Bleaching Powder, Baking Soda, Washing Soda & Plaster of Paris | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 9 PDF Download
Bleaching Powder
We know that chlorine is produced during the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride (brine). This chlorine gas is used for the manufacture of bleaching powder. Bleaching powder is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2]. Bleaching powder is represented as CaOCl2, though the actual composition is quite complex. 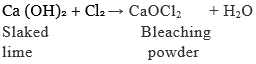
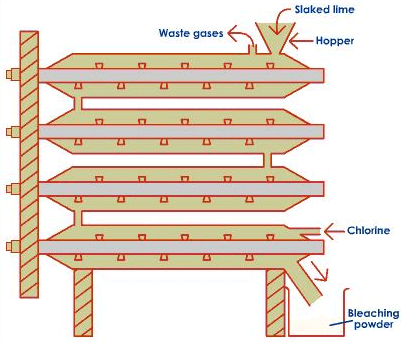 Preparation of Bleaching Powder
Preparation of Bleaching Powder
(a) For bleaching cotton and linen in the textile industry, for bleaching wood pulp in paper factories and for bleaching washed clothes in laundry.
(b) As an oxidising agent in many chemical industries, and
(c) For disinfecting drinking water to make it free of germs.
Baking Soda
The chemical name of baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate or sodium bicarbonate. Baking soda (or sodium bicarbonate) is represented by the formula NaHCO3. The soda commonly used in the kitchen for making tasty crispy pakoras is baking soda. Some time it is added for faster cooking. It is produced using sodium chloride as one of the raw materials.
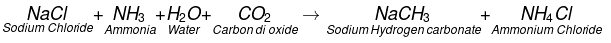
It can be used to neutralise an acid because it is mild non-corrosive base due to the hydrolysis of HCO3- ion.
The following reaction takes place when it is heated during cooking.

Uses of Sodium Hydrogen-carbonate (NaHCO3)
(a) For making baking powder which is a mixture of baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) and a mild edible acid like tartaric acid. When baking powder is mixed with water, the following reaction takes place.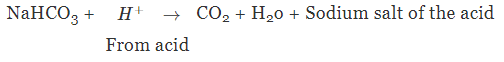
Carbon dioxide so produced during the reaction is responsible for making the bread and cake to rise making them soft and spongy.
(b) As an ingredient in antacids. Being alkaline, it neutralises excess acid in the stomach and provides relief.
(c) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguisher.
Washing Soda (Sodium Carbonate)
The chemical formula of washing soda is Na2CO3.10H2O, (sodium carbonate decahydrate). Anhydrous sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is generally called soda ash. Washing soda is manufactured by Solvay process. This process is also known as Ammonia soda process. The raw material needed for the process are sodium chloride, lime stone (CaCO3) and ammonia (NH3). The reactions involved are.Step-I
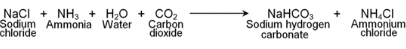
The CO2 required in this reaction is obtained by heating limestone.

Step-II Dry sodium hydrogencarbonate is heated strongly to produce sodium carbonate.

Step-III Washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O) is obtained by crystallisation from a saturated solution of soda ash (Na2CO3)
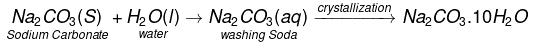
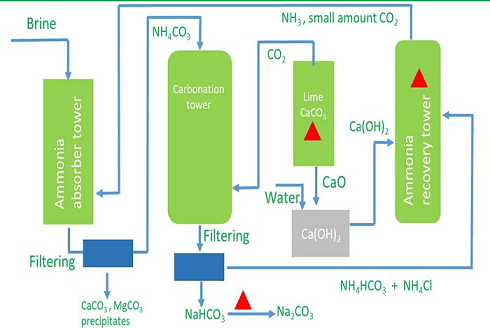 Manufacturing Process of Sodium Carbonate (Solvay Process)
Manufacturing Process of Sodium Carbonate (Solvay Process)
Uses of Washing Soda
(a) Washing soda (or sodium carbonate) is used for washing clothes (laundry purposes).(b) Washing soda is used for softening hard water.
(c) Sodium carbonate (soda ash) is used for the manufacture of detergents.
(d) Sodium carbonate is used for the manufacture of many important compounds, such as borax (Na2B4O7), Hypo (Na2S2O3.5H2O), etc.
(e) Sodium carbonate is also used in paper and paint industries.
Are the Crystals of Salts really Dry?
Crystals of some salts contain certain amount of associated water. The water associated the crystal (or molecule) of any salt is called water of crystallisation.
The salt containing water of crystallisation are called hydrated salts.
Water of Crystallization
It is fixed number of water molecules present in crystalline salt,
Example:

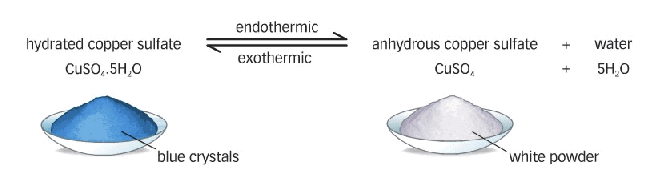 Hydrous to Anhydrous Copper Sulphate
Hydrous to Anhydrous Copper Sulphate
Plaster of Paris: (CaSO4.H2O)
Plaster of paris is hemihydrate (hemi means half and hydrate means water) of calcium sulphate. Its molecular formula is 
In plaster of paris one molecule of water is shared by two CaSO4 as

Preparation of Plaster of Paris
Plaster of paris is obtained by heating gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) at 373K (or 100°C).

or

During the preparation of plaster of paris, temperature should be controlled carefully. Otherwise, anhydrous calcium sulphate (CaSO4) will be formed. Anhydrous calcium sulphate does not set into hard mass when mixed with water. So, if temperature is not controlled carefully, the plaster of paris obtained will have poor setting property.  Sculptures using Plaster of Paris
Sculptures using Plaster of Paris
Properties of Plaster Paris
- Plaster of paris is a white, odourless powder.
- At ordinary room temperature, plaster of paris absorbs water and a large amount of heat is liberated.
- When mixed with a limited amount of water (50% by mass), if forms a plastic mass, evolves heat and quickly sets to a hard porous mass with in minutes. This is called the setting process.
- During setting, a slight expansion in volume occurs. It is due to this that it fills the mould completely and gives sharp impression. The reaction during process is CaSO4.0.5H2O(s) + 1.5H2O H2O(l) → CaSO4 . 2H2O(s)
Plaster of paris Water Gypsum (Hard mass)
Uses of Plaster of Paris
- Plaster of paris is used in making casts and patterns for moulds and statue.
- Plaster of paris is used as cement in ornamental casting and for making decorative materials.
- Plaster of paris is used as a fire proofing material and for making chalks.
- Plaster of paris is used in hospitals for immobilising the affected part in case of bone fracture of strain.
- Plaster of paris (POP) is used to fill small gaps on walls & roofs.
Efflorescence
 Efflorescence
Efflorescence
- Certain hydrated crystalline salts when exposed to atmosphere lose their water of crystallisation spontaneously and change into amorphous powder.
- The spontaneous loss of water of crystallization, wholly or partly, when crystals with water of crystallization are exposed to air is called efflorescence and the substances exhibiting efflorescence are called efflorescent substance.
- For Example : Washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O), Glauber's salt (Na2SO4.10H2O), blue vitriol (CuSO4.5H2O)
Deliquescence
Certain crystalline substance when exposed to atmosphere absorb moisture and change into solution. The absorption of moisture from air by crystals to form a solution is called deliquescence. Sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, calcium chloride etc. are deliquescent substances.Hygroscopic Substances
 Silica Gel is an example of Hygroscopic Substances
Silica Gel is an example of Hygroscopic Substances- Certain substance absorb water from the atmosphere without undergoing change in physical state. Such substances are known as hygroscopic substance.
- Anhydrous sodium carbonate, anhydrous copper sulphate, concentrated sulphuric acid are examples of hygroscopic substances.
|
11 videos|50 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Bleaching Powder, Baking Soda, Washing Soda & Plaster of Paris - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 9
| 1. Are the crystals of salts really dry? |  |
| 2. What is efflorescence? |  |
| 3. What is deliquescence? |  |
| 4. What are hygroscopic substances? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of water of crystallization in salts like Plaster of Paris? |  |
|
11 videos|50 docs|17 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















