Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE > Bank Reconciliation Statements
Bank Reconciliation Statements | Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Purpose of a Bank Reconciliation Statement
What is the purpose of a bank reconciliation statement?
- When the bank statement balance differs from the cash book balance, a bank reconciliation statement is created by the business.
- The bank reconciliation statement clarifies the reasons behind the differing balances.
- Transactions present in the bank statement but not in the cash book can be added to the cash book.
- Conversely, transactions present in the cash book but not in the bank statement cannot be added to the bank statement.
- The bank reconciliation statement is crucial for highlighting and addressing such discrepancies.
- It includes information on unpresented cheques, uncredited deposits, and errors.
Preparing a Bank Reconciliation Statement
How do I prepare a bank reconciliation statement?
- Step 1: Update the cash book using information from the bank statement and calculate the new balance.
- Step 2: Initiate the bank reconciliation statement with the balance displayed on the bank statement, ensuring clarity on whether it represents available funds or an overdrawn amount. A debit balance indicates an overdraft.
- Step 3: Incorporate any deposits not yet credited, which are debit entries in the cash book absent from the bank statement. If multiple entries exist, aggregate their amounts into the left column of the reconciliation statement, then place the total in the right column. Add this total to the bank statement balance.
- Step 4: Include any bank errors that have reduced the bank statement balance, totaling them along with prior entries.
- Step 5: Deduct any outstanding cheques, representing credit entries in the cash book not reflected in the bank statement. If there are multiple entries, sum their amounts in the left column of the reconciliation statement and place the total in the right column. Subtract this total from the current amount in the right column of the statement.
- Step 6: Subtract any bank errors that have inflated the bank statement balance, accumulating them alongside prior entries.
- Step 7: Verify that this reconciled amount matches the bank balance in the cash book. If the balance is negative, it indicates a credit balance in the cash book.
Example of a bank reconciliation statement
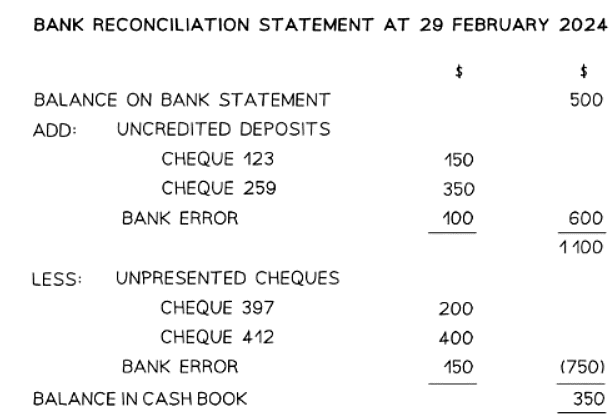
Question for Bank Reconciliation StatementsTry yourself: What is the purpose of a bank reconciliation statement?View Solution
Can I start the bank reconciliation statement with the balance shown in the cash book?
You can alternatively construct the bank reconciliation statement in reverse order by:
- Initiating with the balance indicated in the cash book.
- Adding the amounts of unpresented cheques.
- Subtracting the uncredited deposits.
- Ensuring the reconciled total matches the balance presented on the bank statement.
The document Bank Reconciliation Statements | Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
22 videos|29 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Bank Reconciliation Statements - Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the purpose of a Bank Reconciliation Statement? |  |
Ans. A Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared to ensure that the balance shown in the cash book matches the balance shown on the bank statement, and to identify any discrepancies or errors that may have occurred.
| 2. How do you prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement? |  |
Ans. To prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement, you need to compare the transactions in the cash book with those in the bank statement, reconcile any differences, and adjust the balances accordingly.
| 3. Can I start the bank reconciliation statement with the balance shown in the cash book? |  |
Ans. Yes, you can start the bank reconciliation statement with the balance shown in the cash book, as this is the starting point for reconciling the transactions between the cash book and the bank statement.
| 4. What are some common reasons for discrepancies between the cash book and the bank statement? |  |
Ans. Some common reasons for discrepancies between the cash book and the bank statement include outstanding checks, deposits in transit, bank charges, and errors in recording transactions.
| 5. How often should a Bank Reconciliation Statement be prepared? |  |
Ans. A Bank Reconciliation Statement should ideally be prepared on a monthly basis to ensure that the balances in the cash book and bank statement are accurate and to promptly identify any discrepancies.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















