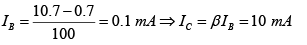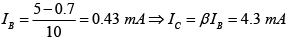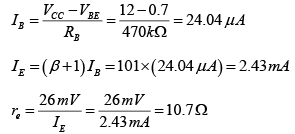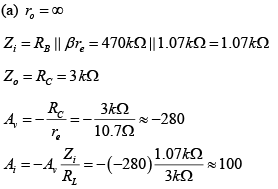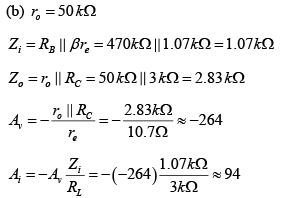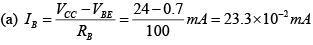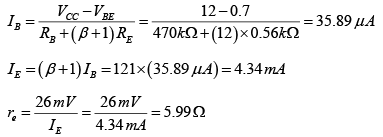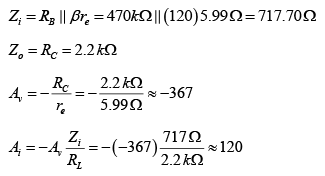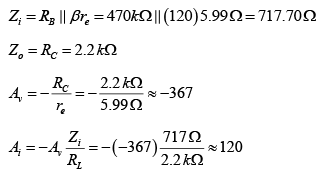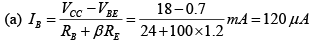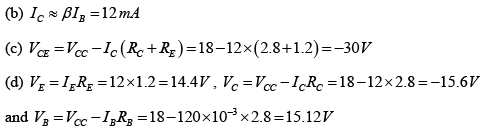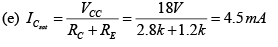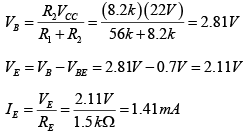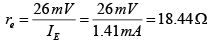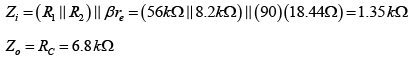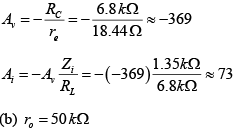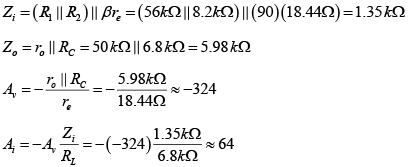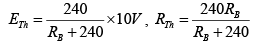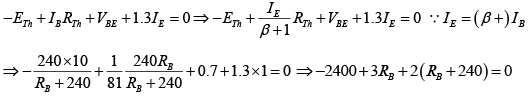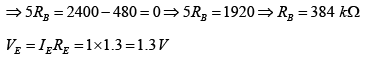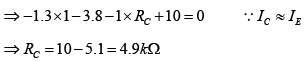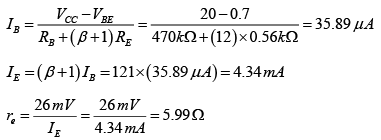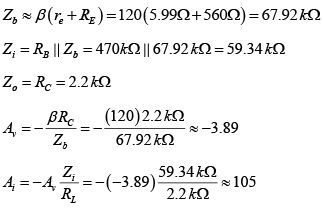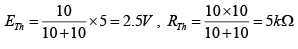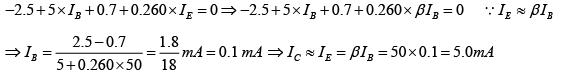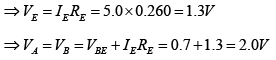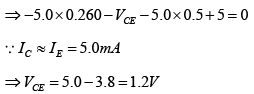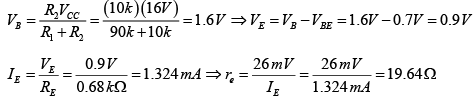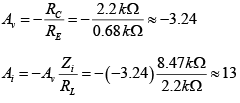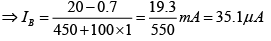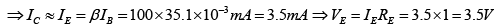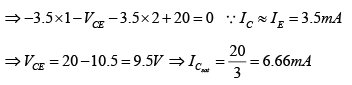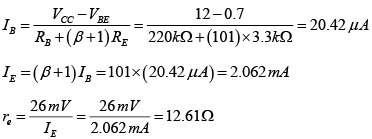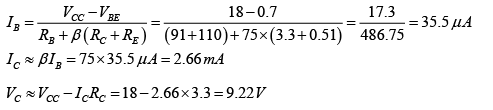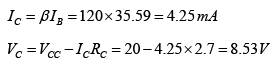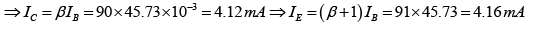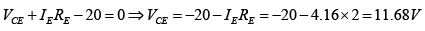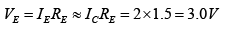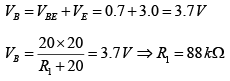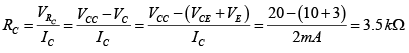Bipolar Junction Transistors: Assignment | Solid State Physics, Devices & Electronics PDF Download
Q.1. Consider the circuits shown in figures (a) and (b) below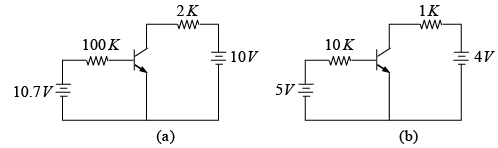 If the transistors in Figures (a) and (b) have current gain (βdc) of 100 and 10 respectively, then check whether they operate in active region, saturation region or cutoff region.
If the transistors in Figures (a) and (b) have current gain (βdc) of 100 and 10 respectively, then check whether they operate in active region, saturation region or cutoff region.
In both case input section is F.B.
For figure (a)
Thus VCB = VC - VB = (10-2x10)-0.7V = -ve ⇒ Output section is F.B.
Since both sections are F.B. So it is in saturation region.
For figure (b)
Thus VCB=VC-VB = (4-4.3x1)-0.7= -ve
⇒ Since both sections are F.B. So it is in saturation region.
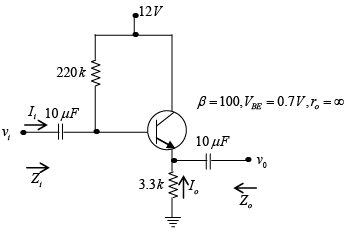
Q.2. For the network shown in figure, determine re, Zi, Zo, Av and Ai. (use re = 26mV/IE)
If (a) ro = ∞
(b) r0 = 50 kΩ
DC Analysis:
AC Analysis:
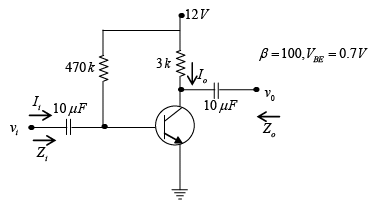
Q.3. Consider the following circuit in which the current gain βdc of the transistor is 100 and VBE = 0.7V.
Find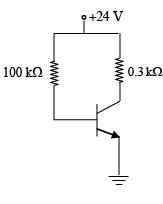 (a) IB
(a) IB
(b) IC
(c) VCE
(d) VC, VB and VE
(e) IC.sat
Q.4. For the network shown in figure, determine re, Zi, Zo, Av and Ai. (use re = 26mV/IE)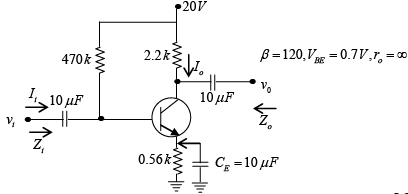
DC Analysis:
AC Analysis:
RE is “shorted out” by CE for the ac analysis. Therefore
Q.5. Consider the following circuit in which the current gain βdc of the transistor is 100, VBE = 0.7V. Find
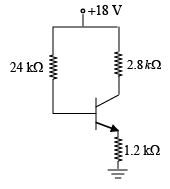
(a) IB
(b) IC
(c) VCE
(d) VC, VB and VE
(e) IC.sat
Q.6. For the network shown in figure, determine re, Zi, Zo, Av and Ai. (use re = 26mV/IE)
If (a) ro = ∞
(b) ro = 50kΩ
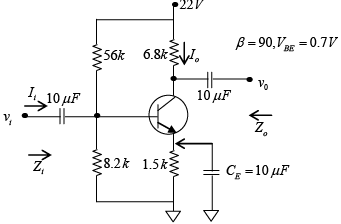
DC Analysis:
βRE = 90 x 1.5 = 135kΩ and 10R2 = 10 x 8.2 = 82kΩ
Thus βRE >> 10R2 (Use approximate meathod)
AC Analysis:
(a) ro = ∞
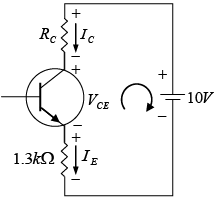
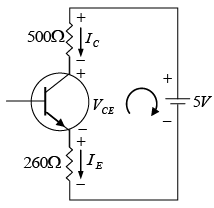
Q.7. For the transistor circuit shown below, evaluate VE, RB and RC, given IC = 1mA, β = 80, VCE = 3.8 V, VBE = 0.7 V and VCC = 10V use the approximation IC ≈ IE.
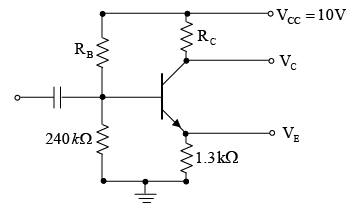
Applying KVL to input section,
Writing Kirchhoff’s voltage law for the indicated loop in the clockwise direction will result in - IERE - VCE - ICRC + VCC = 0
Q.8. For the network shown in figure, determine re, Zi, Zo, Av and Ai. (use re = 26mV/IE)
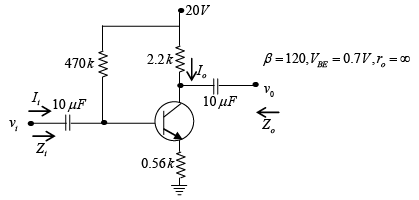
DC Analysis:
AC Analysis:
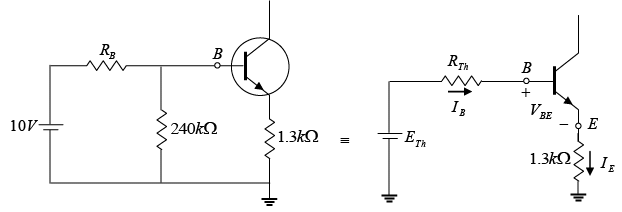
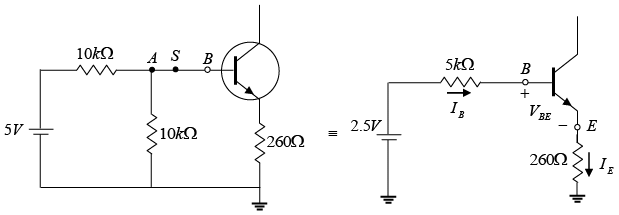
Q.9. For the transistor shown in the figure, the dc current gain βdc = 50 and VBE = 0.7. The switch S is initially open.
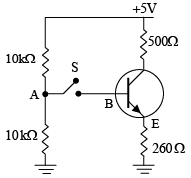
(a) Calculate the voltage at point A. If the switch S is now closed, what would be the voltage at point A?
(b) Draw the dc load line and find the Q-point of the circuit with the switch S remaining closed.
(a) When switch S is open
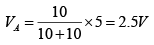
When switch S is closed, draw Thevenin’s equivalent circuit
Applying KVL to input section,
(b) Writing Kirchhoff’s voltage law for the indicated loop in the clockwise direction will result in - IERE - VCE - ICRC + VCC = 0
Thus Q -point is (IC, VCE) (5.0 mA,1.2 V).
Q.10. For the network shown in figure, determine re, Zi, Zo, Av and Ai. (use re = 26mV/IE)
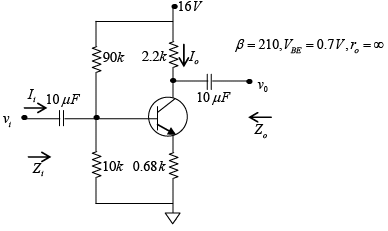
DC Analysis:
AC Analysis:
Zi = (R1||R2) || Zb = (R1 || R2) || βRE = (90kΩ||10kΩ) || (210) (0.68kΩ) = 8.47 kΩ
Zo = RC = 2.2 kΩ
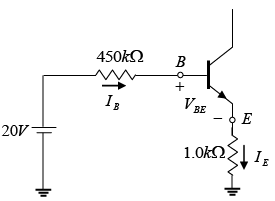
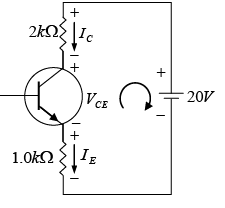
Q.11. For the transistor circuit shown in the figure βdc = 100 and 0.7 VBE = V. Determine the base current IB, the collector-emitter voltage VCE, the emitter voltage VE, the base voltage VB and the saturation current ICsat.
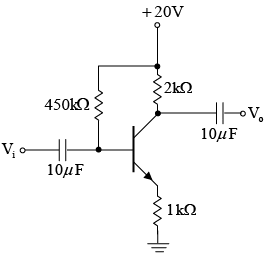
Drawing Equivalent circuit for input section
Applying KVL to input section, -20 + 450 x IB + 0.7 + 1.0 x IE = 0
⇒ -20 + 450 x IB + 0.7 + 1.0 x βIB = 0
∵ IE ≈ βIB
⇒ VB = VBE + IERE = 0.7 + 3.5 = 4.2V
Writing Kirchhoff’s voltage law for the indicated loop in the clockwise direction will result in - IERE - VCE - ICRC + VCC = 0
Q.12. For the network shown in figure, determine re, Zi, Zo, and Av. (use re = 26mV/IE)
It’s a common collector configuration.
DC Analysis:
AC Analysis: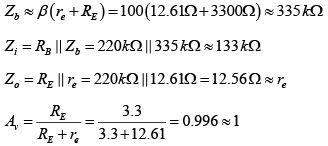
Q.13. Determine the dc level of IB and VC for the network shown in figure below.
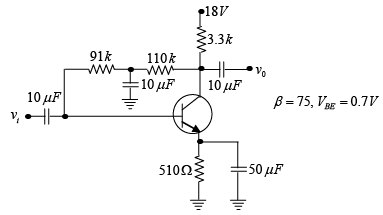
In DC equivalent, capacitor is open circuited.
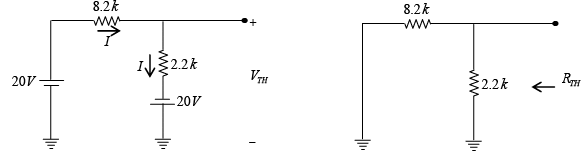
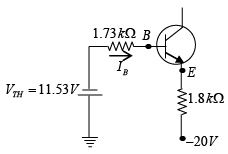
Q.14. Determine the dc level of VC and VB for the network shown in figure below.
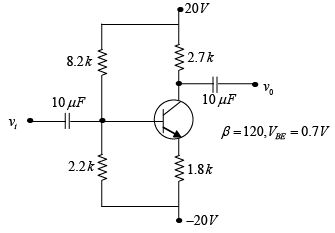
In DC equivalent, capacitor is open circuited. Let’s draw Thevenin’s equivalent circuit for input section.
and RTH = 8.2k||2.2k = 1.73k
11.53 + IB x 1.73 + 0.7 + βIB x 1.8 - 20 = 0
⇒ IB = 35.39μA
VB = -VTH - IBRTH = -11.53 - 35.39μA x 1.73k = -11.59V
Q.15. Determine the dc level of VCE and IE for the network shown in figure below.
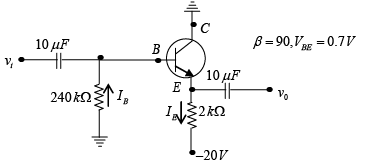
Applying KVL to input section
IB x 240 + 0.7 + 90 x IB x 2 - 20 = 0 ⇒ IB = 45.73μA
Applying KVL to output section
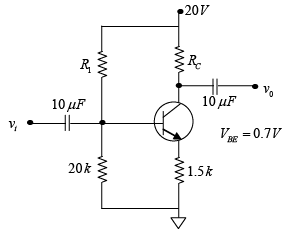
Q.16. Given that 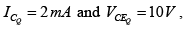 determine R1 and RC for the network shown in figure below.
determine R1 and RC for the network shown in figure below.
|
91 videos|21 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Bipolar Junction Transistors: Assignment - Solid State Physics, Devices & Electronics
| 1. What is a bipolar junction transistor? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of bipolar junction transistors? |  |
| 3. How does a bipolar junction transistor work? |  |
| 4. What are the applications of bipolar junction transistors? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of bipolar junction transistors? |  |