Banking Sector in India | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Historical Background |

|
| Banking Structure in India |

|
| Role of RBI |

|
| Types of Banks |

|
| Non-Banking Financial Institutions |

|
Introduction
A financial institution referred to as a bank primarily engages in the collection of deposits and the distribution of loans, each having distinct characteristics. Oversight for banks, exemplified by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in India, is carried out by the country's central bank. The banking sector in India is a true reflection of a mixed economy, featuring the presence of public, private, and foreign banks.
Aligned with the liberalisation policy, substantial reforms were initiated in the banking sector in 1991, guided by the recommendations of the Narasimham Committee. Before this period, both the banking and industrial sectors were subject to heavy regulation and protection by the RBI. The transformation of the banking sector was deemed crucial to not only support the liberalisation policy but also facilitate the growth of the private sector.
Historical Background
- The development of the banking sector can be divided into three stages:
- Phase I – Early Phase (1770 to 1969) which can be subdivided into Pre Independence Period (1786-1947) and Post Independence Period (1947-1969)
- Phase II – Nationalisation Phase (1969 to 1991)
- Phase III – Liberalisation or Banking Sector Reforms Phase (1991 – till date)
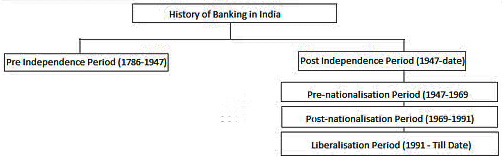
Pre-Independence Period (1786-1947)
- The "Bank of Hindustan," established in 1770 in the then-Indian capital of Calcutta, was the country's first bank. However, this bank did not succeed and closed its doors in 1832.
- Over 600 banks were registered in the country during the pre-independence period, but only a few survived.
- During British rule in India, the East India Company established three banks known as the Presidential Banks: The Bank of Bengal, the Bank of Bombay, and the Bank of Madras.
- These three banks were eventually merged into a single bank in 1921, which was known as the “Imperial Bank of India.”
- The Imperial Bank of India was later nationalised and renamed The State Bank of India, which is now the largest public sector bank in India.
Post-Independence Period (1947-1991)
- At the time of India's independence, all of the country's major banks were privately led, which was a source of concern because people in rural areas were still reliant on money lenders for financial assistance.
- To address this issue, the then-Government decided to nationalise the banks. The Banking Regulation Act of 1949 was used to nationalise these banks.
- The Reserve Bank of India, on the other hand, was nationalised in 1949.
- Following the formation of the State Bank of India in 1955, another 14 banks were nationalised between 1969 and 1991. These were the banks with more than 50 crores in national deposits.
- Another six banks were nationalised in 1980, bringing the total to twenty.
- Aside from the aforementioned 20 banks, seven SBI subsidiaries were nationalised in 1959.
- Except for the State Bank of Saurashtra, which was merged in 2008, and the State Bank of Indore, which was merged in 2010, all of these banks were merged with the State Bank of India in 2017.
Liberalisation Period (1991-Till Date)
- Once the banks have been established in the country, regular monitoring and regulations must be followed in order to maintain the profits generated by the banking sector.
- The final or ongoing phase of the banking sector's development is critical.
- To ensure the stability and profitability of the Nationalised Public Sector Banks, the Government decided to form a committee led by Shri. M Narasimham to oversee the various banking reforms in India.
- The introduction of private sector banks in India was the most significant development. The Reserve Bank of India granted licences to ten private sector banks to establish themselves.
Banking Structure in India
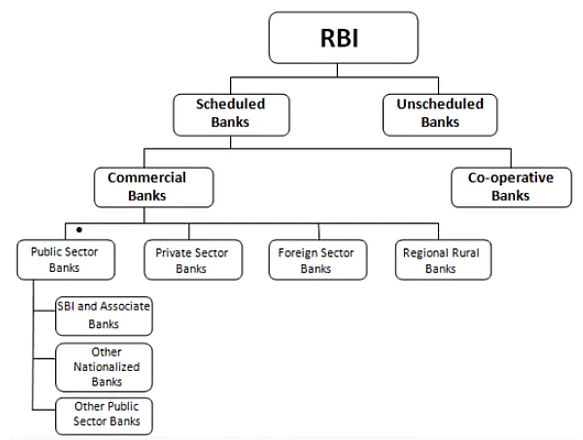
- The Indian banking system is divided into "Scheduled Banks" and "Non-scheduled Banks."
- Schedule banks are those that are listed in the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934 and thus meet the following requirements:
- a bank must have a paid-up capital and reserve of at least Rs. 5 lakh and
- a bank must satisfy the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) that its affairs are not conducted in a manner that is detrimental to the interest of its deposits.
- Non-scheduled banks are those that are not listed in the second schedule of the RBI Act, 1934 and thus do not meet the requirements outlined in that schedule.
- The term "scheduled banks" refers to both "scheduled commercial banks" and "scheduled cooperative banks."
- The Scheduled commercial banks are further subdivided into four groups:
- Public sector banks (also known as "nationalised banks" and "State Bank of India (SBI) banks");
- Private sector banks (divided into "Old Private Sector Banks" and "New Private Sector Banks" that emerged after 1991);
- Foreign banks in India; and
- Regional Rural Banks (that operate exclusively in rural areas to provide credit and other facilities to small and marginal farmers, agricultural workers, and small entrepreneurs).
- Foreign banks are present in the country either through full branch/subsidiary presence or through representative offices.
- Except for foreign banks, these scheduled commercial banks are registered in India under the Companies Act.
Role of RBI
- The RBI is the country's supreme monetary and banking authority, and it controls the Indian banking system. It is known as the Reserve Bank because it holds the reserves of all commercial banks.
- In accordance with the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, the Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935.
- The Reserve Bank's Central Office was initially located in Calcutta but was permanently relocated to Mumbai in 1937. The Governor sits in the Central Office, where policies are developed.
- Though originally privately owned, the Reserve Bank has been wholly owned by the Government of India since its nationalisation in 1949.
- The RBI Nationalisation Act of 1949 has been amended several times by the government in response to changing needs, and its functions have been expanded.
- Its current functions can be objectively summarised as:
- Monetary policy formulation, implementation, and monitoring are all part of it. The overarching goal is to maintain price stability while pursuing growth.
- It issues new currency notes and coins (except for rupee one or its denominations, which are issued by the Ministry of Finance) as well as exchanging or destroying those that are no longer fit for circulation.
(i) This function also includes the responsibility for currency and coin distribution (of those ones also which are issued by the Ministry of Finance).
(ii) The overarching goal is to maintain adequate supplies of quality currency and coins. - It establishes broad parameters for banking operations within which the banking and financial system operates.
- This function's overarching goal is to maintain public trust in the system, protect depositors' interests, and provide cost-effective banking services to the public.
- Itmanagesthe FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999), keeping the country's Forex (foreign exchange) reserves, stabilizing the rupee exchange rate, and representing the Government of India at the IMF and World Bank (and other international financial agencies of which India is a member).
- The goal of this function is to facilitate external trade and payments, as well as to promote the orderly development and maintenance of the country's foreign exchange market.
- It introduces and upgrades safe and efficient payment systems in the country to meet the needs of the general public. The goal is to keep the public's trust in the payment and settlement system.
- As a banker of the Government and the banks, it consists of three categories of functions:
(i) first, performing Merchant Banking functions for the central and state governments; second, acting as their Bankers; and third, maintaining banking accounts of the SCBs (scheduled commercial banks) operating in the country (domestic, foreign, public, and private).
(ii) The broad objectives are to enable governments and banks to mobilise enough liquidity for their operations, under which it lends or manages government borrowing plans and provides short-term and long-term loans to banks (as Lender of Last Resort). - As part of its developmental responsibilities, the RBI established developmental banks such as IDBI, SIDBI, NABARD, NEDB (North Eastern Development Bank), Exim Bank, and NHB.
- The ownership of these banks is gradually being transferred from the RBI to the Government of India.
Types of Banks
There are many types of banks in India, such as:
1. Commercial Banks
- Any banking organisation that deals with the deposits and loans of businesses is referred to as a commercial bank.
- Commercial banks issue bank checks and drafts and accept term deposits.
- Through instalment loans and overdrafts, commercial banks also serve as moneylenders.
- Commercial banks also provide a variety of deposit accounts, including checking, savings, and time deposits.
- These institutions are run for profit and are owned by a group of people.
Commercial Banks are further divided into the following:
- Public Sector Banks - These are banks in which the Government of India owns a majority stake. SBI, Bank of India, Canara Bank, and other public sector banks are examples.
- Private Sector Banks - The majority of a bank's share capital is held by private individuals. These banks are set up as limited-liability corporations. Private sector banks include ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, HDFC, and others.
- Regional Rural Banks - Regional Rural Banks were established in accordance with the provisions of an Ordinance promulgated on September 26, 1975, and the RRB Act, 1976, with the goal of ensuring adequate institutional credit for agriculture and other rural sectors.
- RRBs can only operate in the areas that have been designated by Gol as covering one or more districts in the state.
- RRBs are jointly owned by Gol, the relevant State Government, and Sponsor Banks; the issued capital of an RRB is divided among the owners in the proportions of 50%, 15%, and 35%, respectively.
- Foreign Banks - These banks are registered and have their headquarters in another country, but they have branches in our country.
- Foreign banks in India include HSBC, Citibank, Standard Chartered Bank, and others.
2. Small Finance Banks
- The Small Finance Bank (SFB) is a private financial institution that primarily undertakes basic banking activities such as deposit acceptance and lending to unserved segments such as small business units, small and marginal farmers, micro and small industries, and unorganised sector entities, but without any geographical restrictions, unlike Regional Rural Banks or Local Area Banks.
3. Payment Banks
- A payment bank is a distinct type of bank that performs only the limited banking functions permitted by the Banking Regulation Act of 1949.
- Acceptance of deposits, payments and remittance services, internet banking, and acting as a business correspondent for other banks are examples of some oftheactivities.
- They are initially permitted to collect deposits of up to Rs 1 lakh per individual.
- They can help with money transfers as well as sell insurance and mutual funds. Furthermore, they can only issue ATM/debit cards, not credit cards.
- They are not permitted to establish subsidiaries to provide non-banking financial services. More importantly, they are not permitted to engage in any lending activities.
4. Co-operative Banks
- A cooperative bank is a financial entity that is owned and operated by its members, who are also its customers.
- Co-operative banks are frequently formed by people who belong to the same local or professional community or who share a common interest.
- Co-operative banks typically offer a wide range of banking and financial services to their members (loans, deposits, banking accounts, etc).
- It is further divided into:
- Urban Cooperative Banks
- Rural Cooperative Banks
Non-Banking Financial Institutions
- A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956.
- A non-banking financial company, also known as a non-banking financial institution, provides financial services and products but is not recognised as a bank with a full banking licence.
- NBFCs are not banks, but their activities include lending and other activities such as providing loans and advances, credit facilities, savings and investment products, trading in the money market, managing stock portfolios, money transfers, and so on.
- NBFC Registration is required before NBFC activities can begin.
- Their activities include hiring, leasing, infrastructure finance, venture capital finance, housing finance, and so on.
- Deposits can be accepted by NBFC, but only term deposits and deposits repayable on demand are not accepted.
- Some examples of well-known NBFCs are Kotak Mahindra Finance, SBI Factors, Sundaram Finance, and ICICI Ventures.
Conclusion
The growth of an economy is significantly influenced by the pivotal role banks play, as they extend loans to diverse sectors for the expansion, diversification of established businesses, and the backing of emerging enterprises.
|
1335 videos|1437 docs|834 tests
|















