C++ Data Types | C++ for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Data Types in C++ are Mainly Divided into 3 Types |

|
| Primitive Data Types |

|
| Datatype Modifiers |

|
| Macro Constants |

|
| Advantage |

|
| Disadvantages |

|
In C++, variables are declared with a specific data type to restrict the kind of data they can store. This allows the compiler to allocate the appropriate amount of memory for the variable based on the data type specified. C++ supports various data types, allowing programmers to choose the appropriate type for their needs. Data types also determine the size and type of values that can be stored in a variable. It is worth noting that storage representation and machine instructions for each data type may differ from machine to machine, although the C++ instructions are identical across all machines.
C++ supports the following data types:
- Primary or Built-in or Fundamental data type
- Derived data types
- User-defined data types
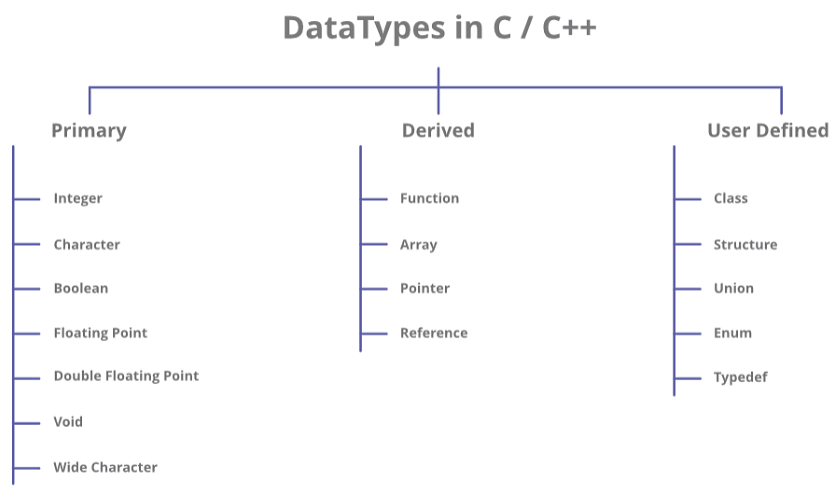
Data Types in C++ are Mainly Divided into 3 Types
1. Primitive Data Types: These data types are built-in or predefined data types and can be used directly by the user to declare variables. example: int, char, float, bool, etc. Primitive data types available in C++ are:
- Integer
- Character
- Boolean
- Floating Point
- Double Floating Point
- Valueless or Void
- Wide Character
2. Derived Data Types: Derived data types that are derived from the primitive or built-in datatypes are referred to as Derived Data Types. These can be of four types namely:
- Function
- Array
- Pointer
- Reference
3. Abstract or User-Defined Data Types: Abstract or User-Defined data types are defined by the user itself. Like, defining a class in C++ or a structure. C++ provides the following user-defined datatypes:
- Class
- Structure
- Union
- Enumeration
- Typedef defined Datatype
Primitive Data Types
- Integer: The integer data type is represented by the keyword int and usually occupies 4 bytes of memory space. Integers can store values between -2147483648 to 2147483647.
- Character: The character data type is represented by the keyword char and typically requires 1 byte of memory space. Characters can store values between -128 to 127 or 0 to 255.
- Boolean: The Boolean data type is represented by the keyword bool and is used for storing Boolean or logical values that can be either true or false.
- Floating Point: The floating-point data type is used for storing single-precision floating-point values or decimal values. The keyword used for this data type is float, and float variables typically require 4 bytes of memory space.
- Double Floating Point: The double floating-point data type is used for storing double-precision floating-point values or decimal values. The keyword used for this data type is double, and double variables typically require 8 bytes of memory space.
- Void: Void data type represents a valueless entity, and it is used for functions that do not return a value.
- Wide Character: Wide character data type is similar to the character data type, but it has a larger size than the normal 8-bit data type. It is represented by wchar_t and is generally 2 or 4 bytes long.
- sizeof() Operator: The sizeof() operator is used to determine the number of bytes occupied by a variable or data type in computer memory.
Example:
int m , x[50];
cout<<sizeof(m); //returns 4 which is the number of bytes occupied by the integer variable “m”.
cout<<sizeof(x); //returns 200 which is the number of bytes occupied by the integer array variable “x”.
The size of variables might be different from those shown in the above table, depending on the compiler and the computer you are using.
// C++ Program to display the size of various data types on your computer.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Display the size of char data type
cout << "Size of char : " << sizeof(char) << " bytes" << endl;
// Display the size of int data type
cout << "Size of int : " << sizeof(int) << " bytes" << endl;
// Display the size of long data type
cout << "Size of long : " << sizeof(long) << " bytes" << endl;
// Display the size of float data type
cout << "Size of float : " << sizeof(float) << " bytes" << endl;
// Display the size of double data type
cout << "Size of double : " << sizeof(double) << " bytes" << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Size of char : 1
Size of int : 4
Size of long : 8
Size of float : 4
Size of double : 8
- This C++ program demonstrates the size of various data types on the computer. The program uses the sizeof() operator to determine the number of bytes occupied by each data type.
- The program displays the size of char, int, long, float, and double data types using cout statements. Finally, the program returns 0 to indicate successful completion.
Datatype Modifiers
As the name suggests, datatype modifiers are used with built-in data types to modify the length of data that a particular data type can hold.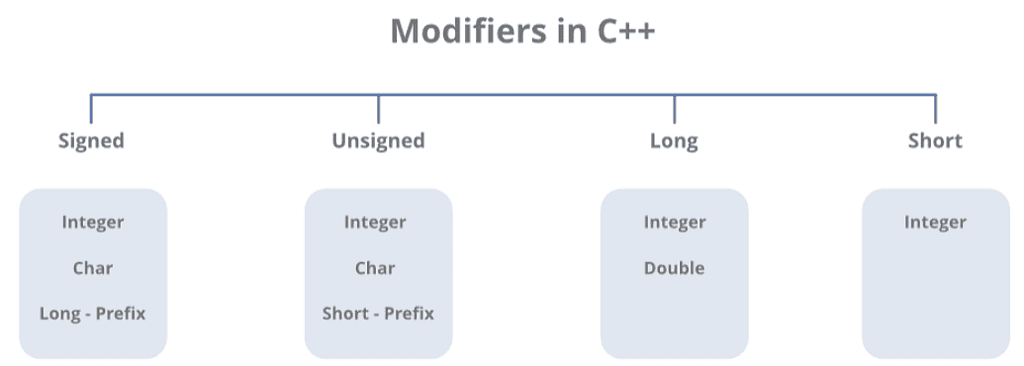
Data type modifiers available in C++ are:
- Signed
- Unsigned
- Short
- Long
The below table summarizes the modified size and range of built-in datatypes when combined with the type modifiers:
Data Type | Size (in bytes) | Range |
short int | 2 | -32,768 to 32,767 |
unsigned short int | 2 | 0 to 65,535 |
unsigned int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
long int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
unsigned long int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
long long int | 8 | -(2^63) to (2^63)-1 |
unsigned long long int | 8 | 0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 |
signed char | 1 | -128 to 127 |
unsigned char | 1 | 0 to 255 |
float | 4 | -3.4×10^38 to 3.4×10^38 |
double | 8 | -1.7×10^308 to1.7×10^308 |
long double | 12 | -1.1×10^4932 to1.1×10^4932 |
wchar_t | 2 or 4 | 1 wide character |
Macro Constants
Name | Expresses |
CHAR_MIN | The minimum value for an object of type char |
CHAR_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type char |
SCHAR_MIN | The minimum value for an object of type Signed char |
SCHAR_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type Signed char |
UCHAR_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type Unsigned char |
CHAR_BIT | Number of bits in a char object |
MB_LEN_MAX | Maximum number of bytes in a multi-byte character |
SHRT_MIN | The minimum value for an object of type short int |
SHRT_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type short int |
USHRT_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type Unsigned short int |
INT_MIN | The minimum value for an object of type int |
INT_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type int |
UINT_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type Unsigned int |
LONG_MIN | The minimum value for an object of type long int |
LONG_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type long int |
ULONG_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type Unsigned long int |
LLONG_MIN | The minimum value for an object of type long long int |
LLONG_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type long long int |
ULLONG_MAX | Maximum value for an object of type Unsigned long long int |
The actual value depends on the particular system and library implementation but shall reflect the limits of these types in the target platform. LLONG_MIN, LLONG_MAX, and ULLONG_MAX are defined for libraries complying with the C standard of 1999 or later (which only includes the C++ standard since 2011: C++11).
C++ Program to Find the Range of Data Types using Macro Constants
Example 1:
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Size of char : " << sizeof(char) << " byte"
<< end1;
cout << "char minimum value: " << CHAR_MIN << end1;
cout << "char maximum value: " << CHAR_MAX << end1;
cout << "Size of int : " << sizeof(int) << " bytes"
<< end1;
cout << "Size of short int : " << sizeof(short int)
<< " bytes" << end1;
cout << "Size of long int : " << sizeof(long int)
<< " bytes" << end1;
cout << "Size of signed long int : "
<< sizeof(signed long int) << " bytes" << end1;
cout << "Size of unsigned long int : "
<< sizeof(unsigned long int) << " bytes" << end1;
cout << "Size of float : " << sizeof(float) << " bytes"
<< end1;
cout << "Size of double : " << sizeof(double)
<< " bytes" << end1;
cout << "Size of wchar_t : " << sizeof(wchar_t)
<< " bytes" << end1;
return 0;
}
Output
Size of char : 1 byte
char minimum value: -128
char maximum value: 127
Size of int : 4 bytes
Size of short int : 2 bytes
Size of long int : 8 bytes
Size of signed long int : 8 bytes
Size of unsigned long int : 8 bytes
Size of float : 4 bytes
Size of double : 8 bytes
Size of wchar_t : 4 bytes
Example 2:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Integer data types
int num1 = 10;
short num2 = 20;
long num3 = 30;
long long num4 = 40;
cout << "Integer data types: " << end1;
cout << "int: " << num1 << end1;
cout << "short: " << num2 << end1;
cout << "long: " << num3 << end1;
cout << "long long: " << num4 << end1;
// Floating-point data types
float dec1 = 3.14f;
double dec2 = 3.141592;
long double dec3 = 3.14159265358979L;
cout << "Floating-point data types: " << end1;
cout << "float: " << dec1 << end1;
cout << "double: " << dec2 << end1;
cout << "long double: " << dec3 << end1;
// Character data types
char letter1 = 'a';
wchar_t letter2 = L'b';
char16_t letter3 = u'c';
char32_t letter4 = U'd';
cout << "Character data types: " << end1;
cout << "char: " << letter1 << end1;
wcout << "wchar_t: " << letter2 << end1;
cout << "char16_t: " << letter3 << end1;
cout << "char32_t: " << letter4 << end1;
// Boolean data type
bool flag1 = true;
bool flag2 = false;
cout << "Boolean data type: " << end1;
cout << "true: " << flag1 << end1;
cout << "false: " << flag2 << end1;
// String data type
string str1 = "Hello, world!";
cout << "String data type: " << end1;
cout << str1 << end1;
return 0;
}
Output
Integer data types:
int: 10
short: 20
long: 30
long long: 40
Floating-point data types:
float: 3.14
double: 3.14159
long double: 3.14159
Character data types:
char: a
wchar_t: b
char16_t: 99
char32_t: 100
Boolean data type:
true: 1
false: 0
String data type:
Hello, world!
This program initializes variables of different data types with values and displays their values. It includes integer data types such as int, short, long, and long long, which store whole numbers of different sizes. The program also includes floating-point data types like float, double, and long double, which store real numbers with varying levels of precision. Moreover, the character data types, char, wchar_t, char16_t, and char32_t, represent individual characters of different sizes. The boolean data type only holds one of two values, either true or false. Finally, the program includes the string data type, which holds a sequence of characters, and the string class is used to declare a string variable and assign a value to it.
Advantage
- Data types provide a way to categorize and organize data in a program, making it easier to understand and manage.
- Each data type has a specific range of values it can hold, allowing for more precise control over the type of data being stored.
- Data types help prevent errors and bugs in a program by enforcing strict rules about how data can be used and manipulated.
- C++ provides a wide range of data types, allowing developers to choose the best type for a specific task.
Disadvantages
- Using the wrong data type can result in unexpected behavior and errors in a program.
- Some data types, such as long doubles or char arrays, can take up a large amount of memory and impact performance if used excessively.
- C++’s complex type system can make it difficult for beginners to learn and use the language effectively.
- The use of data types can add additional complexity and verbosity to a program, making it harder to read and understand.
|
70 videos|45 docs|15 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for EmSAT Achieve exam
|

|
















