Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Physics for Grade 10 > Background Radiation
Background Radiation | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Measuring Radiation Dose |

|
| Differences in Exposure |

|
| Tips |

|
Introduction
- It is important to remember that radiation is a natural phenomenon
- Radioactive elements have always existed on Earth and in outer space
- However, human activity has added to the amount of radiation that humans are exposed to on Earth
- Background radiation is defined as:
- The radiation that exists around us all the time
- There are two types of background radiation:
- Natural sources
- Man-made sources
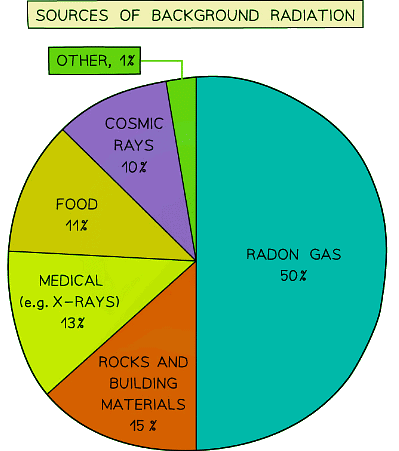 Background radiation is the radiation that is present all around in the environment. Radon gas is given off from some types of rock
Background radiation is the radiation that is present all around in the environment. Radon gas is given off from some types of rock
- Every second of the day there is some radiation emanating from natural sources such as:
- Rocks
- Cosmic rays from space
- Foods
- Man-made sources of radiation increase the background radiation levels, examples include:
- Fallout from nuclear weapons testing and nuclear accidents
- Exposure from medical testing
Example: A student is using a Geiger-counter to measure the counts per minute at different distances from a source of radiation. Their results and a graph of the results are shown here.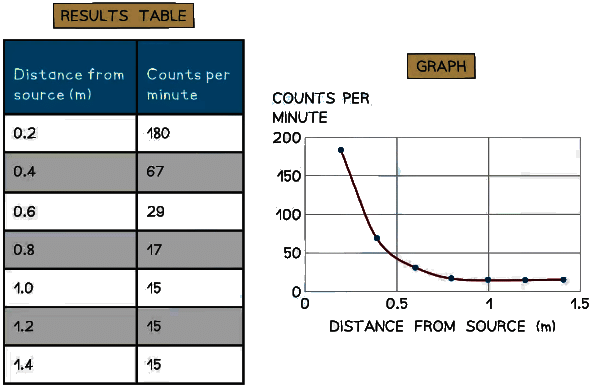 Determine the background radiation count.
Determine the background radiation count.
Step 1: Determine the point at which the source radiation stops being detected
- The background radiation is the amount of radiation received all the time
- When the source is moved back far enough it is all absorbed by the air before reaching the Geiger-counter
- Results after 1 metre do not change
- Therefore, the amount after 1 metre is only due to background radiation
Step 2: State the background radiation count
- The background radiation count is 15 counts per minute
Measuring Radiation Dose
- It is important to regulate the exposure of humans to radiation
- The amount of radiation received by a person is called the dose and is measured in sieverts (Sv)
- One sievert is a very big dose of radiation
- It would cause acute radiation poisoning
- People would normally receive about 3 mSv (0.003 Sv) in one year
- To protect against over-exposure, the dose received by different activities is measured
- A dosemeter measures the amount of radiation in particular areas
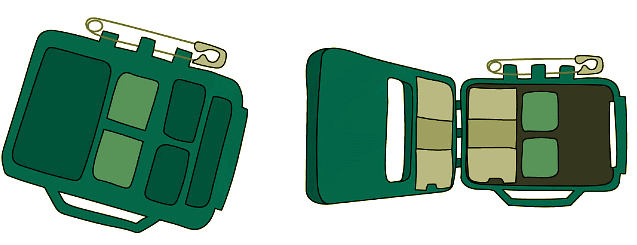 A dosemeter, or radiation badge, can be worn by a person working with radiation in order to keep track of the amount of radiation they are receiving
A dosemeter, or radiation badge, can be worn by a person working with radiation in order to keep track of the amount of radiation they are receiving
Differences in Exposure
- The level of background radiation and radiation dose may be affected by a person’s occupation or location
- Some areas around the world have higher background radiation because they are closer to sources of radiation
- People that work with nuclear radiation receive more radiation
- The UK limit for nuclear industry employees is 20 mSv in one year
- The diagram below compares the dose received by some different activities
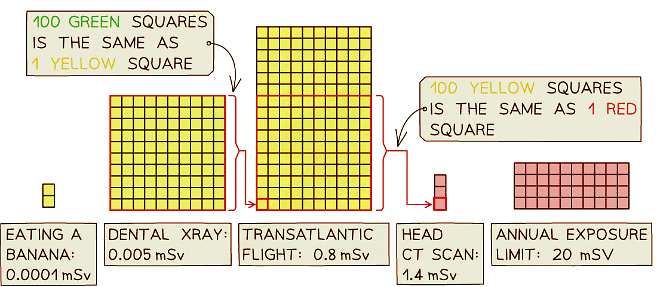 All living things emit a small amount of radiation: the amount of radiation within a banana is tiny, and not at all dangerous!
All living things emit a small amount of radiation: the amount of radiation within a banana is tiny, and not at all dangerous!
Tips
You have been introduced to three different units to do with radiation:
- Becquerels measure the amount of radiation emitted by a source every second
- Counts per second measures the rate at which radiation hits a particular location
- Sieverts measure the received dose of radiation
They are not the same thing!
The document Background Radiation | Physics for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Physics for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
122 videos|150 docs|40 tests
|
Related Searches














