Ques 1: Out of NaCl and AgCl, which one shows Frenkel; defect and why?
Ans: The Frenkel defect is that in which one smaller ion (usually cations) move from its lattice position to an interstitial site i.e. a tetrahedral /octahedral hole to form a vacancy in the lattice.
Of course, AgCl has the defect because, the size of AgCl is intermediate and since, the size of Ag+ cation is smaller than chloride ion so it can move to interstitial spaces causing Frenkel defect while in NaCl (alkali metal halide) they have larger size of cations which do not fit into voids and so the defect is not shown by the alkali metal halides.
Ques 2: Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling points:
(CH3)3N, C2H5OH, C2H5NH2
Ans: This increasing order of boiling point can be explained by intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Tertiary amines, cannot engage in hydrogen bonding because they have no hydrogen atom bonded to the nitrogen atom, while primary amine undergoes intermolecular hydrogen bonding. But in case of alcohol, the extent of hydrogen bonding is more as compared to amines because of more electronegative oxygen atom in alcohols. Therefore, the increasing order of boiling points is
(CH3)3N<C2H5NH2<C2H5OH
Ques 3: Why are medicines more effective in colloidal state?
OR
What is difference between an emulsion and a gel?
Ans: Some medicines are more effective in colloidal form because medicine in colloidal form is easily absorbed by the body tissues. For example, Antibiotics like streptomycin in the form of the colloidal sol is injected into the body for the more effective result.
OR
Emulsion: It is a colloidal mixture in which both the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium are liquids. The two or more liquids present in the mixture are generally immiscible in nature. Example: Milk. Gel: It is a colloid in which the dispersed phase i.e. liquid has combined with the dispersion medium i.e. solid to produce a semisolid material. Example: jellies.
Ques 4: Define ambident nucleophile with an example.
Ans: Ambident nucleophiles are the nucleophiles having two nucleophilic sites through which they can attack. For example, nitrite ion is an ambident nucleophile.

Ques 5: What is the basic structural difference between glucose and fructose? OR
Write the products obtained after hydrolysis of lactose.
Ans: Both Glucose and Fructose are hexose sugars with six carbon atoms but, Glucose is an aldohexose and Fructose is ketohexose which means the functional group present in glucose is aldehyde and the functional group in fructose is ketone.
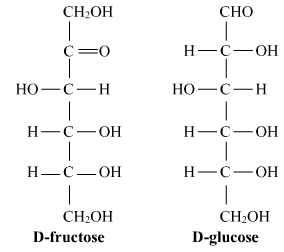 OR
OR
Lactose is composed of β-D galactose and β-D glucose. Thus, on hydrolysis, it gives β-D galactose and β-D glucose.
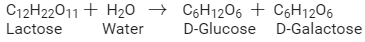
Ques 6: Write balanced chemical equations for the following processes:
(i) XeF2 undergoes hydrolysis.
(ii) MnO2 is heated with conc. HCl.
OR
Arrange the following in order of property indicated for each set:
(i) H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te - increasing acidic character
(ii) HF, HCl, HBr, HI - decreasing bond enthalpy
Ans: (i) 2XeF2(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2Xe(g) + 4HF(aq) + O2(g)
(ii) 4HCl + MnO2 → Cl2 + MnCl2 + 2H2O
OR
(i) The increasing order of acidic character is H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te
(ii) The decreasing order of bond enthalpy is HF > HCl > HBr > HI
Ques 7: (i) Why type of drug is used in sleeping pills?
(ii) What type of detergent are used in toothpastes?
(iii) Why the use of alitame as artificial sweetener is not recommended?
OR
Define the following terms with a suitable example in each:
(i) Broad-spectrum antibiotics
(ii) Disinfectants
(iii) Cationic detergents
Ans: (i)Tranquilizers form an essential component of sleeping pills. They are a class of chemical compounds used for the treatment of stress and mild or even severe mental diseases. These relieve anxiety, stress, irritability or excitement by inducing a sense of well-being.
(ii)Anionic detergents are used in toothpaste. Anionic detergents are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons. In anionic detergents, the anionic part of the molecule is involved in the cleansing action. Sodium salts of alkylbenzenesulphonates are an important class of anionic detergents.
(iii) Alitame, an artificial sweetening agent, is high potency sweetener. The control of sweetness of food is difficult while using it, hence it is not recommended to use it.
OR
(i)Antibiotics which kill or inhibit a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria are said to be broad spectrum antibiotics. Chloramphenicol, Vancomycin, and ofloxacin are broad-spectrum antibiotics.
(ii) Disinfectants are the chemicals which either kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms. They are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments, etc. Chlorine in the concentration of 0.2 to 0.4 ppm in aqueous solution is a disinfectant.
(iii) Cationic detergents are quarternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides or bromides. Cationic part possesses a long hydrocarbon chain and a positive charge on nitrogen atom. Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide is a cationic detergent and is used in hair conditioners.
Ques 8: Arrange the following in increasing order of base strength in gas phase:
(C2H5)3N, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH
Ans: C2H5NH2, (C2H0)2NH, (C2H5)3N
Ques 9: Why conductivity of silicon increases on doping with phosphorus?
Ans: Phosphorus doping introduces phosphorus atoms in silicon crystal leading to change its electrical properties. Phosphorus atoms have 5 valence electrons which cause n-type doping. A phosphorus atom replaces silicon atom(having four valence electrons) in silicon crystal. Four out of five valence electrons of phosphorus take part in bonding while the fifth electron remains free. which lead to an increase in the conductivity of silicon crystal.
Ques 10: Write two differences between an ideal solution and a non-ideal solution.
Ans: (i) Ideal solutions are the homogeneous mixture of two or more liquid which follows Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration.
(ii) In case of an ideal solution, ΔHmix = 0 and ∆Vmix = 0, which indicates that on mixing the two solutions there is no release or absorption of heat and also there is no change in volume at constant pressure.
Example: Benzene and Toluene
(i) Non-ideal solutions are the homogeneous mixture of two or more liquid which is unable to follow Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration.
(ii) Here ΔHmix ≠ 0 and ∆Vmix ≠ 0, which indicates that on mixing the heat is released or absorbed and also there is a change in volume.
Example: Acetone and Ethanol
Ques 11: (i) What is the role of activated charcoal in gas mask?
(ii) A colloidal sol is prepared by the given method in figure. What is the charge on hydrated ferric oxide colloidal particles formed in the test tube? How is the sol represented?
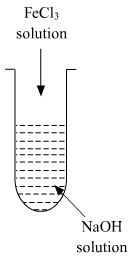 (iii) How does chemisorption vary with temperature?
(iii) How does chemisorption vary with temperature?
Ans: (i) The activated charcoal containing gas masks are used by coal miners to protect them from the suffocating gases and particulate matter or ashes present in the coal mines. The activated carbon binds the materials by van der waal forces. Thus, chemical compounds with large molecules, large molecular weight and insolubility are easily absorbed.
(ii) Colloidal particles usually adsorb those ions which are in excess and are common to its own lattice. This preferential adsorption of a particular type of ions imparts a particular type of charge to colloidal particles.
When FeCl3 is added in NaOH, the constituent of the sol is Fe(OH)3 but the dispersion medium is having an excess of OH- ions. Hence, it gets preferentially adsorbed to the sol giving the overall negative charge. The sol is represented as Fe2O3.xH2O / OH-
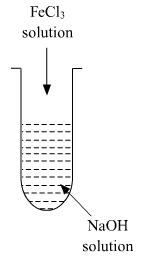 (iii) Effect of temperature on chemisorption: Even though chemical adsorption is an exothermic process, but like most chemical changes, the extent of chemisorption increases with increase in temperature up to a certain limit and then after that, it starts decreasing.
(iii) Effect of temperature on chemisorption: Even though chemical adsorption is an exothermic process, but like most chemical changes, the extent of chemisorption increases with increase in temperature up to a certain limit and then after that, it starts decreasing.
Ques 12: (i) Why bithional is added in soap?
(ii) Why magnesium hydroxide is a better antacid than sodium bicarbonate?
(iii) Why soaps are biodegradable whereas detergents are non-biodegradable?
OR
Define the following terms with a suitable example in each:
(i) Antibiotics
(ii) Artificial sweeteners
(iii) Analgesics
Ans: (i). Bithional is a bacteriostatic agent which is added to impart antibacterial properties to soap.
(ii). Magnesium hydroxide is a better antacid because being insoluble it does not allow the PH to increase above neutral. Hydrogen carbonate being soluble, its excess can make the stomach alkaline and trigger the production of even more acid.
(iii). Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids and they are biodegradable and can be broken down by the bacteria but detergents are not like that they are sulphonate which can't be biodegraded.
OR
(i). Antibiotics are the medicine which inhibits the growth of bacteria and kill them. antibiotics act by blocking certain biochemical pathways which are essential for the survival of bacteria like cell wall formation, protein synthesis. example; penicillin.
(ii). Artificial sweeteners are food additives that replace sugar and add sweetness equal to sugar to the food but with fewer calories than sugar. example: Saccharin
(iii). Analgesic is the medicine which is used to relieve pain. example: aspirin, paracetamol.
Ques 13: Arrange the following in decreasing order of solubility in water:
(CH3)3N, (CH3)2NH, CH3NH2
Ans: Higher the value of hydration enthalpy, more is the solubility. Also, larger the hydrocarbon part attached to the nitrogen of amine, lower is the tendency to form hydrogen bonds and lower is the solubility.
Thus, the decreasing order of solubility in water is CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH > (CH3)3N
Ques 14: What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by ZnS and why?
Ans: The stoichiometric defect shown by ZnS is Frenkel defect which is due the large difference in the size of the ions, i.e. due to small size of Zn2+.
Ques 15: Write one stereochemical difference between SN1 and SN2 reactions.
Ans: SN1 reactions lead to the formation of racemic mixture whereas SN2 reactions lead to inversion in configuration of product.

 OR
OR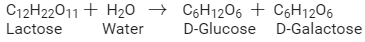
 (iii) How does chemisorption vary with temperature?
(iii) How does chemisorption vary with temperature? (iii) Effect of temperature on chemisorption: Even though chemical adsorption is an exothermic process, but like most chemical changes, the extent of chemisorption increases with increase in temperature up to a certain limit and then after that, it starts decreasing.
(iii) Effect of temperature on chemisorption: Even though chemical adsorption is an exothermic process, but like most chemical changes, the extent of chemisorption increases with increase in temperature up to a certain limit and then after that, it starts decreasing.





















