BFS (Breadth-first search) Algorithm | Algorithms - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
- In this article, we will discuss the BFS algorithm in the data structure. Breadth-first search is a graph traversal algorithm that starts traversing the graph from the root node and explores all the neighboring nodes. Then, it selects the nearest node and explores all the unexplored nodes. While using BFS for traversal, any node in the graph can be considered as the root node.
- There are many ways to traverse the graph, but among them, BFS is the most commonly used approach. It is a recursive algorithm to search all the vertices of a tree or graph data structure. BFS puts every vertex of the graph into two categories - visited and non-visited. It selects a single node in a graph and, after that, visits all the nodes adjacent to the selected node.
Applications of BFS algorithm
The applications of breadth-first-algorithm are given as follows:
- BFS can be used to find the neighboring locations from a given source location.
- In a peer-to-peer network, BFS algorithm can be used as a traversal method to find all the neighboring nodes. Most torrent clients, such as BitTorrent, uTorrent, etc. employ this process to find "seeds" and "peers" in the network.
- BFS can be used in web crawlers to create web page indexes. It is one of the main algorithms that can be used to index web pages. It starts traversing from the source page and follows the links associated with the page. Here, every web page is considered as a node in the graph.
- BFS is used to determine the shortest path and minimum spanning tree.
- BFS is also used in Cheney's technique to duplicate the garbage collection.
- It can be used in ford-Fulkerson method to compute the maximum flow in a flow network.
Algorithm
The steps involved in the BFS algorithm to explore a graph are given as follows:
- Step 1: SET STATUS = 1 (ready state) for each node in G
- Step 2: Enqueue the starting node A and set its STATUS = 2 (waiting state)
- Step 3: Repeat Steps 4 and 5 until QUEUE is empty
- Step 4: Dequeue a node N. Process it and set its STATUS = 3 (processed state).
- Step 5: Enqueue all the neighbours of N that are in the ready state (whose STATUS = 1) and set
their STATUS = 2
(waiting state)
[END OF LOOP] - Step 6: EXIT
Example of BFS algorithm
Now, let's understand the working of BFS algorithm by using an example. In the example given below, there is a directed graph having 7 vertices.
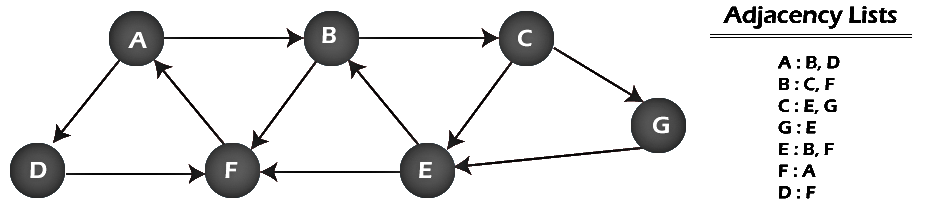
In the above graph, minimum path 'P' can be found by using the BFS that will start from Node A and end at Node E. The algorithm uses two queues, namely QUEUE1 and QUEUE2. QUEUE1 holds all the nodes that are to be processed, while QUEUE2 holds all the nodes that are processed and deleted from QUEUE1.
Now, let's start examining the graph starting from Node A.
Step 1: First, add A to queue1 and NULL to queue2.
QUEUE1 = {A}
QUEUE2 = {NULL}
Step 2: Now, delete node A from queue1 and add it into queue2. Insert all neighbors of node A to queue1.
QUEUE1 = {B, D}
QUEUE2 = {A}
Step 3: Now, delete node B from queue1 and add it into queue2. Insert all neighbors of node B to queue1.
QUEUE1 = {D, C, F}
QUEUE2 = {A, B}
Step 4: Now, delete node D from queue1 and add it into queue2. Insert all neighbors of node D to queue1. The only neighbor of Node D is F since it is already inserted, so it will not be inserted again.
QUEUE1 = {C, F}
QUEUE2 = {A, B, D}
Step 5: Delete node C from queue1 and add it into queue2. Insert all neighbors of node C to queue1.
QUEUE1 = {F, E, G}
QUEUE2 = {A, B, D, C}
Step 6: Delete node F from queue1 and add it into queue2. Insert all neighbors of node F to queue1. Since all the neighbors of node F are already present, we will not insert them again.
QUEUE1 = {E, G}
QUEUE2 = {A, B, D, C, F}
Step 7: Delete node E from queue1. Since all of its neighbors have already been added, so we will not insert them again. Now, all the nodes are visited, and the target node E is encountered into queue2.
QUEUE1 = {G}
QUEUE2 = {A, B, D, C, F, E}
Complexity of BFS algorithm
Time complexity of BFS depends upon the data structure used to represent the graph. The time complexity of BFS algorithm is O(V+E), since in the worst case, BFS algorithm explores every node and edge. In a graph, the number of vertices is O(V), whereas the number of edges is O(E).
The space complexity of BFS can be expressed as O(V), where V is the number of vertices.
Implementation of BFS algorithm
Now, let's see the implementation of BFS algorithm in java.
In this code, we are using the adjacency list to represent our graph. Implementing the Breadth-First Search algorithm in Java makes it much easier to deal with the adjacency list since we only have to travel through the list of nodes attached to each node once the node is dequeued from the head (or start) of the queue.
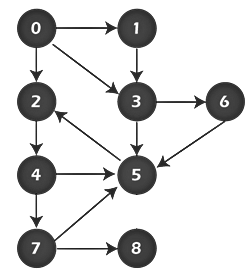
In this example, the graph that we are using to demonstrate the code is given as follows:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class BFSTraversal
{
private int vertex; /* total number number of vertices in the graph */
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[]; /* adjacency list */
private Queue<Integer> que; /* maintaining a queue */
BFSTraversal(int v)
{
vertex = v;
adj = new LinkedList[vertex];
for (int i=0; i<v; i++)
{
adj[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
que = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
void insertEdge(int v,int w)
{
adj[v].add(w); /* adding an edge to the adjacency list (edges are bidirectional in this example) */
}
void BFS(int n)
{
boolean nodes[] = new boolean[vertex]; /* initialize boolean array for holding the data */
int a = 0;
nodes[n]=true;
que.add(n); /* root node is added to the top of the queue */
while (que.size() != 0)
{
n = que.poll(); /* remove the top element of the queue */
System.out.print(n+" "); /* print the top element of the queue */
for (int i = 0; i < adj[n].size(); i++) /* iterate through the linked list and push all neighbors into queue */
{
a = adj[n].get(i);
if (!nodes[a]) /* only insert nodes into queue if they have not been explored already */
{
nodes[a] = true;
que.add(a);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
BFSTraversal graph = new BFSTraversal(10);
graph.insertEdge(0, 1);
graph.insertEdge(0, 2);
graph.insertEdge(0, 3);
graph.insertEdge(1, 3);
graph.insertEdge(2, 4);
graph.insertEdge(3, 5);
graph.insertEdge(3, 6);
graph.insertEdge(4, 7);
graph.insertEdge(4, 5);
graph.insertEdge(5, 2);
graph.insertEdge(6, 5);
graph.insertEdge(7, 5);
graph.insertEdge(7, 8);
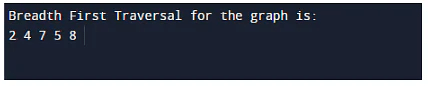
System.out.println("Breadth First Traversal for the graph is:");
graph.BFS(2);
}
}
Output
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the Breadth-first search technique along with its example, complexity, and implementation in java programming language. Here, we have also seen the real-life applications of BFS that show it the important data structure algorithm.
|
81 videos|80 docs|33 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
















