This EduRev document offers 12 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) from the topic Blood Relations (Level - 2). These questions are of Level - 2 difficulty and will assist you in the preparation of CAT & other MBA exams. You can practice/attempt these CAT Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) and check the explanations for a better understanding of the topic.
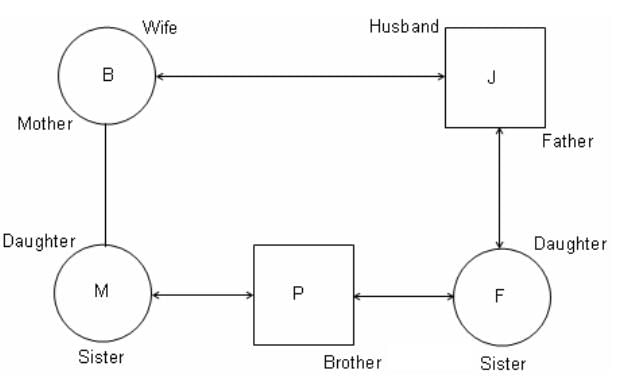
I. J is the father of F, but F is not the son of J. Q. Which of the following statements is not true?
II. M is the daughter of B and sister of P.
III. P is the brother of F.
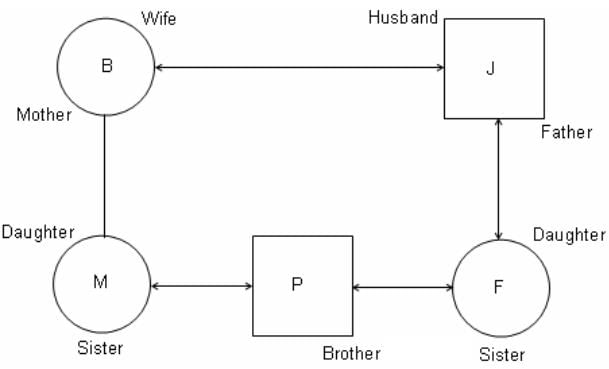
I. J is the father of F, but F is not the son of J. Q. Which of the following statements is/are true?
II. M is the daughter of B and sister of P.
III. P is the brother of F.
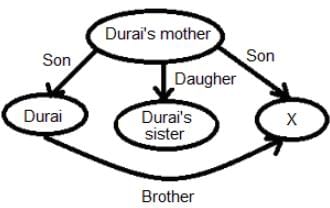
In a family of nine, X and Y are brother and sister and are the only children of their parents. Q is the son of the only daughter of F. L is the grandfather of M. X is the father-in-law of M's wife. E is the daughter-in-law of T, who is the son-in-law of L. F is the wife of L. Q. How is T related to X?
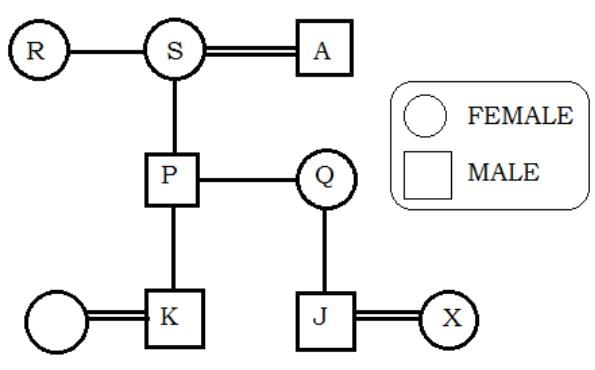
In a family of nine, K is the son of the only son of S. R and S are sisters. Q is the daughter of the only sister of R. J is the nephew of P, who is the only son of A. X is the daughter-in-law of Q. P is the father-in-law of K's wife. A and S are married. Q. How is J related to X?
Rani and Shreshtha are a married couple having two daughters, Medha and Deepti. Deepti is married to Anurag, who is the son of Garima and Tarun. Nidhi is the daughter of Anurag. Komal, who is Anurag's sister, is married to Harshit and has two sons, Aman and Prem. Prem is the grandson of Garima and Tarun. Q. What is the relation between Aman and Nidhi?
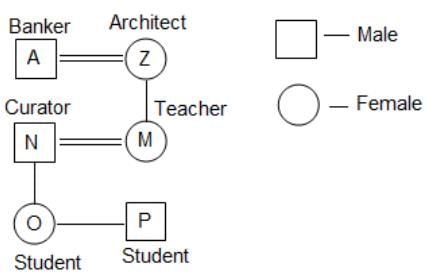
A, Z, N, M, O and P are members of a family. There are two married couples. N is a curator and the father of O, P is the son of the daughter of A, who is a banker. O is the granddaughter of Z, who is an architect. There are two unmarried students in the family. There is one teacher in the family and banker is her father. Q. Who is the husband of M?
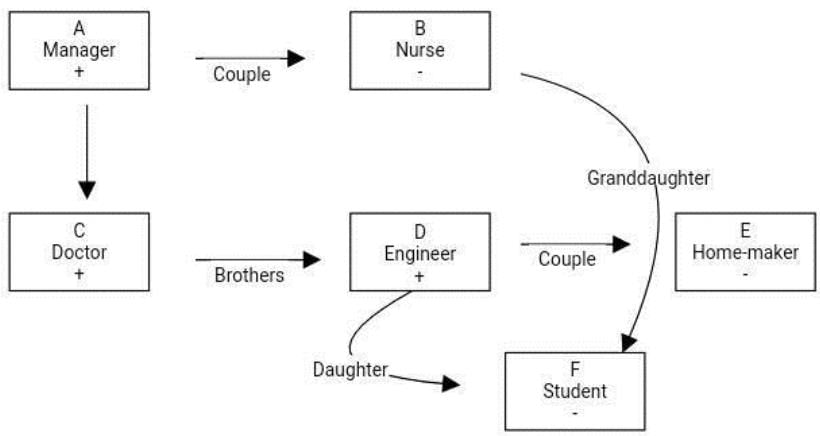
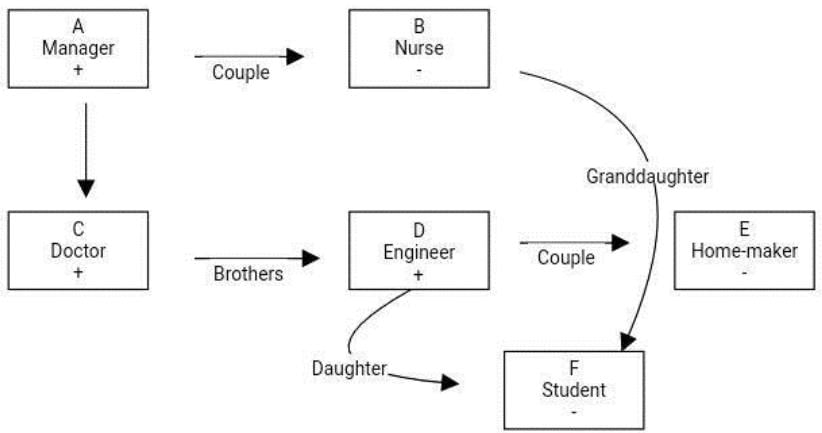
A, B, C, D, E and F are members of a family. E is the sister-in-law of the Doctor, F is the granddaughter of the Manager's wife. C is the son of the Nurse. D is married to the Homemaker and is the father of F. C is the paternal uncle of F. One of the unmarried male members' siblings is an Engineer. B is not the father of D. The Student is not married. Q. What is the profession of D?
A, B, C, D, E and F are members of a family. E is the sister-in-law of the Doctor, F is the granddaughter of the Manager's wife. C is the son of the Nurse. D is married to the Homemaker and is the father of F. C is the paternal uncle of F. One of the unmarried male members' siblings is an Engineer. B is not the father of D. The Student is not married. Q. What is the profession of A?
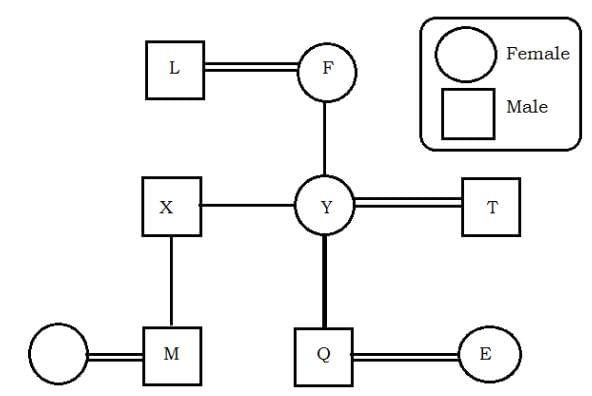
In a family of eleven, M is the son of O's mothers's daughter. Q is the mother of L and T. L and O are brothers. N is the daughter of T, who is the wife of V. P is the son of S, who is the daughter-in-law of Q. L is the father-in-law of P's wife. R is the daughter-in-law of V. Q. Who is M's mother?
A # B - A is brother of B. Q. If the expression G @ H = M $ L % K & J holds true, then how is M related to J?
A @ B - B is the child of A.
A $ B - B is daughter-in-law of A.
A * B - B is elder than A.
A & B- B is son of A.
A % B- A is the wife of B.
A = B - A is husband of B.
A ! B - A is brother-in-law of B.
P ? Q → 'P is the mother of Q.' Q. If E ? B * A @ C & D ? F ^ G, A $ B and the elder child of E is married, then who among the following is the granddaughter-in-law of C?
P # Q → 'P is the child of Q.'
P $ Q → 'Q is the sibling of P.'
P * Q → 'Q is younger than P.'
P & Q → 'Q is the daughter of P.'
P ^ Q → 'P is the husband of Q.'
P % Q → 'P is the grandparent of Q.'
P @ Q → 'P is the sister-in-law of Q.'
In a village of Bastar district in Madhya Pradesh, only two types of people live who belong to a tribal class. The first type is known as class A, while the other is known as class B. In that village, there is no other type of person except these two. The activities of both types of people are governed by perfectly patterned norms of social behaviour. Each person of the tribe has to obey the norms. They are rigid about this. As far as marriage is concerned, the following norms are to be followed: Q. A boy who was born in class B (boy and his wife both can have married and unmarried brothers) can have
(A) The people of class A cannot marry any other member of their own class, though they can marry members of class B.
(B) After being married, each male member ceases to be member of that class in which he was born, but automatically he becomes the member of the other class to which his wife belongs.
(C) As far as females are concerned, they remain the members of their own class after being married.
(D) On its birth, the child automatically becomes the member of its mother's class.
(E) When any male member becomes widower or divorcee, then he again belongs to the group in which he was born.
(F) Nobody can marry more than one person according to social laws.
In a village of Bastar district in Madhya Pradesh, only two types of people live who belong to a tribal class. The first type is known as class A, while the other is known as class B. In that village, there is no other type of person except these two. The activities of both types of people are governed by perfectly patterned norms of social behaviour. Each person of the tribe has to obey the norms. They are rigid about this. As far as marriage is concerned, the following norms are to be followed: Any female of class B can have
(A) The people of class A cannot marry any other member of their own class, though they can marry members of class B.
(B) After being married, each male member ceases to be member of that class in which he was born, but automatically he becomes the member of the other class to which his wife belongs.
(C) As far as females are concerned, they remain the members of their own class after being married.
(D) On its birth, the child automatically becomes the member of its mother's class.
(E) When any male member becomes widower or divorcee, then he again belongs to the group in which he was born.
(F) Nobody can marry more than one person according to social laws.
(P) grandfather (father's father) born in class B
(Q) grandmother (father's mother) born in class B
FAQs on Blood Relations Questions for CAT with Answers PDF
| 1. How are blood relations questions important in the CAT exam? |  |
| 2. What are some common types of blood relations questions asked in the CAT exam? |  |
| 3. How can I improve my skills in solving blood relations questions for the CAT exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific tips to solve complex blood relations questions in the CAT exam? |  |
| 5. Can solving blood relations questions help in other areas of the CAT exam? |  |