Bacterial Binary Fission | Biology for MCAT PDF Download
Introduction
In the mesmerizing world of cell division, where life emerges and perpetuates, we often encounter the intricate process of mitosis. But what about simpler organisms like bacteria? How do they carry out cell division? Enter bacterial binary fission, a fascinating process that allows these microorganisms to reproduce and flourish. In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of bacterial binary fission, exploring its steps, nuances, and how it differs from the more elaborate process of mitosis.
What is Binary Fission?
Bacterial binary fission serves as the cornerstone of cell division for bacteria. While it shares similarities with mitosis, the purpose and outcome of binary fission differ significantly. Mitosis in multicellular organisms contribute to growth and rejuvenation, replacing old cells with new ones. On the other hand, binary fission is primarily a method for bacterial reproduction, facilitating an increase in population. Let us now embark on a journey to uncover the inner workings of this essential process.
Steps of Binary Fission:
1. Chromosomal Duplication: Similar to human cells, a dividing bacterium initiates binary fission by copying its DNA. However, bacterial cells possess a distinct structure: a single, circular chromosome residing in a specialized region known as the nucleoid. Replication enzymes commence DNA replication at a specific point called the origin of replication. This origin acts as the starting point for DNA copying, as the two origins gradually move towards opposite ends of the cell. The rest of the chromosome is pulled along, resulting in an elongation of the cell and a progressive separation of the newly forming chromosomes.
2. Completion of DNA Replication: The process of DNA replication continues until the entire chromosome is fully copied, culminating in the replication enzymes meeting at the far side. At this point, the newly formed chromosomes have reached opposite ends of the cell and cleared the central region. This crucial milestone signifies the readiness for cytoplasmic division.
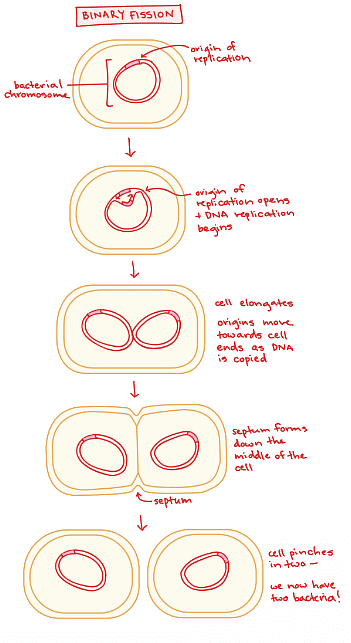
3. Cytoplasmic Division: In binary fission, the final step involves the division of the cytoplasm to create two distinct cells. The cell membrane undergoes a remarkable transformation as it pinches inward, initiating the formation of a septum—a new dividing wall—down the middle of the cell. Since bacteria possess a cell wall, regeneration of this wall is essential during cell division. Finally, the septum splits in the center, releasing the two individual bacteria, now ready to embark on their unique journeys of life.
4. Comparing Binary Fission and Mitosis: Although bacterial binary fission shares similarities with mitosis, the mechanics and sequence of these two processes significantly differ. While both involve the replication and separation of chromosomes, bacterial binary fission lacks the formation of a mitotic spindle observed in eukaryotes. Additionally, a noteworthy distinction lies in the timing of DNA replication. In binary fission, DNA replication occurs simultaneously with DNA separation, unlike mitosis, where DNA is copied during the S phase long before its separation in the M phase.
Conclusion
Bacterial binary fission, the remarkable process behind bacterial cell division, holds intrinsic beauty in its simplicity. Through a series of meticulously orchestrated steps, bacteria duplicate their DNA, form new cell walls, and ultimately release two independent cells into the world. By understanding the nuances of binary fission and its distinctions from mitosis, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse mechanisms of life. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of cell division, bacterial binary fission remains a captivating example of nature's ingenuity in perpetuating life.|
233 videos|16 docs|32 tests
|




















