Financial Market Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Stock Exchange |

|
| Trading |

|
| NSE (National Stock Exchange of India) |

|
| BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd) |

|
| SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) |

|
Understanding Financial Markets
A financial market is a platform where financial assets are created and exchanged. It plays a crucial role in the economy by facilitating the transfer of funds from savers to borrowers, thereby supporting economic growth and development.
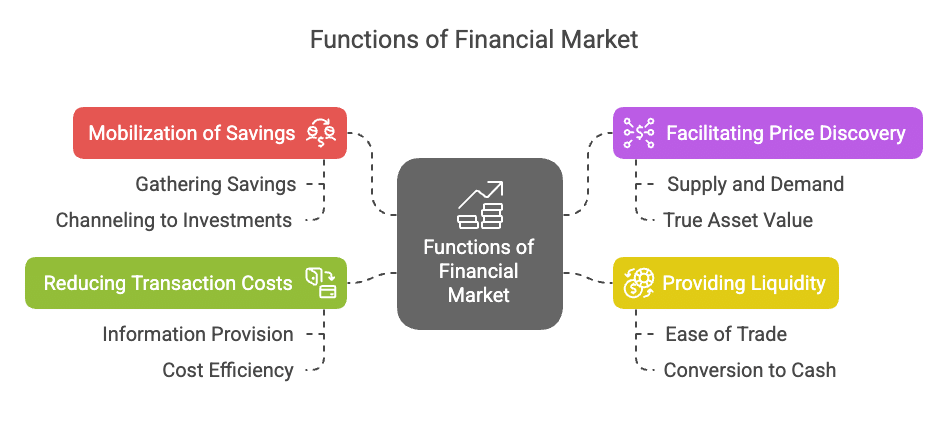
Functions of the Financial Market
1. Mobilisation of Savings and channelling them into the most productive uses: The financial market facilitates the transfer of savings from savers to investors and thus helps to channelise surplus funds into the most productive use.
2. Helps in Price Determination: Financial Market helps in interaction between savers and investors, which in turn helps in the determination of prices of the financial assets such as shares, debentures, etc.
3. Provides Liquidity to Financial Assets: The financial market facilitates the easy purchase and sale of financial assets. Thus, it provides liquidity to them so that they can be easily converted into cash whenever required.
4. Reduces Cost of Transactions: The financial market provides valuable information about securities, which helps in saving time, efforts and money, and thus it reduces the cost of transactions.
Types of Financial Markets
Financial markets can be classified into two main categories: the money market and the capital market.
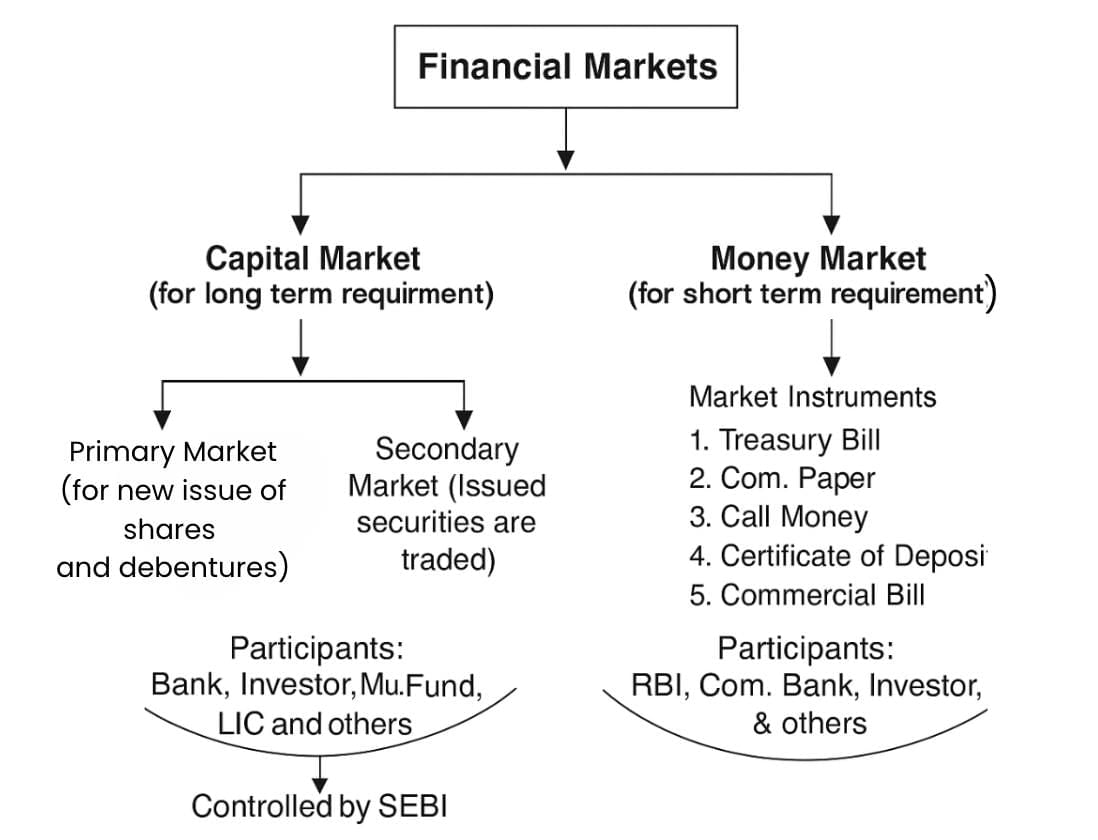
Money Market
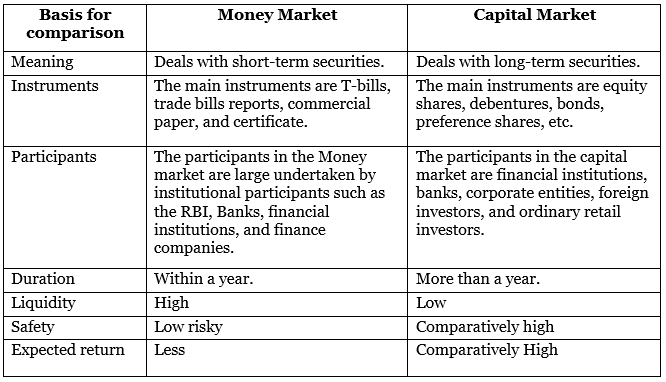
The money market deals with short-term funds and monetary assets with a maturity period of up to one year. Major participants in the money market include the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), commercial banks, non-banking finance companies (NBFCs), state governments, large corporate houses, and mutual funds.
Money Market Instruments:
- Treasury Bill: They are issued by the RBI on behalf of the Central Government to meet its short-term requirement of funds. They are issued at a price which is lower than their face value and are repaid at par. They are available for a minimum amount of Rs 25000 and in multiples thereof. They are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds. They are negotiable instruments, i.e., they are freely transferable.
- Commercial Paper: It is a short-term unsecured promissory note issued by large creditworthy companies to raise short-term funds at lower rates of interest than market rates. They are negotiable instruments transferable by endorsement and delivery with a fixed maturity period of 15 days to one year.
- Call Money: It is short-term finance repayable on demand, with a maturity period of one day to 15 days, used for interbank transactions. Call Money is a method by which banks borrow from each other to be able to maintain the cash reserve ratio as per the RBI. The interest rate paid on call money loans is known as the call rate.
- Certificate of Deposit: It is a negotiable money market instrument issued in dematerialised or usance promissory note form by commercial banks and select financial institutions. CDs are issued to individuals, corporations, and companies for a short-term period ranging from 7 days (for FIs) / 91 days (for banks) to up to one year (banks) and up to three years (FIs).
- Commercial Bill: It is a bill of exchange used to finance the working capital requirements of business firms. A seller of the goods draws the bill on the buyer when goods are sold on credit. When the bill is accepted by the buyer, it becomes a marketable instrument and is called a trade bill. These bills can be discounted with a bank if the seller needs funds before the bill's maturity.
Capital Market
The capital market is where long-term funds, both debt and equity, are raised and invested. Shares and debentures are the main securities traded in this market. An ideal capital market offers finance at a reasonable cost.
The capital market can be divided into two parts:
- Primary market: The primary market is where securities are sold for the first time to raise long-term capital. It is also known as the New Issues Market. Companies can raise capital through equity shares, preference shares, debentures, loans, and deposits in this market.
- Secondary market: The secondary market is where existing securities are bought and sold without the intervention of the issuing company. Its primary purpose is to create liquidity in securities.
Distinction between Capital Market and Money Market
Stock Exchange
A stock exchange is an institution that provides a platform for buying and selling existing securities. It plays a crucial role in helping companies raise finance, providing liquidity and safety of investment to investors, and enhancing the creditworthiness of individual companies.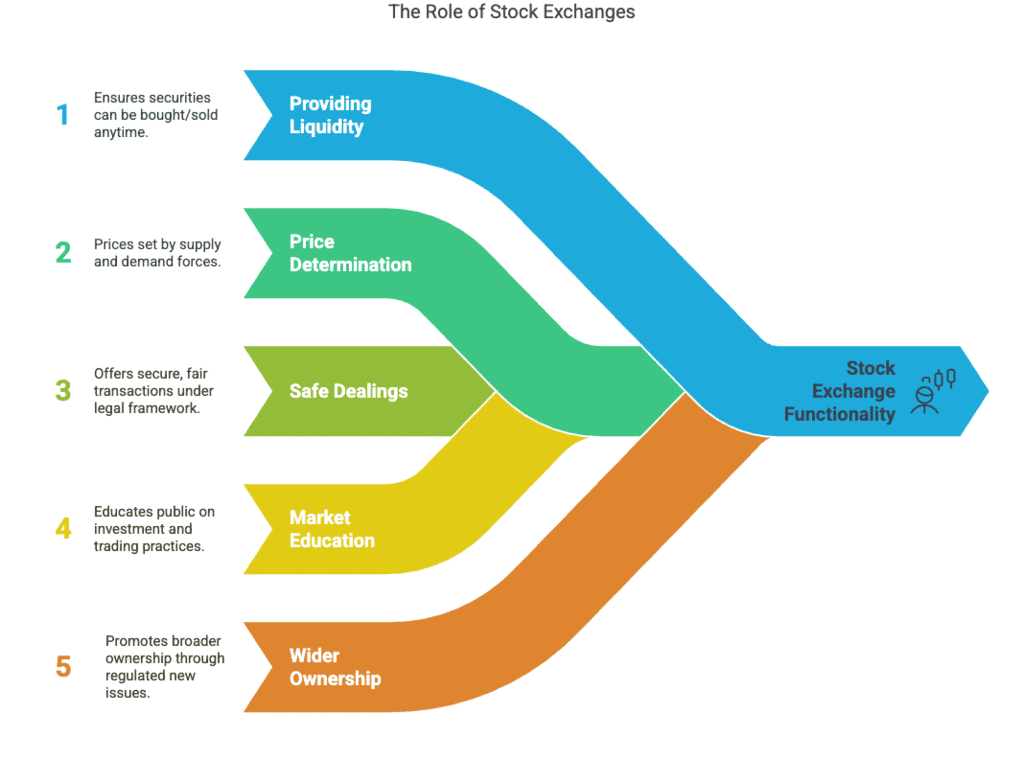
Definition of stock exchange according to the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act 1956:
- Stock exchange means any individual or individuals, whether incorporated or not, constituted for the purpose of assisting, regulating or controlling the business of buying and selling or dealing in securities.
Functions of a Stock Exchange:
- Providing Liquidity and Marketability to Existing Securities.
- Share prices are determined by the forces of demand and supply.
- The investing public gets a safe and fair deal because its dealings are well defined according to the existing legal framework.
- A stock exchange provides liquidity to securities. This gives the investor a double benefit –first, the benefit of the change in the market price of securities can be taken advantage of, and secondly, in case of need for money, they can be sold at the existing market price at any time.
- The stock exchange ensures a wider ownership by regulating new issues, better trading practices and taking effective steps in educating the public about investment.
- When securities are purchased with a view to making a profit as a result of a change in their market price, it is called speculation.
Trading
All buying and selling of shares and debentures are done through a computer terminal. Trading in securities is conducted through brokers who are members of the stock exchange. Each broker must have access to a computer terminal connected to the main stock exchange.Advantages of electronic trading systems:
- It ensures transparency, increases the efficiency of information, and enhances the efficiency of operations.
Steps in the Trading and Settlement Procedure:
- If an investor wishes to buy or sell any security, he must first register as a broker or sub-broker and enter into an agreement. This requires mandatory information such as PAN number, date of birth and address, educational qualification and occupation, residential status, bank account details, depository account details, name of any other broker with whom registered, and client code number in the client registration form.
- The investor must open a ‘demat’ account or a ‘beneficial owner’ account.
- The investor places an order with the broker.
- The broker goes online to match the shares and the best prices available.
- When the final deal is done, the broker issues a trade confirmation slip and contract note to the investor.
- After receiving a contract note, the investor must deliver the shares sold or pay cash for the shares bought.
Dematerialisation and Depositories:
- Dematerialisation: Dematerialisation is the process of converting a share certificate from physical form to electronic form.
- Depository: The investor must open a Demat Account with an organisation called a depository.
- Rematerialisation: Electronic holdings can be reconverted into physical certificates, a process called rematerialisation.
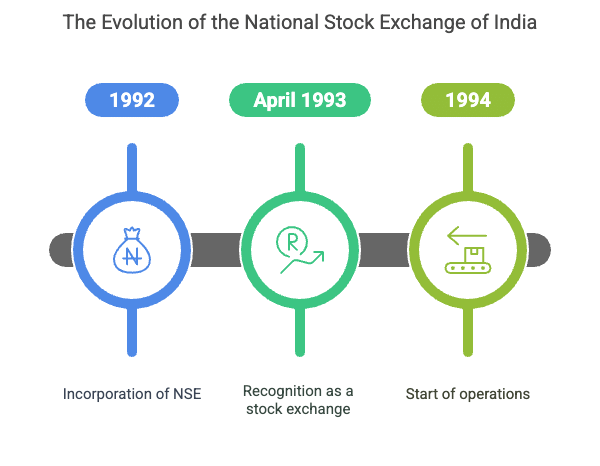
NSE (National Stock Exchange of India)
- Establishment: NSE was incorporated in 1992, recognised as a stock exchange in April 1993, and started operations in 1994. It was set up by leading financial institutions, banks, insurance companies, and other financial intermediaries.
- Objective: The objectives of NSE include establishing a nationwide trading facility for all types of securities, ensuring equal access to investors across the country through an appropriate communication network, providing a fair, efficient, and transparent securities market using an electronic trading system, enabling shorter settlement cycles and book entry settlements, and meeting international benchmarks and standards.
- Market Segments: NSE provides trading in two segments: the Wholesale Debt Market Segment and the Capital Market Segment.
Wholesale Debt Market Segment:
- This segment offers a trading platform for a wide range of fixed-income securities, including central government securities, treasury bills, state development loans, bonds issued by public sector undertakings, floating rate bonds, zero coupon bonds, index bonds, commercial paper, certificate of deposit, corporate debentures, and mutual funds.
Capital Market Segment:
- This segment provides an efficient and transparent platform for trading in equity, preference shares, debentures, exchange-traded funds, and retail government securities.
BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd)
- Establishment: BSE Ltd was established in 1875 and is Asia’s first stock exchange. It was granted permanent recognition under the Securities Contract Act, 1956.
- Objective: BSE aims to provide a fair and transparent market for trading in equity, debt instruments, derivatives, and mutual funds. It also offers a trading platform for equities of small and medium enterprises and conforms to international standards. In addition to trading, BSE provides risk management, clearing, settlement, market data, and education.
SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India)
- Establishment: SEBI was established in 1988 and given statutory status through an Act in 1992. It was set up to protect the interests of investors and regulate the securities market.
- Purpose and Role: SEBI aims to create an environment for efficient mobilisation and allocation of resources through the securities markets. It also seeks to stimulate competition and encourage innovation. SEBI’s role includes providing a marketplace for issuers to raise finances easily and fairly, protecting the rights and interests of investors, and offering a competitive and professionalised market for intermediaries.
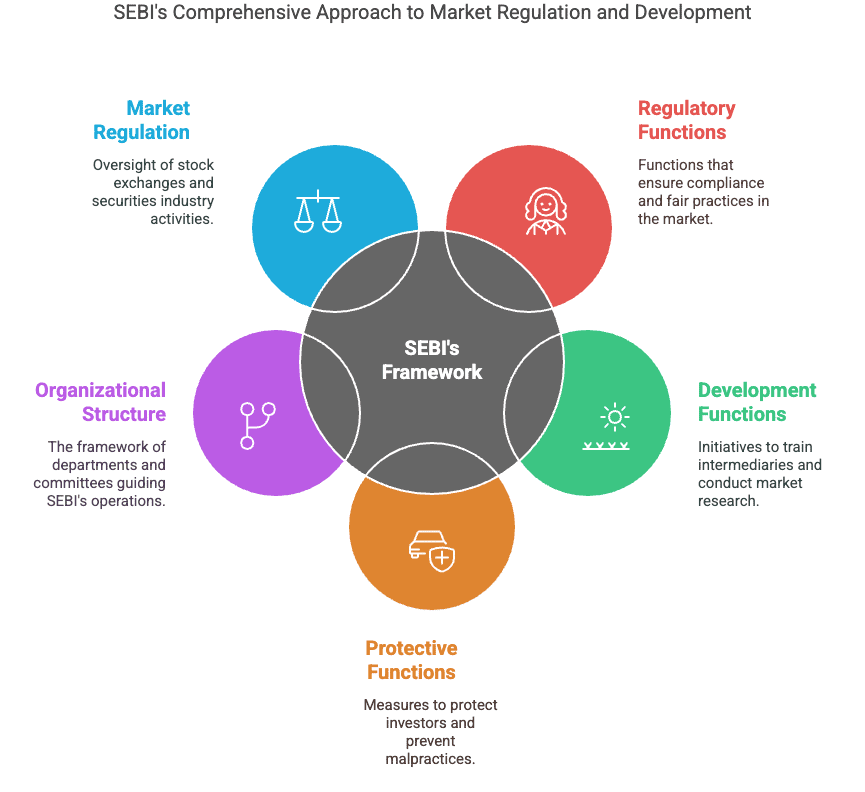
- Objective: SEBI's objective is to regulate stock exchanges and the securities industry to promote orderly functioning, protect the rights and interests of investors, prevent insider trading and malpractices, and develop a code of conduct for intermediaries.
- Functions: SEBI’s functions are divided into regulatory, development, and protective functions. Regulatory functions include registering brokers, sub-brokers, and other market players, regulating stock brokers and other market participants, and overseeing takeover bids by companies. Development functions involve training intermediaries and conducting research to benefit all market participants. Protective functions focus on investor protection, controlling insider trading, and promoting fair practices in the securities market.
- Organisational Structure: SEBI is divided into five operational departments, each headed by an executive director. Its office is in Mumbai, with regional offices in Kolkata, Delhi, Chennai and Ahmedabad. SEBI also has advisory committees to advise on the regulation and development of the primary and secondary markets.
|
51 videos|230 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Financial Market Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the different types of financial markets? |  |
| 2. What is the role of stock exchanges like NSE and BSE? |  |
| 3. How does trading work in financial markets? |  |
| 4. What is the function of SEBI in the Indian financial market? |  |
| 5. How can investors benefit from participating in financial markets? |  |
















