Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
What is a Sequence?
A sequence is a list of numbers in a special order. It is a string of numbers following a particular pattern, and all the elements of a sequence are called its terms. There are various types of sequences which are universally accepted, but the one which we are going to learn right now is the arithmetic progression.
Arithmetic Progression (AP)

In an arithmetic sequence, the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant. The constant difference is commonly known as common difference and is denoted by d.
Let us understand this with one example.
Let’s check whether the given sequence is A.P: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 1. To check if the given sequence is A.P or not, we must first prove that the difference between the consecutive terms is constant. So, d = a2– a1 should be equal to a3– a2 and so on… Here,
d = 3 – 1 = 2 equal to 5 – 3 = 2
Here we can see that the difference is common to both the terms. So we can say that the given sequences are in arithmetic progression
The nth term of an AP
We can find the nth term of an AP by using the formula,
an = (a1 + (n – 1) d)
Here a1 is the first term and d is the common difference of an AP. The constant difference between any two terms of an AP is commonly known as common difference and is denoted by d.
Properties of Arithmetic Progression
Before understanding the properties let us first write the general form of an A.P: a1 a2 a3……an and if its common difference is d. If we add or subtract any constant, to every term of this arithmetic progression, the resulting sequence will also be an arithmetic progression. So,
(a1 + (n – 1) d) is the general (nth) term of an AP
S = [(n/2) * (2a1 + (n – 1) d)] is the sum of first n terms of an AP
• If a constant number is added or subtracted from each term of an A.P, then the resulting term in the sequence are also in A.P with the same common difference.
• If each term in an A.P is divided or multiply with a constant non-zero number, then the resulting sequence is also in an A.P
• Three number x, y and z are in an A.P if 2y = x + z
• A sequence is an A.P if its nth term is a linear expression.
• If we select terms in the regular interval from an A.P, these selected terms will also be in AP
Solved Examples
Question: If l = 20, d = -1 and n = 17, then the first term is?
A. 30
B. 32
C. 34
D. 36
Solution: The correct option is D
Given: l = 20, d = -1, n = 17
We need to find a. By using l = a + (n – 1)d,
∴ 20 = a + (17 – 1) -1
20 = a – 17
a = 36
Question: 30 trees are planted in a straight line at intervals of 55 metres. To water them, the gardener needs to bring water to each tree, separately from a well, which is 10 metres from the first tree in line with the trees. How far will he have to walk in order to water all the trees beginning with the first tree? Assume that he starts from the first well, and he can carry enough water to water only one tree at a time.
A. 4785 meters
B. 4795 meters
C. 4800 meters
D. None of these
Solution: Correct option is B. For the first tree, he has to walk = 10 meters. For the second tree = 25 meters. third tree = 35 meters and fourth tree = 45 meters. So the total distance travelled = 10 + 25+ 35…..30 terms
= 10 + ( 25 + 35+ …29 terms)
= 10 + 29/2 (2 × 25 + 28 × 10) [S = n/2 * (2a + (n-1)d) ]
= 4795
Geometric Progression

A geometric sequence is a sequence in which any element after the first is obtained by multiplying the preceding element by a constant called the common ratio which is denoted by r. For example, the sequence 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32… is a geometric sequence with a common ratio of 2.
Here each number gets doubled as it moves to its consecutive number. That means here when 1 is multiplied by 2 it becomes 2 when 2 is multiplied by 2 it becomes 4 when this is multiplied by 2 it becomes 8 and so on… What do you think is happening? Can we say that the ratio of the two consecutive terms is constant?
Let’s talk about a1= 1, a2= 2
So, a2/a1 = 2/1 = 2
Now, a3 = 4. Let us try to find the ratio of a3 and a2
a3a2 = 4/2 = 2
Now since the value of a/4 = 8
a4/a3 = 8/4 = 2
So we can say, a2/a1 = a3/a2 = a4/a3
So, the ratio of the two consecutive terms, of this particular sequence is a constant. Such sequence is as called Geometric Progression. The geometric progression is the sequence in which the first term should be non zero and each consecutive termed is derived by multiplying the preceding term by a constant quantity.
Example
Check whether the given sequence is a geometrical progression: 9, 3, 1, 1/3, 1/9……
Solution: Let us find the ratio of the consecutive terms, a1= 9 and a2 = 3. So,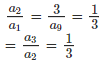
So we can say that the ratio of the consecutive termof given sequences is 13 or a constant. So this sequenece is forming a geometrical progression.
The General Form of a GP
The general form of a GP is : a1, a1r, a1r², a1r³, a1rn-1, a1 rn
General (nth) Term of a GP
Each term of Geometric Progression as a1, a2, a3, a4….am,….an all these terms according to the first term a1will give,
a1= a1
a2 = a1r
a3= a2r = (a1r) r = a1r²
a4 = a3r =( a2r²) = r = a1r³
Like that, nth term will be
an = a1rn-1
Common Ratio of a GP
We get the common ratio of Geometric Progression by dividing any term by the preceding term:
Common Ratio of a GP
We get the common ratio of Geometric Progression by dividing any term by the preceding term:
r = a2/a1
What is the sum of first n terms of a Geometric Progression?
To calculate the sum of first n term of a GP we use the following formula: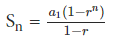
Where r ≠1. Here n is the number of terms, a1 is the first term and r is the common ratio.
Properties of Geometric Progression
The following are the properties of the G.P:
• If we multiply or divide a constant non zero quantity term to each term of a G.P then the resulting term of the sequence is also in G.P with the common difference.
• In G.P reciprocal of all the term in G.P are also form a G.P.
• If all the term in a G.P is raised to the same power then the new series are also in G.P.
• Three non-zero terms x, y and z are in G.P if y² = xz
Solved Examples
Question: Five numbers are in A.P. with common difference ≠0. Here the first, third and fourth term is in G.P then?
A. Fith term is always zero
B. The third term is zero
C. The first term is always zero
D. Middle term is zero
E. Middle term is always 2
Solution: The correct option is A. If the first, third and fourth term is in G.P then the fifth term is always zero.
Question: How many terms of the series 1 + 3+ 9+….sum to 121.
A. 5
B. 6
C. 4
D. 3
Solution: The correct option is A. The given series is a G.P,
Sum of n terms of GP is a * (rn – 1)/ (r – 1)
Here a = 1 and r = 3
Substituting in the equation we get n = 5
|
75 videos|238 docs|91 tests
|
FAQs on Arithmetic Progression and Geometric Progression - Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is an arithmetic progression? |  |
| 2. How can I find the nth term of an arithmetic progression? |  |
| 3. What is a geometric progression? |  |
| 4. How can I find the nth term of a geometric progression? |  |
| 5. What is the sum of an arithmetic series? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|

















