Cell - Notes, Biology | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
When observing the world around us, we encounter both living and non-living entities. A question that arises is what distinguishes living organisms from non living objects. The key lies in the presence of cells, the fundamental unit of life, which is found in all living beings. Living organisms are made up of cells, with some being unicellular, consisting of just one cell, while others, such as humans, are multicellular, comprising multiple cells.
What is a Cell?
Unicellular organisms possess the ability to exist autonomously and carry out vital life functions. Without a fully formed cell structure, independent living is not possible.
Thus, the cell stands as the fundamental building block and operational unit of all living beings.
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe and describe live cells, while Robert Brown identified the nucleus. Advancements in microscopy, especially with the electron microscope, revealed the detailed structure of cells.
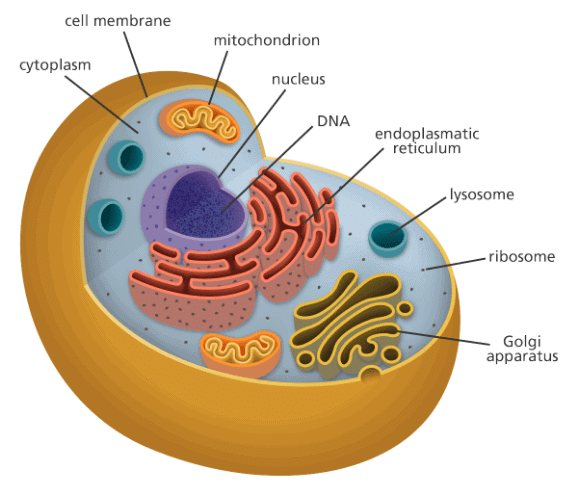 Cell
Cell
[Question: 1088756]
Cell Theory
In 1838, Matthias Schleiden, a German botanist, discovered that plants are composed of various types of cells, forming the plant's tissues. Around the same time, Theodore Schwann, a British Zoologist, identified a thin outer layer in animal cells, known today as the 'plasma membrane.' Schwann also concluded that plant cells possess a unique feature, the cell wall, based on his studies of plant tissues.Schwann proposed the hypothesis that both animal and plant bodies are constructed from cells and their products.
Schleiden and Schwann collaborated to formulate the cell theory, which initially lacked an explanation for cell formation.
Rudolf Virchow, in 1855, provided the missing explanation by demonstrating that cells divide and give rise to new cells from existing ones ("Omnis cellula-e cellula").
Virchow's work refined the cell theory, establishing two key principles:
All living organisms are composed of cells and their products.
All cells originate from pre-existing cells
An Overview of Cell
- Onion cells, typical of plant cells, are characterized by a distinct cell wall as the outer boundary, followed by the cell membrane.
- Human cheek cells have an outer membrane as the defining structure, enclosing a dense membrane-bound nucleus containing chromosomes and DNA.
- Eukaryotic cells possess membrane-bound nuclei, while prokaryotic cells lack such a feature. Both types of cells contain cytoplasm, a semi-fluid matrix where cellular activities take place.
- Eukaryotic cells additionally contain membrane-bound organelles like endoplasmic reticulum, golgi complex, lysosomes, mitochondria, microbodies, and vacuoles, which are absent in prokaryotic cells.
- Ribosomes, non-membrane bound organelles, are present in all cells, located in the cytoplasm, chloroplasts (in plants), mitochondria, and rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- Animal cells possess the centrosome, another non-membrane bound organelle aiding in cell division.
[Question: 1088757]
Size and Shape of Cells
Cells vary in size, with Mycoplasmas being the smallest at 0.3 µm, bacteria ranging from 3 to 5 µm, and the ostrich egg being the largest isolated single cell.
Human red blood cells have a diameter of about 7.0 µm, while nerve cells are among the longest.
Cells exhibit diverse shapes, such as disc-like, polygonal, columnar, cuboid, thread-like, or irregular, often corresponding to their specific functions.
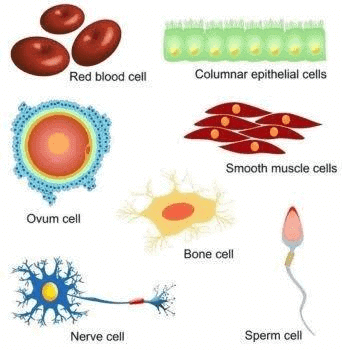
Types of Cells
1. Prokaryotic Cells
A prokaryotic cell is a single-celled or unicellular organism that has neither a true nucleus nor membrane-bound organelles. Organisms belonging to the Bacteria and Archaea domains are based on the prokaryotic cell. Prokaryotic cells are covered with a cell membrane which acts as an extra layer of protection.
2. Eukaryotic Cells
Any cell or organism with a clearly defined nucleus is called a eukaryotic cell. A eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus and contains well-defined chromosomes. Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes
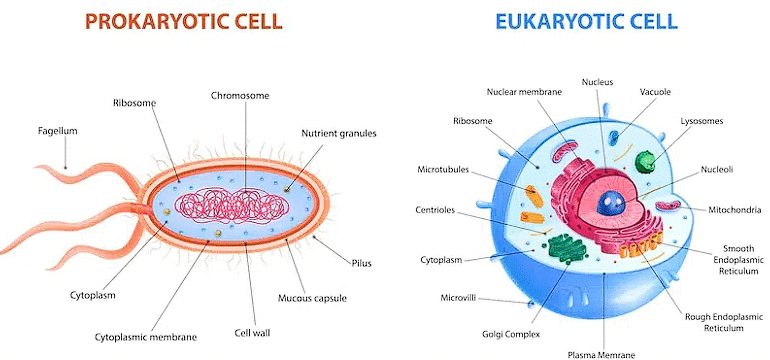
Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
It is simple and primitive in nature. | It is developed and comparatively complex in nature. |
The nucleus is not well organized. It has no nuclear membrane and nucleolus. | The nucleus is well organized. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus are present. |
The cell has no membrane bound organelles except ribosomal granules. | The cell contains almost all the membrane bound organelles. |
Chromosomes are not formed in this cell during cell division. | Chromosomes are formed in the nucleus during cell division. |
Single DNA thread remains freely in the nuclear material. | DNA is present in the nuclear reticulum or chromosomes. |
Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
A plant cell has a rigid wall on the outside. | Cell wall is absent. |
It is usually larger in size. | An animal cell is comparatively smaller in size |
It cannot change its shape | An animal cell can often change its shape |
Plastids are found in plant cells. | Plastids are usually absent. |
Plant cells exposed to sunlight possess chlorophyll containing plastids called chloroplasts. | Chlorophyll is absent |
A mature plant cell contains a large central vacuole. | An animal cell often possesses many small vacuoles. |
Nucleus lies on one side in the peripheral cytoplasm. | Nucleus usually lies in the center. |
Mitochondria are comparatively fewer. | Mitochondria are generally more numerous. |
Cristae are tubular in plant mitochondria. | Cristae are plate - like in animal mitochondria. |
Plant cells do not burst if placed in hypotonic solution due to the presence of cell wall. | Animal cells usually burst if placed in hypotonic solution unless and until they possess contractile vacuoles. |
Cell Envelope and its Modifications
(i) Prokaryotic cells, especially bacteria, feature a complex cell envelope comprising three tightly bound layers:
- Glycocalyx: The glycocalyx varies in composition and thickness, with some bacteria having a slime layer and others forming a capsule.
- Cell wall: The cell wall shapes the cell and provides structural support.
- Plasma membrane: Selectively permeable, interacts with the external environment and resembles that of eukaryotes.
- Mesosomes: mesosomes are formed by plasma membrane extensions, play roles in cell wall formation, DNA processes, respiration, and increasing membrane surface area.
(ii) These layers, while distinct, function together as a protective unit.
(iii) Bacteria are categorized as Gram-positive (retain Gram stain) or Gram-negative (do not retain Gram stain) based on their cell envelope differences.
Note: Bacteria are categorized as either Gram-positive or Gram-negative based on their cell envelope structure and response to a staining procedure called the Gram stain:
- Gram-Positive Bacteria: They have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall that retains the stain, making them appear purple when stained.
- Gram-Negative Bacteria: They have a thinner peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane that does not retain the stain, causing them to appear pink or red after staining
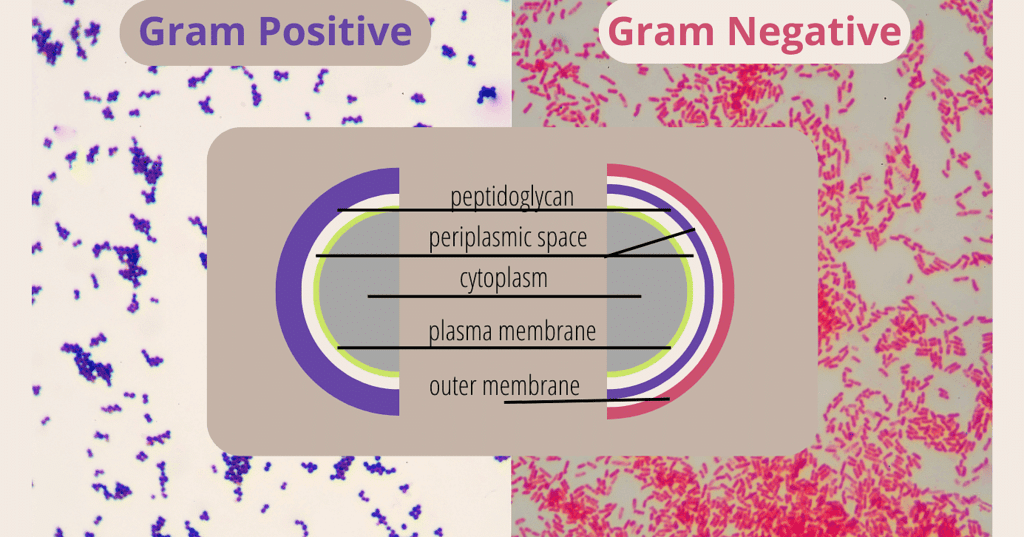 Gram-positive & Gram-negative
Gram-positive & Gram-negative
- Chromatophores: Pigment-containing structures found in various cells.
- Bacterial Cell Mobility: Bacterial cells can be either motile or non-motile.
- Flagella: Thin, filamentous extensions from the cell wall of motile bacteria.
- Composed of three parts: filament, hook, and basal body.
(i) Filament is the longest part and extends outside the cell.
(ii) Pili (Pilus, Singular): Elongated tubular structures made of a specialized protein.
(iii) Fimbriae: Small, bristle-like fibers on the surface of bacterial cells.
Ribosomes and Inclusion Bodies
Location: Prokaryotic ribosomes are found at the cell's plasma membrane.
Size: They are about 15 nm by 20 nm in size and consist of 50S and 30S subunits, forming 70S ribosomes.
Function: These ribosomes are where protein synthesis takes place, and multiple ribosomes can attach to one mRNA, forming polysomes.
Inclusion Bodies
Storage: Prokaryotic cells store reserve materials as inclusion bodies in the cytoplasm.Characteristics: Inclusion bodies are not enclosed by membranes and include materials like phosphate, cyanophycean, and glycogen granules.
(c) Gas Vacuoles
Presence: Gas vacuoles are found in specific photosynthetic bacteria, such as blue-green and purple-green varieties.
- Primary and Secondary Wall: The primary wall of a young plant cell is capable of growth, which gradually diminishes as the cell matures, and the secondary wall is formed on the inner (towards membrane) side of the cell.
1. Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid, protective structure that surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells, fungi, and some bacteria. It was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665.
The composition of cell walls varies depending on the type of organism. In plant cells, the primary component of the cell wall is cellulose, a complex carbohydrate made up of glucose molecules. Fungal cell walls contain chitin, while bacterial cell walls can be composed of peptidoglycan or other materials.
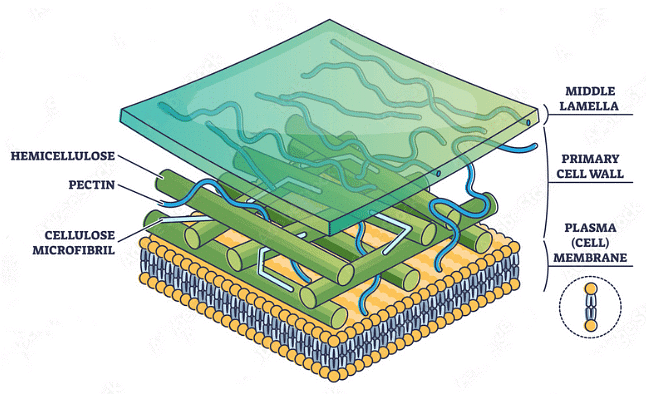 Components of Cell Wall
Components of Cell Wall
Components of Cell wall
- Cellulose is the primary structural component of the plant cell wall. It is a complex carbohydrate (polysaccharide) made up of glucose molecules linked together.
- Hemicellulose is another type of polysaccharide found in the plant cell wall. It helps in binding cellulose microfibrils together, contributing to the overall structural integrity of the cell wall.
- Pectin is a complex polysaccharide that is found in the middle lamella of plant cell walls. It acts as a cementing substance, holding adjacent cells together and helping to maintain the structure of tissues.
- Primary and Secondary Wall: The primary wall of a young plant cell is capable of growth, which gradually diminishes as the cell matures, and the secondary wall is formed on the inner (towards membrane) side of the cell.
- Middle Lamella: The middle lamella is a layer mainly of calcium pectate that holds or glues the different neighbouring cells together.
(i) Composition: The middle lamella primarily consists of pectin, a complex polysaccharide. Pectin molecules are rich in negatively charged ions and have the ability to form bonds with other pectin molecules. This adhesive quality of pectin makes the middle lamella effective in cementing adjacent cell walls.
(ii) Function: The primary function of the middle lamella is to hold plant cells together, especially in plant tissues. It ensures the structural integrity of the tissue by firmly joining the cell walls of neighboring cells.
(iii) Plasmodesmata: Plasmodesmata (singular: plasmodesma) are microscopic channels that traverse the cell wall and middle lamellae, connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells.
2. Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a fundamental structural component of all cells in living organisms. It is a selectively permeable barrier that separates the interior of the cell from its external environment. The cell membrane plays several crucial roles in maintaining the integrity and function of the cell.
Every living cell is externally covered by a thin transparent electron microscopic, elastic regenerative and selective permeable membrane called plasma membrane.
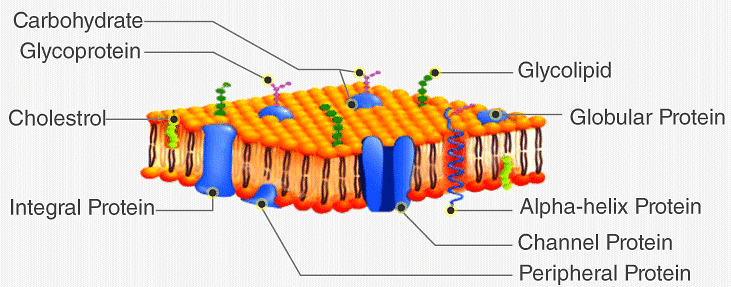 Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
According to Singer and Nicolson, it resembles a "protein iceberg floating in a lipid sea."
- In plant cells, various microorganisms, some protists, and fungal cells, there exists an outer cell wall situated outside the plasma membrane.
- Membranes are also found within cells, and these are collectively referred to as biomembranes.
The term "cell membrane" was initially coined by C. Nageli and C. Cramer in 1855 to describe the outer membrane covering of the protoplast. However, the term "plasmalemma" or "plasma membrane" was introduced by Plowe in 1931 to replace "cell membrane."
Functions of Plasma Membrane
(i) Involved in Membrane Functions: Supports cell growth, intercellular junctions, secretion, endocytosis, and cell division. Selectively permeable for molecules on both sides. passive transport takes place.
(ii) Transfer of Molecules without energy: Simple diffusion for neutral solutes (from high to low concentration). Osmosis for water (movement by diffusion).
(iii) Active Transport: Requires energy (typically ATP). Moves ions or molecules against their concentration gradient. Example: Na+/K+ Pump.
What are Cell Organelles?
- More than 8.7 million species are living on the planet. Every single species is composed of a cell and it includes both single-celled and multicellular organisms.
- A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of a living organism. According to cell theory postulates, a cell is the basic building block of life, which makes anything alive and is self-sufficient to carry out all the fundamental functions of an organism.
- The cells provide shape, structure and carries out different types of functions to keep the entire system active. The cell contains different functional structures which are collectively called Organelles, and they are involved in various cellular functions.
The cellular components are called cell organelles. These cell organelles include both membrane and non-membrane bound organelles, present within the cells and are distinct in their structures and functions. They coordinate and function efficiently for the normal functioning of the cell. A few of them function by providing shape and support, whereas some are involved in the locomotion and reproduction of a cell.
Classification of Cell Organelles
There are various organelles present within the cell and are classified into three categories based on the presence or absence of membrane.- Organelles without membrane: The Cell wall, Ribosomes, and Cytoskeleton are non-membrane-bound cell organelles. They are present both in prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell.
- Single membrane-bound organelles: Vacuole, Lysosome, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum are single membrane-bound organelles present only in a eukaryotic cell.
- Double membrane-bound organelles: Nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast are double membrane-bound organelles present only in a eukaryotic cell.
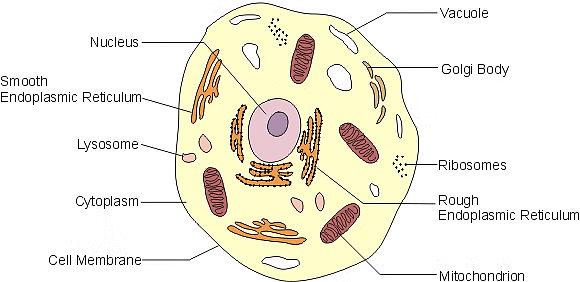 Cell Organelles
Cell Organelles
List of Cell Organelles and their Functions
1. Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is also termed a Cell Membrane or Cytoplasmic Membrane. It is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell, which is composed of a lipid bilayer and proteins.- The plasma membrane is present both in plant and animal cells, which functions as the selectively permeable membrane, by permitting the entry of selective materials in and out of the cell according to the requirement.
- In an animal cell, the cell membrane functions by providing shape and protecting the inner contents of the cell. Based on the structure of the plasma membrane, it is regarded as the fluid mosaic model.
- According to the fluid mosaic model, the plasma membranes are subcellular structures, made of a lipid bilayer in which the protein molecules are embedded.
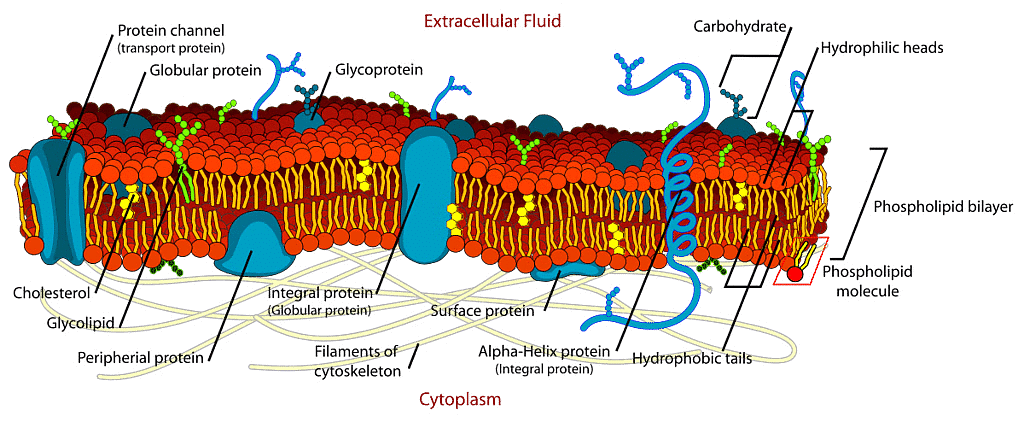 Fluid Mosaic Model
Fluid Mosaic Model
2. Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is present both in plant and animal cells. They are jelly-like substances, found between the cell membrane and nucleus. They are mainly composed of water, organic and inorganic compounds.- The cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell, where all the cell organelles are embedded. These cell organelles contain enzymes, mainly responsible for controlling all metabolic activity taking place within the cell and are the site for most of the chemical reactions within a cell.
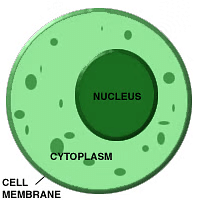 Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
3. Nucleus
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle, which functions as the control centre of cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cell’s DNA.
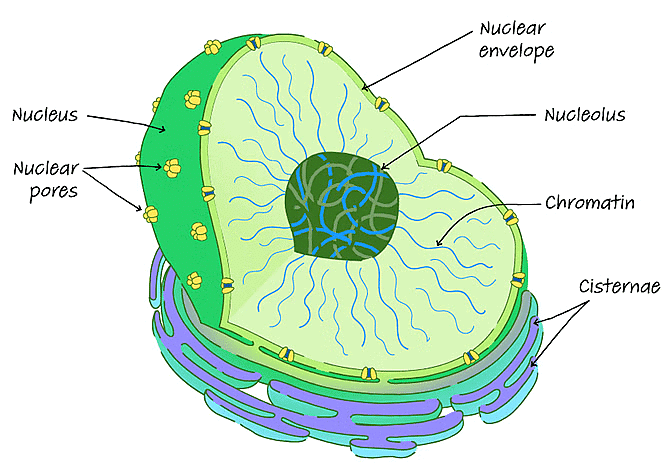 Structure of a nucleus
Structure of a nucleus
- By structure, the nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane. It is a porous membrane (like a cell membrane) and forms a wall between the cytoplasm and nucleus.
- Within the nucleus, there are tiny spherical bodies called the nucleolus. It also carries another essential structure called chromosomes.
- Chromosomes are thin and thread-like structures that carry another important structure called a gene. Genes are a hereditary unit in organisms i.e., it helps in the inheritance of traits from one generation (parents) to another (offspring).
- Hence, the nucleus controls the characters and functions of cells in our body. The primary function of the nucleus is to monitor cellular activities including metabolism and growth by making use of DNA’s genetic information.
- Nucleoli in the nucleus are responsible for the synthesis of protein and RNA.
4. Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of membranous canals filled with fluid. They are the transport system of the cell, involved in transporting materials throughout the cell. There are two different types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:(i) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – They are composed of cisternae, tubules, and vesicles, which are found throughout the cell and are involved with protein manufacture.
(ii) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum – They are the storage organelle, associated with the production of lipids, steroids, and are also responsible for detoxifying the cell.
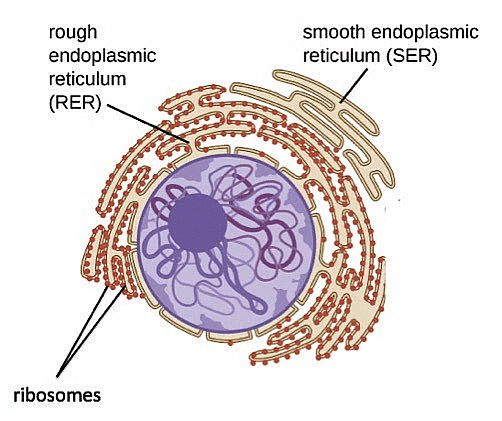 Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum
5. Mitochondria
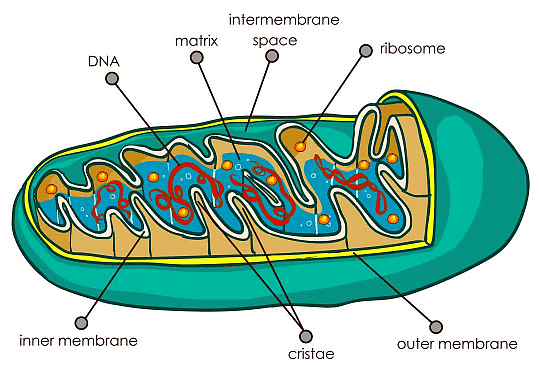 Mitochondria
Mitochondria
- Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell as they produce energy-rich molecules for the cell. The mitochondrial genome is inherited maternally in several organisms. It is a double membrane-bound, sausage-shaped organelle, found in almost all eukaryotic cells.
- The double membranes divide its lumen into two distinct aqueous compartments. The inner compartment is called ‘matrix’ which is folded into cristae whereas the outer membrane forms a continuous boundary with the cytoplasm. They usually vary in their size and are found either round or oval in shape.
- Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration in the cell, produces energy in the form of ATP and helps in the transformation of the molecules.
For instance, glucose is converted into adenosine triphosphate – ATP. Mitochondria have their own circular DNA, RNA molecules, ribosomes (the 70s), and a few other molecules that help in protein synthesis.
6. Plastid
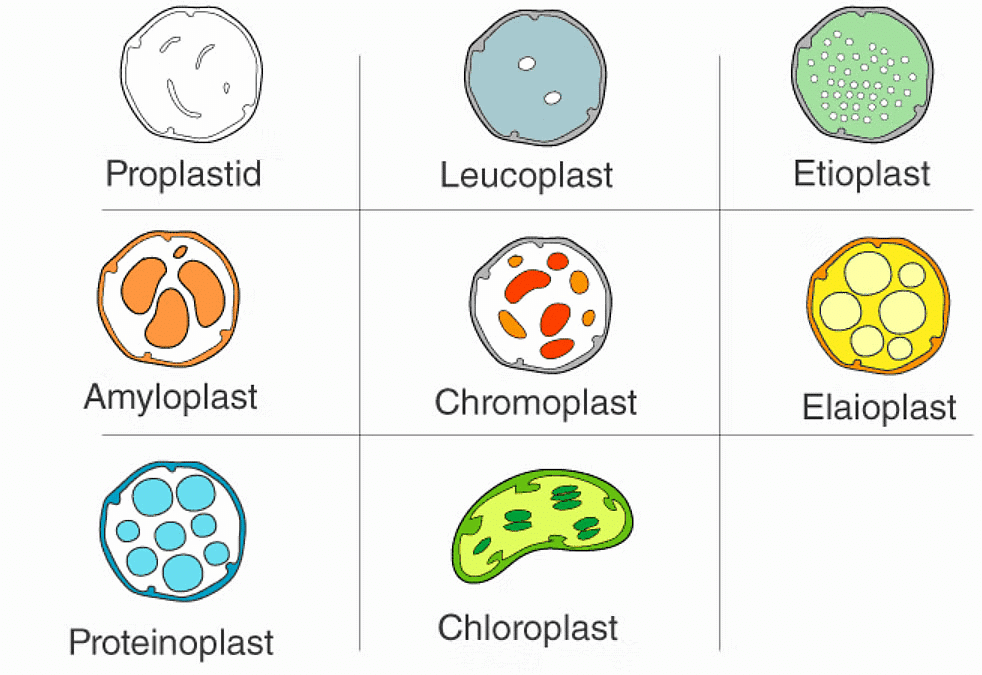
Plastids are double-membrane organelles which are found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are responsible for manufacturing and storing of food. These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell.Types of Plastids
 Types of Plastids
Types of Plastids
There are different types of plastids with their specialized functions. Among them, a few are mainly classified based on the presence or absence of the Biological pigments and their stages of development.(i) Chloroplasts
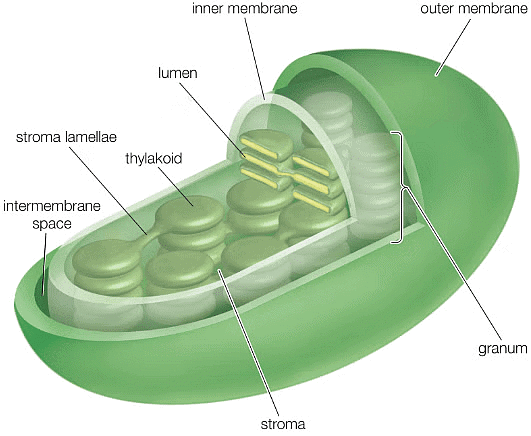
- Chloroplasts are double membrane-bound organelles, which usually vary in their shape from a disc shape to spherical, discoid, oval and ribbon.
- They are present in mesophyll cells of leaves, which store chloroplasts and other carotenoid pigments.
- These pigments are responsible for trapping light energy for photosynthesis.
- The inner membrane encloses a space called the stroma.
- Flattened disc-like chlorophyll-containing structures known as thylakoids are arranged in a stacked manner like a pile of coins.
- Each pile is called granum (plural: grana) and the thylakoids of different grana are connected by flat membranous tubules known as stromal lamella.
- Just like the mitochondrial matrix, the stroma of chloroplast also contains double-stranded circular DNA, 70S ribosomes, and enzymes required for the synthesis of carbohydrates and proteins.
 Chloroplast(ii) Chromoplasts
Chloroplast(ii) Chromoplasts
- The chromoplasts include fat-soluble, carotenoid pigments like xanthophylls, carotene, etc. which provide the plants with their characteristic colour – yellow, orange, red, etc.
(iii) Leucoplasts
- Leucoplasts are colourless plastids that store nutrients. Amyloplasts store carbohydrates (like starch in potatoes), aleuroplasts store proteins, and elaioplasts store oils and fats.
7. Ribosomes
 Cell Showing Ribosomes
Cell Showing Ribosomes
- Ribosomes are nonmembrane-bound and important cytoplasmic organelles found in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Ribosomes are found in the form of tiny particles in a large number of cells and are mainly composed of 2/3rd of RNA and 1/3rd of protein.
- They are named as the 70s (found in prokaryotes) or 80s (found in eukaryotes) The letter S refers to the density and the size, known as Svedberg’s Unit. Both 70S and 80S ribosomes are composed of two sub-units.
- Ribosomes are either encompassed within the endoplasmic reticulum or are freely traced in the cell’s cytoplasm.
- Ribosomal RNA and Ribosomal proteins are the two components that together constitute ribosomes.
- The primary function of the ribosomes includes protein synthesis in all living cells that ensure the survival of the cell.
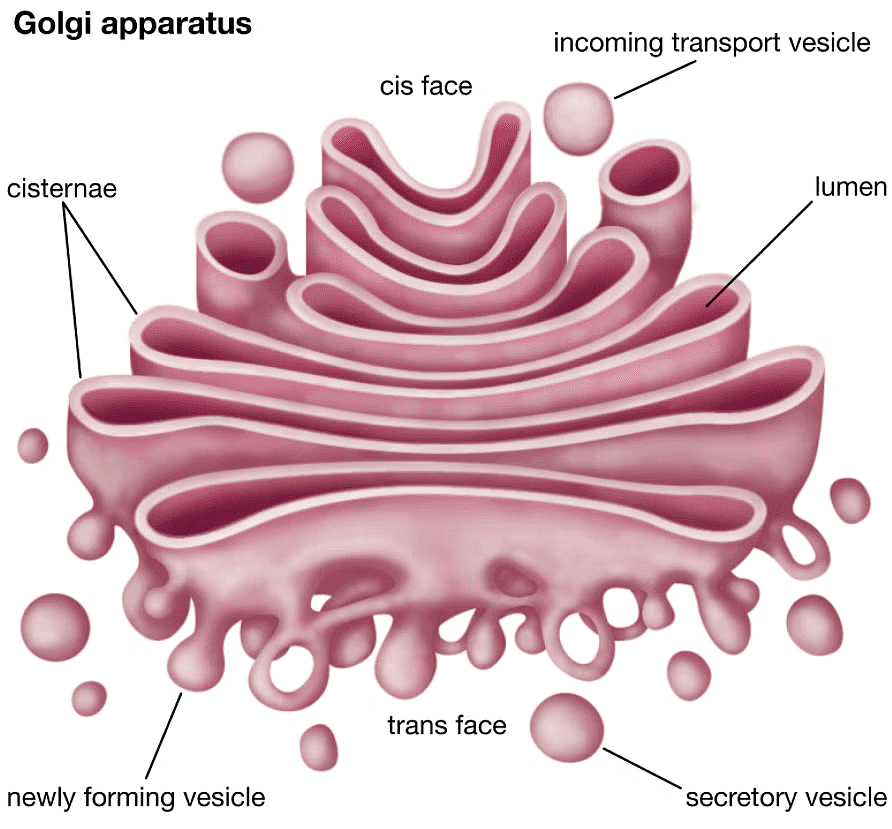
8. Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus is also termed as Golgi Complex. It is a membrane-bound organelle, which is mainly composed of a series of flattened, stacked pouches called cisternae.- This cell organelle is primarily responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids to targeted destinations.
- Golgi Apparatus is found within the cytoplasm of a cell and is present in both plant and animal cells.
 Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus
9. Microbodies
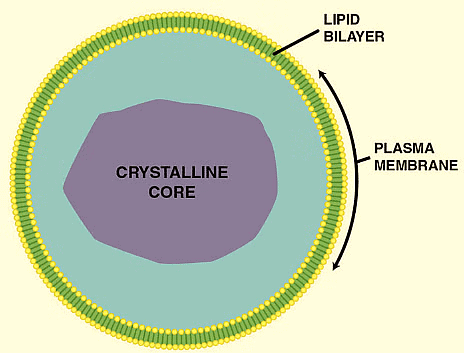 Microbodies
Microbodies
- Microbodies are membrane-bound, minute, vesicular organelles, found in both plant and animal cells.
- They contain various enzymes and proteins and can be visualized only under the electron microscope.
10. Cytoskeleton
It is a continuous network of filamentous proteinaceous structures that run throughout the cytoplasm, from the nucleus to the plasma membrane. It is found in all living cells, notably in the eukaryotes.- The cytoskeleton matrix is composed of different types of proteins that can divide rapidly or disassemble depending on the requirement of the cells.
- The primary functions include providing the shape and mechanical resistance to the cell against deformation, the contractile nature of the filaments helps in motility and during cytokinesis.
11. Cilia and Flagella
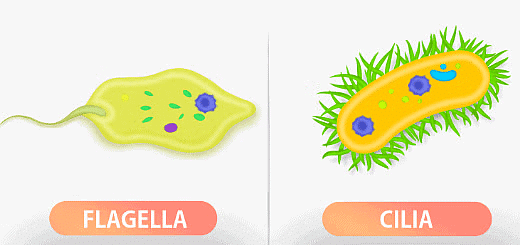 Flagella and Cilia
Flagella and Cilia
- Cilia are hair-like projections, small structures, present outside the cell wall and work like oars to either move the cell or the extracellular fluid.
- Flagella are slightly bigger and are responsible for the cell movements. The eukaryotic flagellum structurally differs from its prokaryotic counterpart.
- The core of the cilium and flagellum is called an axoneme, which contains nine pairs of gradually arranged peripheral microtubules and a set of central microtubules running parallel to the axis.
- The central tubules are interconnected by a bridge and are embedded by a central sheath.
- One of the peripheral microtubular pairs is also interconnected to the central sheath by a radial spoke. Hence there is a total of 9 radial spokes.
- The cilia and flagella emerge from centriole-like structures called basal bodies.
12. Centrosome and Centrioles
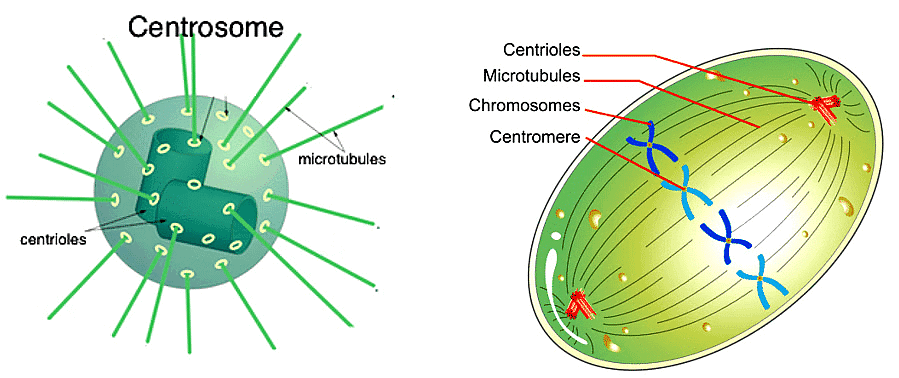 Centrosome and the alignment of the chromosomes during metaphase
Centrosome and the alignment of the chromosomes during metaphase
- The centrosome organelle is made up of two mutually perpendicular structures known as centrioles. Each centriole is composed of 9 equally spaced peripheral fibrils of tubulin protein, and the fibril is a set of interlinked triplets.
- The core part of the centriole is known as a hub and is proteinaceous. The hub connects the peripheral fibrils via radial spoke, which is made up of proteins.
- The centrioles from the basal bodies of the cilia and flagella give rise to spindle fibres during cell division.
13. Vacuoles
- Vacuoles are mostly defined as storage bubbles of irregular shapes which are found in cells. They are fluid-filled organelles enclosed by a membrane.
- The vacuole stores the food or a variety of nutrients that a cell might need to survive.
- In addition to this, it also stores waste products. The waste products are eventually thrown out by vacuoles. Thus, the rest of the cell is protected from contamination.
- The animal and plant cells have different sizes and numbers of vacuoles. Compared to animals, plant cells have larger vacuoles.
 Vacuoles
Vacuoles
A Brief Summary on Cell Organelles


|
365 videos|700 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Cell - Notes, Biology - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What is a cell? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of cells? |  |
| 3. How do cells communicate with each other? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the cell membrane? |  |
| 5. How do cells reproduce? |  |






















