Basics of Thermodynamics | Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| System |

|
| Types of System |

|
| Thermodynamic Equilibrium |

|
| Important Terms in Thermodynamics |

|
| Reversible and Irreversible Process |

|
Introduction
Thermodynamics is the science of energy transfer and its effect on the properties of a system.System
A system can be defined as a quantity of matter (control mass) or a region (control volume) in space selected for the study.
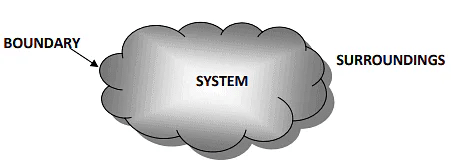
1. Surrounding
- Everything external to the system is known as the surrounding or the environment.
- Energy interaction is studied between the system and surroundings i.e. every energy leaving the system will be absorbed by the surroundings and vice versa.
2. Boundary
- An imaginary or real surface that demarcates the system from its surroundings is known as the boundary.
- The boundary is the surface of contact between the system and surrounding, thus, shared by both the system and the surroundings.
- Mathematically, the boundary has no thickness, and can neither occupy any volume in space nor contain any mass.
- The boundary may either be moving or fixed.
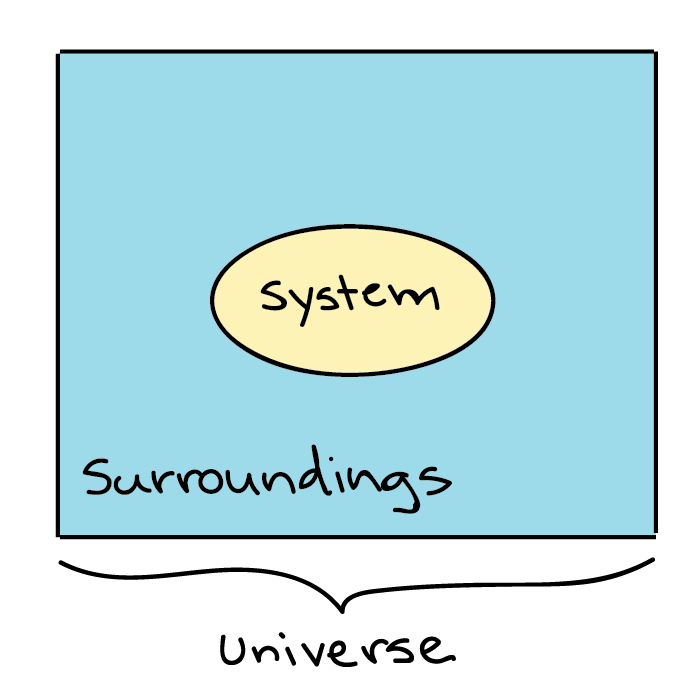
- A system and its surroundings together constitute the universe.
- Everything is contained in the universe, so everything occurring whether energy transfer or transformation or losses remains inside the universe.
Types of System
Depending upon the mass and energy interaction.(i) Open System
When there is mass as well as energy transfer across the boundary, that type of system is called an Open system.
Example - air compressor, boiler, pump, IC engine with the valve open, etc. The majority of engineering devices come under this category.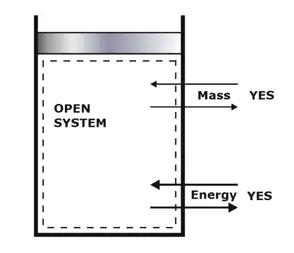
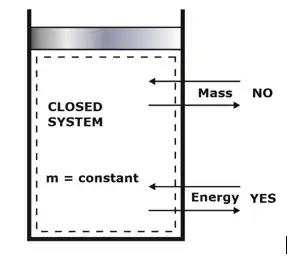
(ii) Closed System
When in a system, the mass remains fixed or constant, but there may be energy transfer into or out of the system i.e., no mass transfer occurs across the system boundary, but only energy transfer.
Example: Tea in the kettle, automobile engine with the valve closed etc.
(iii) Isolated System (Special case of Closed System)
An isolated system is a thermodynamic system that cannot exchange either energy or matter outside the boundaries of the system.
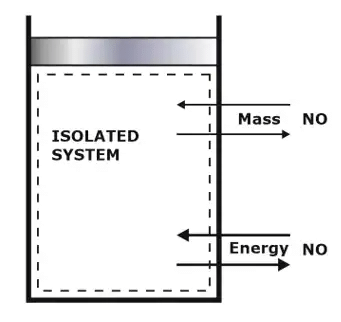
There are two ways in which this may occur:
- The system may be so distant from another system that it cannot interact with it.
- The system may be enclosed such that neither energy nor mass may enter or exit.
Macroscopic v/s Microscopic Approach
- Macroscopic Approach - When a certain quantity of matter is considered, without getting into the molecular level, such systems are called Isolated systems (also called classical approaches). Every property will be the average of that property of each molecule passing through that space.
- Microscopic Approach - When the study is made on a molecular level, as the matter is composed of a large number of molecules, such approach is called a microscopic approach. The behaviour of the gas is determined by considering the behaviour of each molecule.
CONCEPT OF CONTINUUM- The concept of the continuum is the idealization of the continuous description of matter where the properties of the matter are considered as continuous functions of space. The space between the molecules (mean free path) is almost zero or negligible when compared to the size of the system.
Extensive Properties v/s Intensive Properties
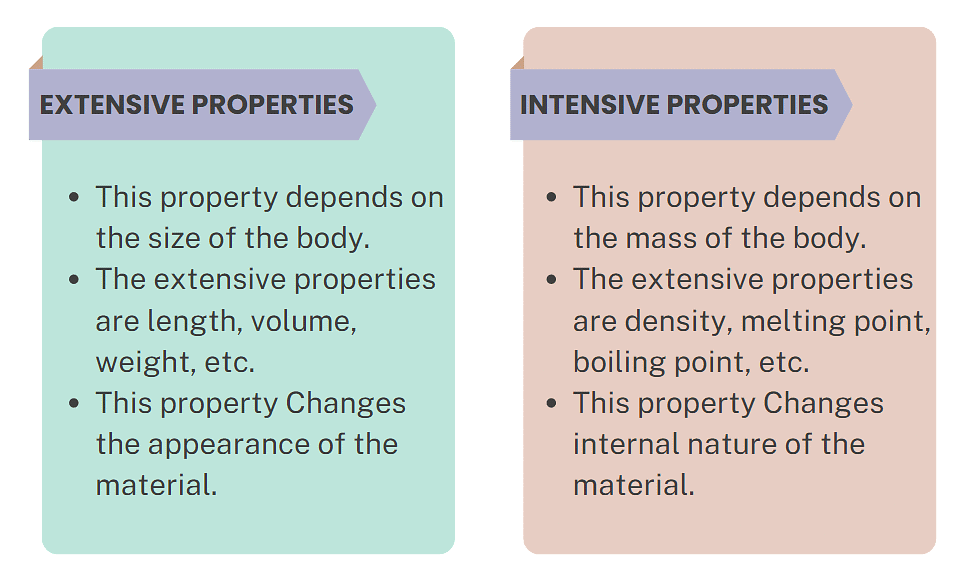
1. Extensive Properties
- An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. The mass of an object is a measure of the amount of matter that an object contains.
2. Intensive Properties
- An intensive property is a property of matter that depends only on the type of matter in a sample and not on the amount.
Example: color, temperature, density, and solubility.
Thermodynamic Equilibrium
When no change in macroscopic properties is observed, a system is said to be in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium. A system will be in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium if the following conditions are met:
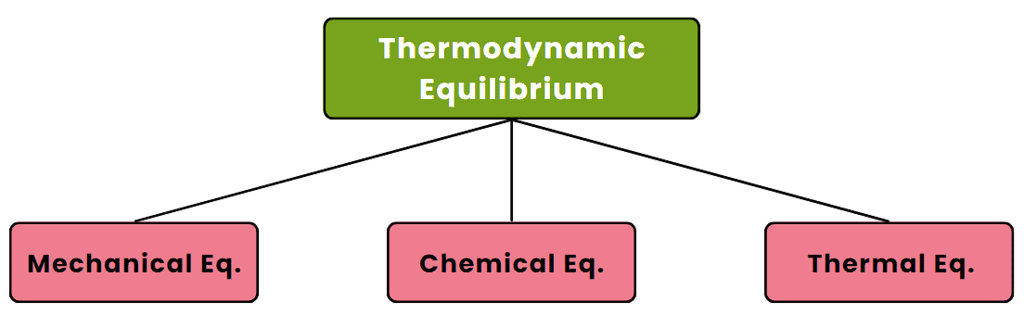
(i) Mechanical Equilibrium - without the presence of an unbalanced force within the system itself and also between the system and the surroundings.
(ii) Chemical Equilibrium - an absence of any chemical reaction or transfer of matter from one part of the system to another.
(iii) Thermal Equilibrium - When a system exists in mechanical as well as a chemical equilibrium when separated from its surroundings by a diathermic wall (diathermic means ‘which allows heat to flow’).
⇨ Even when one of these conditions is not met, the system can't be in thermodynamic equilibrium.
⇨ The thermodynamic properties are defined only for thermodynamic equilibrium states.
Important Terms in Thermodynamics
1. Process: Any change of state that a system undergoes, from one equilibrium state to another equilibrium state is known as a process.
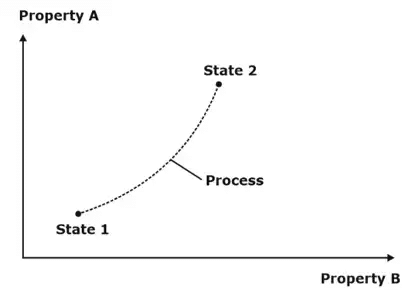
2. Path: The succession of states passed through during a change of state from an initial condition to the final required condition, is called the path of the change of state.
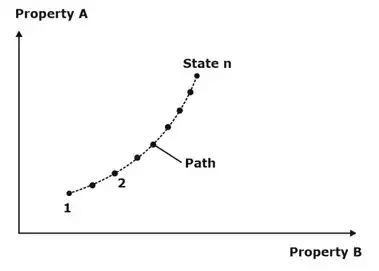
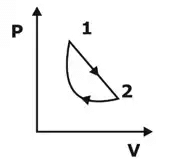
3. Cycle: A series of changes in states of a system, such that the final point of the system coincides with the initial point is termed as a cycle.
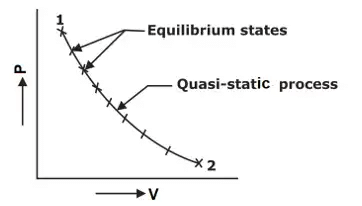
4. Quasi-static Process: The meaning of ‘Quasi’ is ‘almost’ and the meaning of ‘Static’ is ‘at rest’. The characteristic feature of a quasi-static process is its infinite slowness. A process that is the locus of all the equilibrium states the system passes through from an initial condition to the final desired condition is known as a quasi-static process. Every state of the system through which it passes during this process is an equilibrium state.
Reversible and Irreversible Process
(a) Reversible Process
- A process is said to be a reversible process if when reversed follows the same path without leaving any effect on the system and surroundings.
- The quasi-static process is called a reversible process
- All reversible processes can be shown on diagrams.
Example: P–V, T–S, P–T diagrams
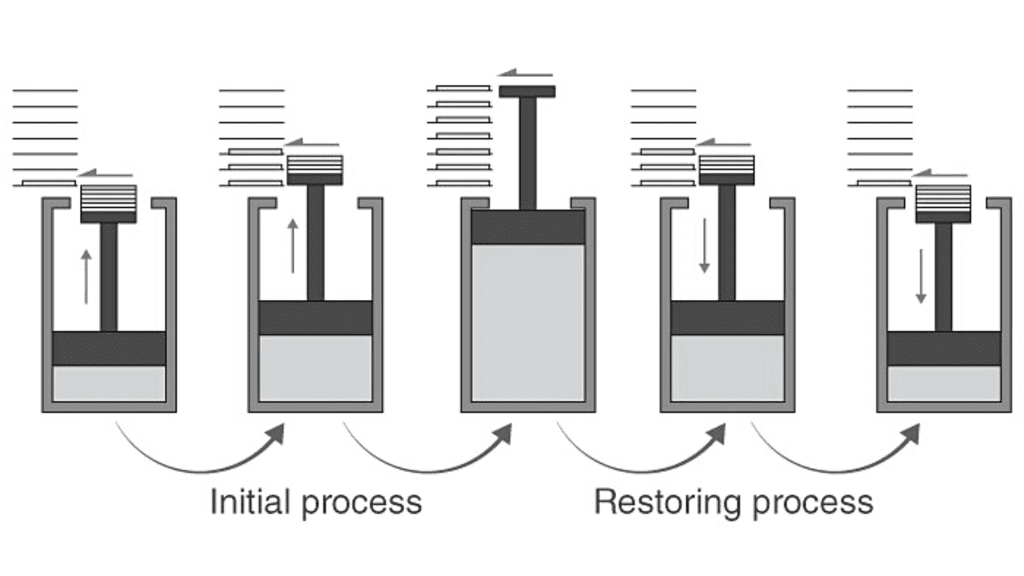 Reversible Process
Reversible Process
(b) Irreversible Process
- A process is said to be an irreversible process if when reversed follows a different path, leaving an effect on the system & surroundings.
- All spontaneous processes are irreversible processes.
- The irreversible process cannot be shown on diagrams. They are shown as dotted lines.
Example: Heat transfer to finite temperature difference, Free expansion.
|
29 videos|152 docs|36 tests
|
FAQs on Basics of Thermodynamics - Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What are the different types of systems in thermodynamics? |  |
| 2. What is thermodynamic equilibrium? |  |
| 3. What are some important terms in thermodynamics? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between reversible and irreversible processes in thermodynamics? |  |
| 5. How are the basics of thermodynamics relevant to the SSC JE exam? |  |
















