Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Notes > Chapter 4 -Elasticity of Demand Economics
Chapter 4 -Elasticity of Demand Economics - Class 12 PDF Download



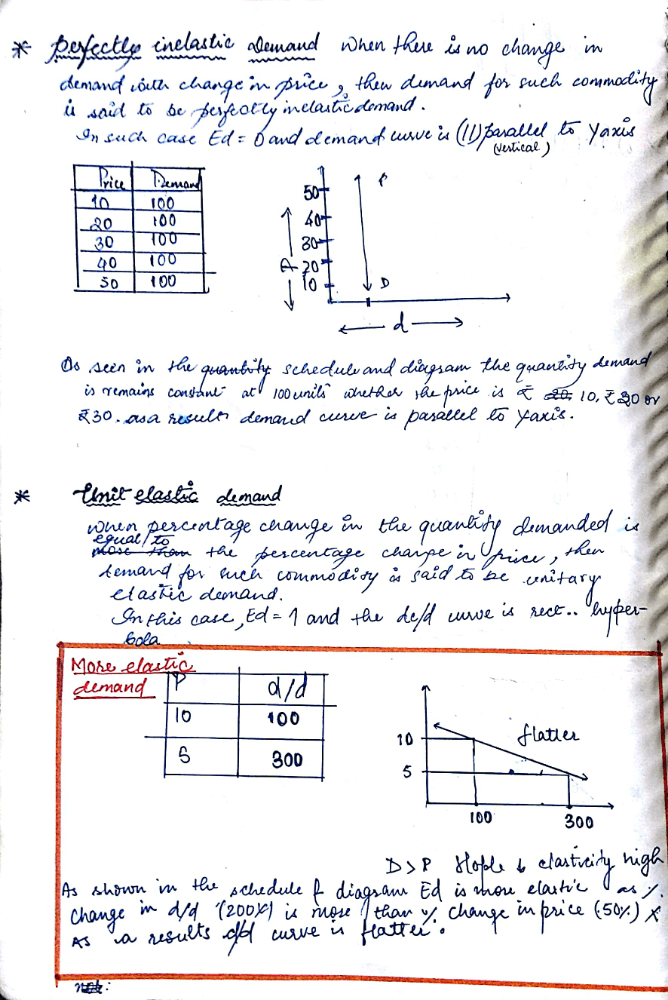
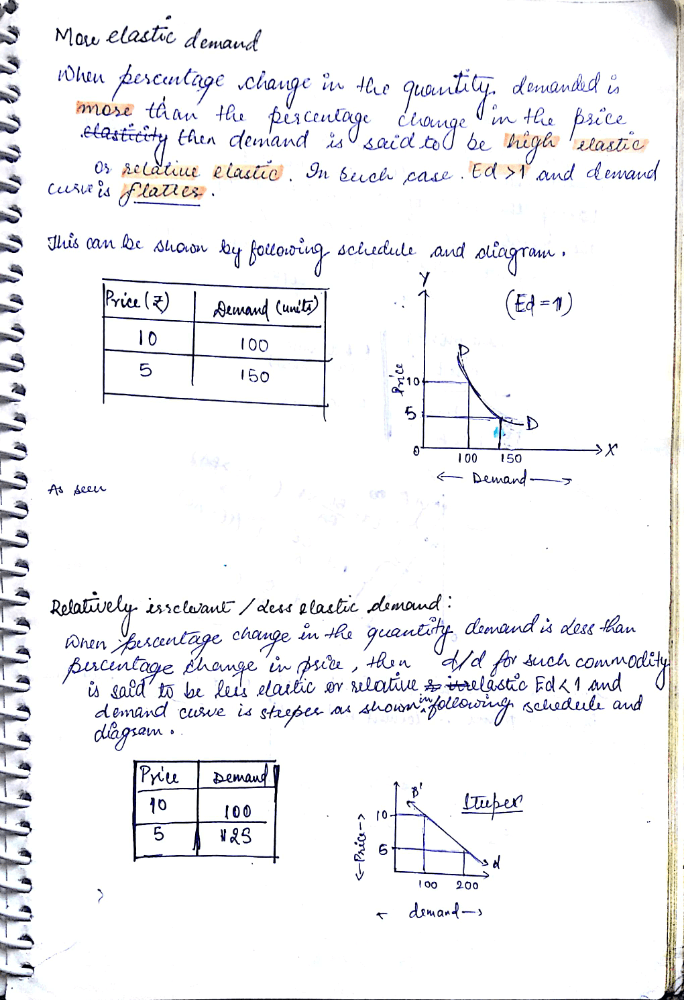


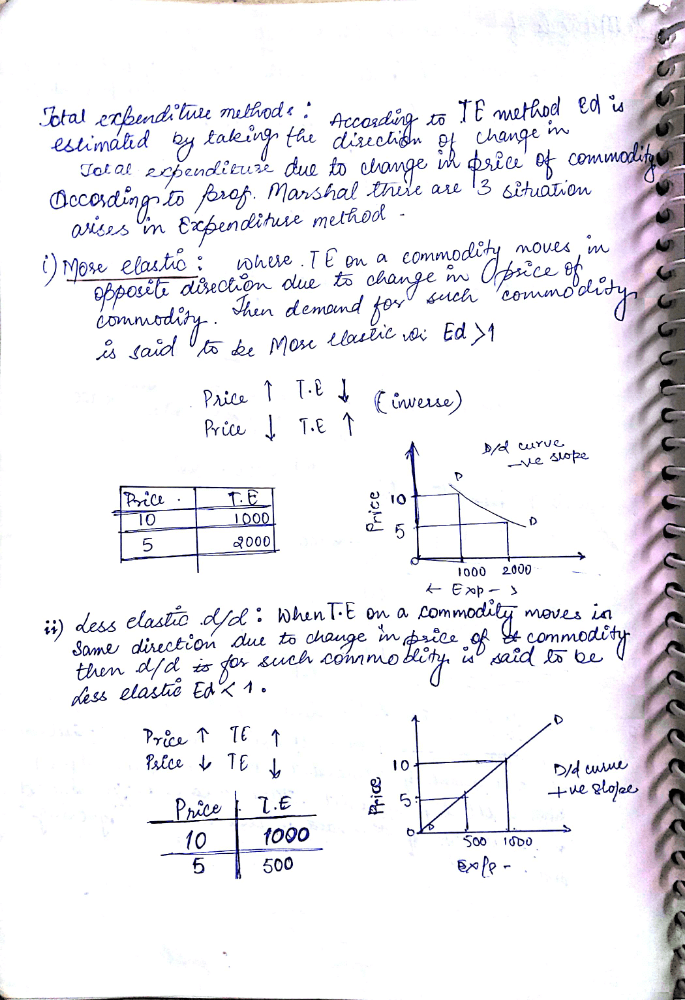


 This is Hand written note of class 12 Micro-Economics chapter 4 elasticity of demand . It could be complete note.
This is Hand written note of class 12 Micro-Economics chapter 4 elasticity of demand . It could be complete note. summary-:
Introduction Important Questions for Class 12 Economics,Concept of Price Elasticity of Demand and Its Determinants
Sample question with explanations---:
Elastic demand: Pepsi, chocolate, and Oriental rugs
Inelastic demand: Home heating oil, water, and heart medication
Inelastic demand: Home heating oil, water, and heart medication
Problem : If supply is unit elastic and demand is inelastic, a shift in which curve would affect quantity more? Price more?
Shifting the demand curve would affect quantity more, and shifting the supply curve would affect price more.Problem : Katherine advertises to sell cookies for $4 a dozen. She sells 50 dozen, and decides that she can charge more. She raises the price to $6 a dozen and sells 40 dozen. What is the elasticity of demand? Assuming that the elasticity of demand is constant, how many would she sell if the price were $10 a box?
To find the elasticity of demand, we need to divide the percent change in quantity by the percent change in price.% Change in Quantity = (40 - 50)/(50) = -0.20 = -20%
% Change in Price = (6.00 - 4.00)/(4.00) = 0.50 = 50%
Elasticity = |(-20%)/(50%)| = |-0.4| = 0.4
The elasticity of demand is 0.4 (elastic).
To find the quantity when the price is $10 a box, we use the same formula:
Elasticity = 0.4 = |(% Change in Quantity)/(% Change in Price)|
% Change in Price = (10.00 - 4.00)/(4.00) = 1.5 = 150%
Remember that before taking the absolute value, elasticity was -0.4, so use -0.4 to calculate the changes in quantity, or you will end up with a big increase in consumption, instead of a decrease!
-0.4 = |(% Change in Quantity)/(150%)|
|(%Change in Quantity)| = -60% = -0.6
-0.6 = (X - 50)/50
X = 20
The new demand at $10 a dozen will be 20 dozen cookies.
Follow for more such notes
FAQs on Chapter 4 -Elasticity of Demand Economics - Class 12
| 1. What is the concept of elasticity of demand in economics? |  |
Ans. Elasticity of demand refers to the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a product or service to a change in its price. It measures the sensitivity of demand to price changes and helps in understanding consumer behavior and market dynamics.
| 2. How is the price elasticity of demand calculated? |  |
Ans. Price elasticity of demand is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price. The formula for price elasticity of demand is:
Elasticity = (% change in quantity demanded) / (% change in price)
If the elasticity value is greater than 1, demand is considered elastic; if it is less than 1, demand is inelastic; and if it is equal to 1, demand is unitary elastic.
| 3. What factors determine the elasticity of demand? |  |
Ans. The elasticity of demand is influenced by several factors, including the availability of substitutes, the necessity of the good or service, the proportion of income spent on the good, and the time period under consideration. Goods with close substitutes, luxury items, and goods that consume a large portion of income are usually more elastic in nature.
| 4. How does elasticity of demand affect pricing decisions for businesses? |  |
Ans. The elasticity of demand plays a crucial role in pricing decisions for businesses. If the demand for a product is elastic, meaning that a small change in price leads to a significant change in quantity demanded, businesses may need to lower their prices to attract more customers and increase sales. On the other hand, if the demand is inelastic, businesses can increase prices without affecting the quantity demanded significantly.
| 5. What are some real-life examples of elastic and inelastic demand? |  |
Ans. Examples of goods with elastic demand include luxury items like designer clothing, high-end smartphones, and vacation packages. When the prices of these goods increase, consumers tend to reduce their quantity demanded significantly. In contrast, goods with inelastic demand are typically necessities like food, medication, and basic utilities. Even if the prices of these goods increase, consumers still require them and are willing to pay the higher prices, resulting in a relatively smaller decrease in quantity demanded.
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















