Basic Electrical Concepts | Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
Some of the Basic Concepts include :
1. Electric Current
The rate of flow of electric charge through any point of the circuit is called electric current. Its unit is ampere.

2. Coulomb's Law
According to this law, the force of attraction or repulsion between stationary point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.


Where K = 9 X 
 Newton
Newton

3. Electric Field
It is the region surrounding an electric charge or group of charges, in which another charge experiences a force of attraction or repulsion.

4. Electric Lines of Forces
- An electric lines of force field along which a free isolated unit positive charge moves.
- Electric lines of force start from the positive charge and end to the negative charge.
- No two lines of force can intersect each other because if they do so, then at the point of intersection two tangents can be drawn which would mean two directions of force at that point which is impossible.
- These lines have a tendency to separate from each other in the direction perpendicular to their length.
- Lines of force of uniform field are parallel.
- Lines of force leaves the surface of the conductor normally.
5. Electric Flux
- It is defined as that total number of lines of force passing normally through a curved surface placed in the field or the dot product of
 and normal.
and normal. 1 unit = Volt-meter
1 unit = Volt-meter 
6. Ohm's Law
- According to this law if there is no charge the physical state of conductor (Such as temp.) then the current flowing through the conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied i, e.
I α V .
I =
- A graph between applied voltage and current is a straight line shows that it follows ohm's law.
- Ohm's law is valid for metallic conductors only.
7. Resistance
It is property of: 
ρ = specific resistance or resistivity.
Note: The reciprocal of resistivity is called conductivity.
 (Ohm – m)–1 = mho/meter.
(Ohm – m)–1 = mho/meter.
Colour Code for Resistances:
- These resistances are usually carbon resistances and whose code is used to indicate the value of resistance.
- A carbon resistance has usually 4 concentric rings or bands A, B, C, D of different colours.

- The colour of first two bands A and B indicate the 1st two significant figures of resistance in ohms & those of 3rd band C indicate the decimal multiplies. The 4th band D (Which is either silver or gold) tells the tolerance.
- Sometimes only 3 colours band is there (A, B and C).
NOTE: B. ROY Great Britain Very Good Wife. 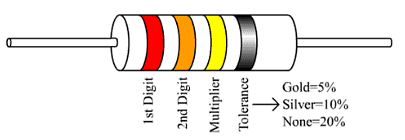

8. Electric Potential
- The electric potential at a point in an electric field is the ratio of the work done in bringing a test charge from infinity to that point to the magnitude of the test change.
- If the work done in moving a test charge q0 from infinity to that point against the field is W, then


9. Potential Gradient
Rate of charge of potential w.r.t distance in called potential gradient.

10. Electric Potential Energy
- The electric potential energy of a system of charges is the work that has to be done in bringing these charges from infinity to near each other to form the system.
- The potential energy of a system of charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance 'r' is

11. Capacitor
An element in which energy is stored in the form of an electrostatic field is called a capacitor.
 Practical Capacitor
Practical Capacitor
 Capacitor Circuit diagram
Capacitor Circuit diagram
12. Capacitance
Defined as the ratio of charge given to the plate of the capacitor to the potential difference produced between the plate.
 Area of Plane
Area of Plane
D → Distance between the planes.
∈0 = 8.85 x 10-12
∈0 = Permittivitty of free space.
Unit – c2N–1 M–2
For a capacitor, v ∝ q


Energy stored in a capacitor:
Energy(E) = 
= 
= C. 

13. Inductor
It is an element in which energy is stored in the form of an electromagnetic field (Unit → Henry.)


Energy stored in Inductor:

= L. 
14. Inductance
Inductance results from the fact that a flow of current produces a magnetic field, according to magnetic field along tends to induce a voltage (or current) in a wire according to Faraday's law.

(i) For RL Load :
V=Vm sin wt


show I lags by 90º R-L Load phasor :-



(ii) For RC Load:


Shows I leads by 90º
(iii) For RC phases:



(iv) For RLC Load:
Case 1: |VL| > |Vc|

Case 2: |VL| < |Vc|


Case 3: |VL| = |Vc|
V = VR
Ø = 0
CosØ = 1(UPF)
Note:- Reactive power is consumed by energy storing demands.
|
23 videos|89 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Electrical Concepts - Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What are the basic concepts of electrical engineering? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between AC and DC electricity? |  |
| 3. What is Ohm's Law and how is it used in electrical engineering? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of electrical circuits? |  |
| 5. How is power calculated in electrical engineering? |  |
|
23 videos|89 docs|42 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|


















