UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Notes > Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for UGC NET > Notes: Basics of Internet - 2
Basics of Internet - 2 - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes
Basics
- The Internet is a worldwide telecommunications system that provides connectivity for millions of other, smaller networks; therefore, the Internet is often referred to as a network of networks.
- It allows computer users to communicate with each other across distance and computer platforms (Including other ICT Based Devices such as Mobile & Other electronic devices)
- The Internet began in 1969 as the U.S. Department of Defense’s Advanced Research Project Agency (ARPA) for war communication
- The World Wide Web—usually called the Web for short—is a collection of different websites you can access through the Internet.
- Internet Service Provider- An ISP offers a variety of services for a variety of prices: web page access, email, web page hosting and so on. Most ISPs offer various internet connection speeds for a monthly fee
- A browser is a program that allows you to interact and view the internet and contents of the Web. The Web Browser, Internet Explorer, or IE is developed by Microsoft and comes pre-installed when you buy a Windows computer.
- A browser is a free software package or mobile app that lets you view web pages, graphics, and most online content. The most popular web browsers include Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, and Safari, but there are many others.
- A webpage is what you see in your browser when you are on the internet. Think of the webpage as a page in a magazine. You may see text, photos, images, diagrams, links, advertisements and more on any page you view.
- Uniform Resource Locators—URLs— are the web browser addresses of internet pages and files.
- URLs consist of three parts to address a page or file:
- The protocol is the portion ending in //: Most web pages use the protocol http or https, but there are other protocols.
- The host or top-level domain, which frequently ends in .com, .net, .edu or .org but can also end in one of many others that have been officially recognized.
- The filename or page name itself.
- A domain name is the unique, alphabetically-based part of a URL. This domain name can be officially registered with a domain registrar by a person, business, or non-profit organization
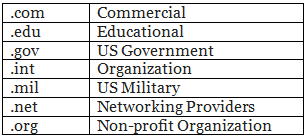
- The top level domain name that designates what kind of site it is; for example, .com (for commercial domains), .org (organizations), .edu (for educational institutions).
- Top-level domain names include:

- Domain name country codes include, but are not limited to:

- Domain name system- An Internet address has four fields with numbers that are separated by periods or dots. This type of address is known as an IP address. Rather than have the user remember long strings of numbers, the Domain Name System (DNS) was developed to translate the numerical addresses into words.
- SSL- The acronym SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. SSL is a secure encryption Web protocol used to make data safe when transmitted over the Internet.
- Web Hosting- A web host is a business/company that offers space, storage, and connectivity in order to enable a website to be viewed by Internet users.
- Web Server- The Term Web server refers to a specialized computer system or dedicated server specifically designed to host or deliver Web sites.
- Hypertext Markup Language is the programming language of webpages. HTML commands your web browser to display text and graphics in a specific fashion. Beginning internet users don’t need to know HTML coding to enjoy the webpages the programming language delivers to browsers.
- XML is eXtensible Markup Language, a cousin to HTML. XML focuses on cataloging and databasing the text content of a web page.
- XHTML is a combination of HTML and XML.
- HTTP- The client/server protocol used to exchange hypertext documents is called HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol). The main thing you need to know is that HTTP is a language spoken between your web browser (client software) and a web server (server software) so that they can communicate with each other and exchange files
The document Basics of Internet - 2 - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes is a part of the UGC NET Course Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for UGC NET.
All you need of UGC NET at this link: UGC NET
|
30 videos|17 docs|8 tests
|
|
30 videos|17 docs|8 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches