Fuels & Combustion | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
FUELS AND COMBUSTION
- The primary fuels which are burned to release heat and generate steam in boilers are the fossil fuels in the form of coal, fuel oil and natural gas, which represent the remains of plant and animal life that are preserved in the sedimentary rocks.
- When more than one type of fuel is simultaneously burned to meet the total heating requirement, the boiler is said to have a combination firing.
Coal
- Coal originated from vegetable matter which grew millions of years ago. Trees and plants falling into water decayed and latter produced peat bogs.
- According to geological order of formation coal may be of the following types.
- Peat
- Lignite
- Sub bituminous
- Bituminous
- Sub anthracite
- Anthracite
- These are in the increasing percentage of carbon.
- Anthracite contains more than 86% fixed carbon and less volatile matter, volatile matter helps in the ignition of coal.
- So it is often difficult to burn anthracite.
- Bituminous coal is the largest group containing 46-86% of fixed carbon and 20- 40% of volatile matter. It can be low volatile, medium volatile and high volatile.
- The lower the volatility, the higher the heating value.
- Lignite is the lowest grade of coal containing moisture as high as 30% and high volatile matter.
- Peat contains up to 90% moisture and is not attractive as a utility fuel.
- Lignite is considered to be low rank and anthracite to be high rank.
- Coal Analysis: There are two types of coal analysis.
- Proximate analysis
- Ultimate analysis
- Both done on mass percent basis.
- Both these types may be based on;
- as-received basis, useful for combustion calculations.
- dry or moisture free basis.
- dry mineral-matter-free or combustible basis
COAL PROPERTIES
Swelling Index
- Some types of coal during and after release of volatile matter becomes soft and pasty and form agglomerates. These are called caking coal.
- A qualitative method, called the swelling index, has been devised to determine the extent of caking of a coal.
Grindability
- This property of coal is measured by the standard grindability index, which is inversely proportional to the power required to grind the coal to a specified particle size for burning.
Weatherability
- It is a measure of how well coal can be stock piled for long periods of time without crumbling to pieces.
Sulphur Content
- Sulphur content in coal is combustible and generates some energy by its oxidation to SO2. Sulphur dioxide is a major source of atmospheric pollution.
Heating Value
- The heating value or calorific value of coal is the heat transferred when the products of complete combustion of a sample of coal are cooled to the initial temperature of air and fuel. Two different heating values are cited for coal. The Higher Heating Value (HHV) assumes that the water vapour in the product condenses and thus includes the latent heat of vapourization of the water vapour formed by combustion. The Lower Heating Value (LHV) assumes that the water vapour formed by combustion leaves as vapour itself. Hence
LHV = HHV–mw hfg
where, mw is the mass of water vapour formed given by - If the ultimate analysis is known, the HHV of anthracite and bituminous coals can be determined approximately by using Dulong and Petit formula as:
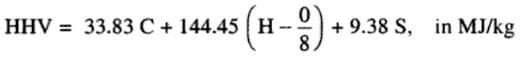
- Assuming the latent heat of vaporization hfg at the partial pressure of water vapour in the combustion products as 2.395 MJ/kg, the lower heating value of coal is
LHV = HHV – 2.395 mw in MJ/kg.
Ash Softening Temperature
- The ash softening temperature is the temperature at which the ash softens and becomes plastic. This is somewhat below the melting point of ash.
Spontaneous Combustion
- Combustion of coal takes place rapidly as in a furnace of slowly on a stockpile. If it takes place slowly, there is a degradation or loss of energy content and hence in the value of fuel. The factors which influences spontaneous combustion and which can lead to a big fire are the following:
- Rank of coal, low rank coals are more susceptible because of their higher porosity.
- Amount of surface area exposed to air.
- Ambient temperature, with high solar insolation aiding it.
- Oxygen content of coal.
- Free moisture in coal.
Coal Liquification
- The conversion of coal into a liquid fuel requires the addition of hydrogen to coal. Coal has a ratio of hydrogen atoms to carbon atoms of only 0.8 to 1 while in petroleum this ratio is 1.75 to 1. There are three basic modes that have been used to liquify coal. These are:
- hydrogenation
- catalytic conversion
- hydropyrolysis
Combustion Reaction
- The combustible elements in coal and fuel oil are carbon hydrogen and sulphur. The basic equations for complete combustion are:

- When insufficient oxygen is present, the carbon will be burned incompletely with the formation of carbon monoxide.

- In order to burn a fuel completely, four basic conditions must be fulfilled:
- Supply enough air for complete combustion of fuel.
- Secure enough turbulence for thorough mixing of fuel and air.
- Maintain a furnace temperature high enough to ignite the incoming fuel airmixture
- Provide a furnace volume large enough to allow time for combustion to be completed.
1. (a) Fuel Oil
- Liquid fuel is obtained as crude oil which by fractional distillation gives various products such as gasoline, aviation fuel, kerosene, light diesel oil, heavy diesel oil, lubrication oil etc.
- The desired physical properties of fuel oil are specific gravity, viscosity, pour point, flash point, heating value.
(b) Natural and Petroleum Gas
- Compressed natural gas is now considered as alternative fuel for automobiles.
- Natural gas was formed millions of year ago from decaying vegetable matter along with petroleum.
- Natural gas is transported through pipelines and is about used as power plant flue.
- Its major constituents are methane (critical temp = – 83ºC)
(c) Emulsion Firing
- An emulsion of water is heavy oil has been tried for boiler firing.
- Due to atomization, micro-explosion takes place which inturn enhances fuel surface to volume ratio. Hence better combustion.
- It reduces carbon loss by way of soot, reduces excess air-requirement conserves fuel oil.
(d) Coal oil and Coal Water Mixture
- Coal is grinded in fine particles and mixed with oil or water from a colloidal solution.
- Appropriate stabilizers are used to stabilize the solution and then it is transported and used as power plant fuel.
- It is cheaper then oil can be handled like oil in pipe and pumps. Good combustion efficiency eliminates the possibility of spontaneous combustion in coal. Lower ash content better utilizes low rank coal, other fuel are industrial waste and by products biomass etc.
Coal Gasification
- Coal gasification is the process of producing syngas–a mixture consisting primarily of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), natural gas (CH4) , and water vapour (H2O)–from coal and water, air and/or oxygen.
- The principle of water gas production is straightforward. Steam is forced over red-hot or white-hot carbon-based fuel, producing the following reaction:
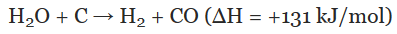
- Coal gasification results in mixture of three gas mixture classified according to their heating value as low, medium and high heating value gas.

ACTUAL AIR-FUEL RATIO
- The actual amount of air supplied per kg. Fuel can be ascertained from the measured volumetric composition of combustion products. These methods includes:
- Orsat analyzer
- Haldane apparatus
- Infrared gas analyzer
- Gas chromatograph
- Orsat gas analyzer measures the volume or mole fraction of CO2, CO and O2 in the dry flue gas. An orsat analyzer contains three pipettes containing chemical solutions.

- The reagents normally used are a KOH solution to absorb the CO2 gas. Pyrogallol solution to absorb the O2 gas and a Cuprous Chloride mixture (CuCI2) to absorb the CO gas.
- The remaining unabsorbed gas is nitrogen. Since the sample is collected over water, any water vapour in the flue gas would have condensed during the collection process. The SO2 gas will react with water in the container. So
CO2 + CO + O2 + N2 = 100% by volume - The total heat released by complete combustion of 1 kg coal is
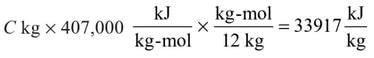
Control of Excess Air
- Proper control of the right amount of excess air maintains optimum combustion efficiency. Amounts of CO2 and O2 in combustion gases are indexes of excess air.
DRAUGHT (OR DRAFT) SYSTEM
- The function of draught system is basically two-fold:
- To supply to the furnace the required quantity of air for complete combustion of fuel.
- To remove the gaseous products of combustion from the furnace and throw these through chimney or stack to the atmosphere.
Natural Draught
- The natural draught is produced by a chimney or a stack. It is caused by the density difference between the atmospheric air and the hot gas in the stack. For a chimney of height H meters the draught or pressure difference (N/m2) produced is given by:
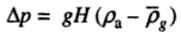

where,
ρa = density of atmospheric air; kg/m3.
ρg = average gas density in the chimney, kg/m3.
g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s2)
Assuming both air and gas as ideal gases.
- If m kg of air is used for 1 kg fuel combustion then total (m + 1) kg of combustion products will be produced.
- Draught produced
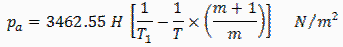
T1 = Temperature of air
T = Temperature of flue gases
Fans are added for producing mechanical draught.
Stacks have thus two functions:
- To assist the fans in overcoming pressure losses.
- To help disperse the gas effluent into the atmosphere at a sufficient height to cause minimum atmosphere pollution.
- Dispersion of flue gases into the atmosphere is defined as the movement of the flue gases horizontally as well as vertically and their dilution by the atmosphere. The exit velocity of flue gases at stack exit results in a plume rise ΔH above the actual stack. The gases been in the direction on wind flow. The effective Height:
He = H + ΔH

Mechanical Draught
- Mechanical Draught is produced by fans. There are types of fans in use:
- Forced draught (FD) fans
- Induced draught (ID) fans.
When either one is used alone, it should overcome the total air and gas pressure losses within the steam generator.
- Forced draught fans are installed at inlet to the air preheater. They handle cold air. So they have less maintenance problems, consumes less power (since cold air has less specific volume, and work input per unit mass flow rate is given by ò vdp) and therefore the capital and operating costs are lower.
- If Wf is the fuel burning rate, v is the specific volume of inlet air and ΔpFD is the pressure head developed by the fan to overcome all the pressure losses, then the power required to drive the FD fan is:
Power Input(FD fan) =
hFD = Efficiency of forced draught
A/F = air-fuel ratio.
- For good reliability two forced draught fans operating in parallel are normally used, each capable of undertaking at least 60% of full load air flow, when the other is out of service.
- The forced draught fan maintains the entire system up to the stack entrance under positive gauge pressure. The furnace is said to be pressurized.
- The stack in such situation is shorter and meant only for disposal of flue gases.
- Induced draught fans are normally located at the foot of the stack. They handle not combustion gases. There power requirements are, therefore, greater than forced draught fans. In addition they must cope with corrosive combustion product and fly ash. Induced draught fans are seldom used alone. They discharge essentially at atmospheric pressure and place they system upstream under negative gauge pressure.
- If V g is the specific volume of the flue gases handled by the ID fan and ΔpID is the pressure head developed, then the power needed to drive the ID fan is
Power Input(ID fan) = [Wf.(1 + A/F).Vg.DPID]/hID
hID = Efficiency of induced draught
A/F = air-fuel ratio
- When both forced and induced draught fans are used in a steam generator, the FD fans push atmospheric air through the air preheater, dampers, various air ducts and burners into the furnace, and ID fans suck out the flue gases through the heat transfer surfaces in the superheaters, reheaters, economiser gas-side air preheater and dust collectors and discharge into the stack. In such a cases the furnace is said to be operate with balanced draught, meaning that the pressure in it is approximately atmospheric. Actually, it is maintained at a slightly negative gauge pressure to insure that any leakage would be inward.

- Fans: There are two types of fans viz. centrifugal and axial. In the centrifugal fan, the gases are accelerated radially through curved or flat impeller blades from rotor to a spiral or volute casing.
- In the axial fan, gases are accelerated parallel to the rotor axis. Axial fans have higher capital costs.
- Centrifugal fans have forward-curved, flat or backward curved impeller blades.
- The absolute velocity V is the same in all three cases. For same V, the blade tip velocity Vb is the highest for the backward curve blades and the lowest for forward curve blades.
- Since
 (p=π)for same tip diameter D, the rpm N is the highest for back wardcurve blades and lowest for forward-curved blades.
(p=π)for same tip diameter D, the rpm N is the highest for back wardcurve blades and lowest for forward-curved blades. - FD fans should have high Vb so as to rotate at high speeds and handle large volume flow of air. Therefore, centrifugal fans with backward - curved blading are normally used for FD fans.
- ID fans handle dust laden flue gases and so the blades are subject to erosion by the fly ash. The erosion rate of blades is lower if the blade tip speed Vb is less and fan rotates at lower speeds.
- Therefore centrifugal fans having forward-curved or flat blading are used for ID fans. Low-speed fans with flat blades are used for particularly dirty or corrosive gases.
- In damper control, a damper is used to control the flow of gas by regulating the flow area according to the load. It has the advantage of low capital cost since it needs a simple constant speed induction ac motor. Dampers are usually put on the outside of the fan, although dampers at inlet to the fan are sometimes used.
- Inlet dampers consume less power than outlet dampers but are only effective for moderate load changes near full load.
- Variable-Speed control has the advantage of less power consumption and is the most efficient method for fan control. The effect of speed on fan performance is:
- Volume flow α N
- Pressure head α N2
- Power input α N3
where, N is the rpm of the fan.
- The types of drives are:
- Variable-speed steam turbine
- Hydraulic coupling
- Variable-speed dc motor
- Multiple speed ac motor
- Electronically adjustable motor drive.
- Primary air fans supply air to dry and transport the pulverized coal to the furnace.
- Fans are a major source of noise in power plants. To reduce this noise, they are often housed in thick masonary acoustical enclosures or equipped with silencers or both.
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Fuels & Combustion - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What is the role of fuels in combustion? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of fuels used in combustion? |  |
| 3. How does combustion impact the environment? |  |
| 4. What factors affect the efficiency of combustion? |  |
| 5. What are some common combustion technologies used in industry? |  |
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|


















