Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Physics for Grade 10 > Changing Shape
Changing Shape | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Forces & Changing Shape |

|
| Compression |

|
| Stretching |

|
| Bending |

|
| Elastic Deformation |

|
| Inelastic Deformation |

|
Forces & Changing Shape
- For stationary objects, more than one force has to be applied to change their shape
- Their shape can change by:
- Stretching (forces in opposite directions away from the object)
- Bending (forces that distort the object)
- Compressing (forces in opposite directions towards the object)
- A combination of all three shape changes can also occur
Compression
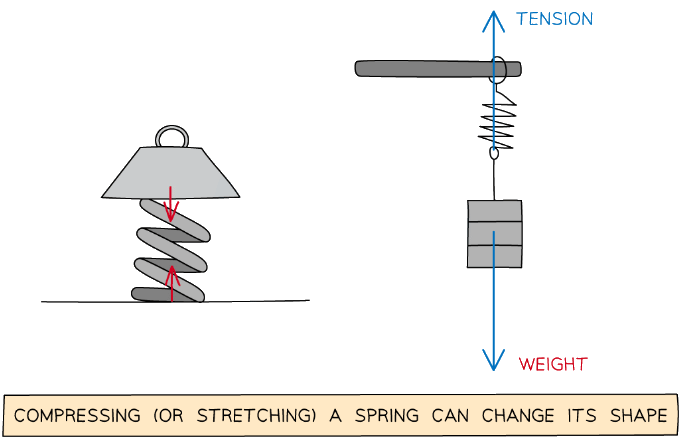
- An example of compression is placing a mass on top of a spring placed on a flat surface
- The two forces are:
- The weight of the mass
- The reaction force from the surface to the spring
- These two forces are towards each other
 The compression or stretching of a spring requires two forces
The compression or stretching of a spring requires two forces
Stretching
- An example of stretching is placing a mass on the bottom of a vertically hanging spring
- The two forces are:
- The weight of the mass
- The tension in the spring
- These two forces are away from each other
- These opposite forces are a result of Newton's Third Law
Bending
- An example of bending is a diving board bending when a swimmer stands at the far end
- The two forces are:
- The weight of the swimmer
- The reaction force from the block to the dividing board
- These two forces act towards each other, but at different points on the object
- Bending can also be caused by two forces at an angle to each other
 Forces on a diving board cause it to be bend when a swimmer stands on one end
Forces on a diving board cause it to be bend when a swimmer stands on one end
 More than one force on an object can cause it to bend
More than one force on an object can cause it to bend
- When some objects, such as springs or rubber bands, are stretched they will return to their original shape and length once the forces are removed
- Other materials, such as plastic, remain permanently distorted (stretched)

Elastic materials return to their original shape and size after stretching whilst plastic materials don’t
- Other materials, such as plastic, remain permanently distorted (stretched)
- A change of shape is called a deformation and can either be:
- Elastic
- Inelastic
Elastic Deformation
- Elastic deformation occurs:
When objects return to their original shape when the stretching force is removed - Examples of materials that undergo elastic deformation are:
- Rubber bands
- Fabrics
- Steel springs
Inelastic Deformation
- Inelastic deformation occurs:
- When objects remain stretched and do not return completely to their original shape even when the stretching force is removed
- Examples of materials that undergo inelastic deformation are:
- Plastic
- Clay
- Glass
The document Changing Shape | Physics for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Physics for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
124 videos|149 docs|37 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches