Fluid Properties | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
FLUID PROPERTIES
Definition of Fluids:- A fluid is a substance which flow continuously under the action of shear force (however small the force may be), as long as shear force is there the fluid moves or deforms.
E.g: - Liquids, gases, vapour etc.
For a static fluid shear force = 0
- Density or mass density (S):- Mass per unit volume of a fluid is called its density
s = (m/v) - Density of water is maximum at 4ºC.
- Density of water at 4ºC = 1000 kg/m3.
- Ideal Fluid (Perfect Fluid)
- Non-viscous, friction less & incompressible.
- Does not offer shear resistance against flow.
- Bulk modulus is infinite
- Used in mathematical analysis and flow problems.
- Ideal fluid has no surface tension
- Real Fluid
- Possess the properties such as viscosity, surface tension and compressibility.
- Offers resistance against flow.
- Specific gravity (G or S)
- G or S = Density of substance / Density of water at 40C
- Specific gravity for water is 1.0 at 4ºC and that of mercury is 13.6
- Specific gravity varies with temperature therefore it should be determined at specified temperature (4ºC)
- Specific weight (unit weight) or weight density (g')
g'=rg
r = mass density
g = due to gravity, acceleration
Newton's Law of Viscosity
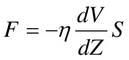

Non-Newtonian Fluids
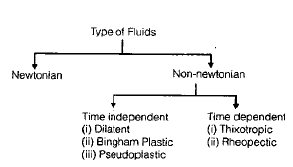
- These do not follow Newton's law of viscosity. The relation between shear sterss and velocity gradient is
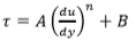
Where A and B are constants depending upon type of fluid and condition of flow.(i) For Dilatant Fluids: n > 1 & B = 0
Ex. Butter, Quick sand
(ii) For Bingham Plastic Fluids: n = 1 & B ¹ 0 Ex. Sewage sludge, Drilling mud These fluids always have certain minimum shear stress before they yield.
(iii) For Pseudoplastic Fluids: n < 1 & B = 0 Ex. Paper pulp, Rubber solution, Lipsticks, Paints, Blood, Polymetric solution etc.
(iv) For Thixotropic Fluids : n < 1 & B ¹ 0 Viscosity increase with time.
Ex. Printers ink and Enamels.
(v) For Rheopectic Fluids: n > 1 & B ¹ 0 Viscosity decreases with time
Ex. Gypsum solution in water & Bentonite solution.

- Viscosity
- Due to viscosity a fluid offers resistance to flow. It is due to cohesion and intermolecular attraction.
(i) Dynamic Viscosity ( m) Its SI unit is Pascal second or N-s/m2 Its CGS unit is Poise = Dyne-sec/cm2 1 poise = 0.1 N–s/m2
(ii) Kinematic Viscosity

- Due to viscosity a fluid offers resistance to flow. It is due to cohesion and intermolecular attraction.
Its SI unit is m2/s.
Its CGS unit is cm2/s or stoke
1 Stoke = 10–4 m2/s
- Viscosity of liquids decrease with temperature whereas viscosity of gases increase with temperature.
- fluids with increasing order of viscosity are air, gasoline, water, crude oil, castor oil.
- Viscosity of water at 1ºc is 1 centipoise.
- Viscosity of fluids is due to cohesion and molecular momentum transfer.
- Surface Tension (S)
- Surface tensions is due to cohesion only.
- Surface tension decrease with increase in temperature and it alos act when fluid is at rest
- It is a surface phenomenon
- At critical point liquid and vapour are at same state thus suface tension is zero swater = 0.0736 N/m at 20ºC
Smercury = 4.51 N/m - (i) Pressure inside a liquid drop, in excess of atmospheric pressure
p= 4s/d, where s is surface tension d is dia. of drop
- (ii)Pressure inside a soap bubble, in excess of atmospheric pressure
p= 8s/d - (iii) Pressure inside jct
p = 2s/d
- Capillary Action
- Capillary action is due to adhesion and cohesion, both.
- Height of water in capillary tube
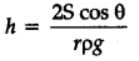
where,
g = Specific weight,
h = rise in capillary
ρ = density of fluid
S = surface tension of water & glass
r = radius of tube
θ = angle of contact between the liquid and the material
θ — 0º for water and glass
θ — 128º for mercury and glass
For capillary action dia of tube should be less than 3cm.
- When a liquid surface supports another liquid of density " rb ", then rise in capillary is given as

Compressibility
- It refers to change in volume/density due to change in pressure.
- The compressibility reciprocal of bulk modulus of elasticity (K).
Compressibility = 1/k
- In compressible fluids the velocity of sound is given by

C = velocity of sound in fluid
K = Bulk modulus of fluid
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Fluid Properties - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What are the properties of fluids? |  |
| 2. How is viscosity measured? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of density in fluid mechanics? |  |
| 4. How does temperature affect fluid properties? |  |
| 5. Can fluids be compressed? |  |
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|


















