Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Notes > Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) > Flow Measurement
Flow Measurement | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
FLOW MEASUREMENT
| Device | Measurement |
| Venturimeter | rate of flow (discharge) |
| Flow nozzle | rate of flow |
| Orifice meter | rate of flow |
| Bend meter | rate of flow |
| Rotameter | rate of flow |
| Pitot tube | velocity |
| Hot wire anemometer | air & gas velocity |
| Current meter | velocity in open channels |
Venturimeter
- Cone angle of convergence side (20°) is greater than cone angle of divergence side (5° to 7°).
- Position of venturimeter does not play any role in discharge thus it is constant for horizontal, inclined or vertical position.
Qac = Cd Qth
Cd = coefficient of discharge = 0.95 to 0.98
h = venturi head which is difference between pressure heads
- Throat diameter is known as size of the venturimenter.
Orifice meter
- It is a cheaper arrangement but has more energy loss.
Cd for orifice meter = 0.68 - 0.74
Cd for orifice meter = 0.68 - 0.74
a1 = πd2/4
a2 = πdc2/4
Pitot Tube
- It is based on principle of conversion of kinetic head into pressure head. The point at which velocity reduces zero is called stagnation point.

- For theoretical velocity, we do not multiply the equation by C.
- Velocity head is indicated by the difference in liquid level between the Pitot tube and the piezometer. The Pitot tube measures the total head and therefore known as total head tube.
Hydraulic Coefficients
- Contraction coefficient (Cc) =
- Coefficient of velocity of (Cv) =
- Coefficient of discharge (Cd) =
- Cd = Cv.Cc
Flow through orifice in the tank
Time required to lower the level from H to h
Discharge through orifice when head over orifice is h
- Rectangular Weir/Notch
L = length of crest H = head above crest
- Triangular weir
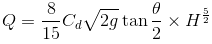
- Trapezoidal weir
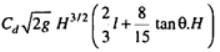
The document Flow Measurement | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) is a part of the Mechanical Engineering Course Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical).
All you need of Mechanical Engineering at this link: Mechanical Engineering
|
6 videos|104 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Flow Measurement - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What is flow measurement in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. Flow measurement in mechanical engineering refers to the process of quantifying the rate at which a fluid (liquid or gas) flows through a particular system or device. It involves determining the volume, velocity, or mass flow rate of the fluid, which is essential for various engineering applications such as designing efficient systems, controlling processes, and ensuring safety.
| 2. What are the different types of flow measurement devices used in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. There are several types of flow measurement devices commonly used in mechanical engineering, including:
- Venturi meters: These devices use a converging-diverging nozzle to create a pressure difference that is directly related to the flow rate.
- Orifice plates: They consist of a plate with a hole (orifice) through which the fluid flows, and the pressure drop across the plate is used to determine the flow rate.
- Turbine flow meters: These devices utilize a turbine rotor that rotates as the fluid flows past it, and the rotational speed is proportional to the flow rate.
- Magnetic flow meters: They employ electromagnetic principles to measure the flow rate of conductive fluids by generating a magnetic field and measuring the induced voltage.
- Ultrasonic flow meters: These devices use ultrasound waves to measure the flow rate by analyzing the time it takes for the waves to travel through the fluid.
| 3. What factors can affect the accuracy of flow measurement in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. Several factors can influence the accuracy of flow measurement in mechanical engineering, including:
- Fluid properties: Viscosity, temperature, density, and composition of the fluid can all impact the accuracy of flow measurement.
- Flow profile: Disturbances or irregularities in the flow profile, such as turbulence or swirl, can affect measurement accuracy.
- Installation effects: Improper installation, such as incorrect pipe alignment or obstructions, can introduce errors in flow measurement.
- Sensor calibration: Inaccurate calibration of flow measurement devices can lead to significant errors in the measured flow rate.
- Repeatability: The ability of a flow measurement device to provide consistent results for repeated measurements is crucial for accuracy.
| 4. How can flow measurement be calibrated in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. Flow measurement devices can be calibrated in mechanical engineering by comparing their readings to a known standard. This calibration process involves introducing a known flow rate through the device and comparing it to the indicated flow rate. Any discrepancies can then be corrected by adjusting the device or applying calibration factors. Calibration can be performed using calibration rigs, master meters, or other reference standards, ensuring accurate and reliable flow measurement.
| 5. What are the applications of flow measurement in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. Flow measurement has various applications in mechanical engineering, including:
- HVAC systems: Flow measurement is used to ensure proper air and water flow rates in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for efficient operation.
- Oil and gas industry: Accurate flow measurement is essential for monitoring and controlling the flow of oil, gas, and other fluids in pipelines, wells, and refineries.
- Chemical processing: Flow measurement is crucial in chemical plants for controlling the flow of raw materials, monitoring reaction rates, and ensuring accurate dosing of chemicals.
- Water and wastewater treatment: Flow measurement is used to monitor and control the flow of water and wastewater in treatment plants, optimizing the process and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Power generation: Flow measurement is employed in power plants to monitor the flow rates of steam, water, or fuel, optimizing efficiency and maintaining safe operation.
Related Searches

















