Directing Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Directing? |

|
| Supervision |

|
| What is Motivation? |

|
| Leadership |

|
| Communication |

|
Introduction
- Imagine organising a school event, like your farewell party.
- It’s not enough to assign tasks—someone has to guide the decoration team, motivate the volunteers when things get stressful, offer suggestions when challenges arise, and lead everyone toward a fun and memorable event.
- If no one takes charge, the event might fall apart.
- This is what directing in management is all about. It’s not just about telling employees what to do—it involves supervising their efforts, motivating them to perform better, and leading by example.
What is Directing?
Directing as a function of management, refers to the process of instructing, guiding, counselling, motivating and leadingpeople in the organization to achieve its objectives.
- It does not mean only instructions but also includes supervising the employees when they are performing the job, motivating them to perform more efficiently and leading them towards the achievement of organizational goals.

Characteristics of Directing
- Initiates Action: Directing is essential for starting action within an organization. While planning, organizing, staffing, and controlling set the stage, directing is what triggers action.
- Present at Every Level: Every manager, from top executives to supervisors, is involved in directing. It occurs wherever there are superior-subordinate relationships.
- Continuous Process: Directing is an ongoing activity that happens throughout the life of the organization, regardless of who holds managerial positions. Examples like Infosys and Tata show that directing continues even with changing managers.
- Flows from Top to Bottom: Directing starts at the top level and flows down through the organizational hierarchy. This means that every manager can direct their immediate subordinates while receiving instructions from their superiors.
Importance of Directing
1. Initiates Action
- Directing is responsible for initiating action by individuals in the organization towards achieving the desired objectives.
- For example, when a supervisor guides and clarifies doubts for subordinates, it helps them meet work targets effectively.
2. Integrates Employee Efforts
- Directing ensures that individual efforts are aligned with organizational goals.
- A manager with strong leadership skills can convince employees that their individual and team efforts contribute to the overall success of the organization.
3. Realizes Employee Potential
- Effective directing involves motivating and providing leadership to help employees realize their full potential.
- A good leader can identify the capabilities of employees and inspire them to perform at their best.
4. Facilitates Change
- Directing plays a crucial role in introducing necessary changes within the organization.
- People often resist change, but effective directing through motivation, communication, and leadership can reduce this resistance.
- For instance, when a manager wants to implement a new accounting system, explaining the purpose, providing training, and offering incentives can help employees accept the change.
5. Brings Stability and Balance
- Effective directing fosters cooperation and commitment among employees, leading to stability and balance within the organization.
- It helps achieve harmony among different groups, activities, and departments, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the organization.
Principles of Directing
Principles of Directing
Providing good and effective directing is a challenging task as it involves many complexities. A manager has to deal with people with diverse backgrounds and expectations. This complicates the directing process. Certain guiding principles of directing may help in the directing process.
1. Maximum Individual Contribution:
- Directing techniques should enable every individual in the organization to contribute their maximum potential towards achieving organizational objectives.
- It aims to tap into the untapped energies of employees to enhance organizational efficiency.
- For instance, a well-designed motivation plan with appropriate monetary and non-monetary rewards can inspire an employee to give their best efforts, knowing that their contributions will be duly rewarded.
2. Harmony of Objectives:
- Directing should create harmony between the individual objectives of employees and the organizational objectives.
- Often, these objectives may seem conflicting, such as an employee seeking higher salaries while the organization aims for increased productivity.
- Effective directing involves convincing employees that their rewards and the need for work efficiency are complementary, fostering a win-win situation.
3. Unity of Command:
- This principle asserts that each person in the organization should receive instructions from only one superior.
- Receiving instructions from multiple superiors can lead to confusion, conflict, and disorder.
- Adhering to this principle ensures clear and effective direction, reducing ambiguity for subordinates.
4. Appropriateness of Direction Technique:
- Directing techniques should be tailored to the needs, capabilities, attitudes, and situational variables of subordinates.
- For example, while some individuals may be motivated by monetary incentives, others may respond better to promotion opportunities.
- Using appropriate motivational and leadership techniques enhances the effectiveness of directing.
5. Managerial Communication:
- Effective communication at all levels of the organization is vital for successful directing.
- Clear instructions and feedback are essential to ensure that subordinates understand their tasks and responsibilities.
- Managers should encourage feedback to confirm that instructions are understood, fostering better communication and understanding.
6. Use of Informal Organization:
- Managers should recognize and leverage informal groups or organizations that naturally exist within formal structures.
- Identifying and utilizing these informal networks can enhance the effectiveness of directing by tapping into existing social dynamics and relationships.
7. Leadership:
- Effective leadership is crucial while directing subordinates, as it positively influences their behaviour and motivation.
- Good leadership involves guiding and inspiring employees without causing dissatisfaction and fostering a positive work environment.
8. Follow Through:
- Simply giving an order is not sufficient; managers should continuously monitor and review the implementation of directives.
- Regular follow-up ensures that orders are being carried out as intended and helps identify any issues or challenges.
- If necessary, managers should make suitable modifications to directions based on feedback and observations.
Elements of Directing
1. Supervision:
- Supervision involves overseeing the work of employees to ensure that they are performing their tasks correctly and efficiently.
- Supervisors play a vital role in providing guidance, feedback, and support to workers on the shop floor.
- Effective supervision helps maintain quality standards and keeps the workflow smooth.
2. Motivation:
- Motivation is about inspiring and encouraging employees to put in their best effort.
- Managers can motivate their teams through various means, such as offering incentives, recognizing achievements, and creating a positive work environment.
- A motivated workforce is more productive and committed to the organization's goals.
3. Leadership:
- Leadership involves guiding and influencing employees towards achieving organizational objectives.
- A good leader sets a vision, leads by example, and fosters a collaborative and supportive atmosphere.
- Leadership is not just about giving orders; it's about inspiring trust and respect among team members.
4. Communication:
- Communication is the backbone of effective directing.
- Managers need to communicate clearly and openly with their teams to ensure everyone is on the same page.
- This includes sharing information, providing feedback, and encouraging open dialogue.
- Good communication helps prevent misunderstandings and keeps the team aligned with organizational goals.
Let's learn about these elements in detail.
Supervision
Supervision can be understood in two ways:
As part of directing: Every manager supervises their team by guiding employees' efforts and overseeing tasks to ensure resources are used efficiently and goals are achieved.
As a specific role: A supervisor holds a position just above the workers, directly managing their activities. This role is crucial since supervisors have close interaction with workers, unlike higher-level managers.
Importance of Supervision
The role of a supervisor is as follows:
1. Link between workers and management because the supervisor explains management policies to workers and brings workers' problems to the notice of the management.
2. Ensures issuing Instructions: To make sure that the instructions are communicated to each and every employee.
3. Facilities Control: Control means a match between actual and planned output. It ensures checking on the methods in use and the progress of work according to the planned schedule.
4. Maintenance of discipline: The strict supervision and guidance of the supervisor encourage the employees and workers to be more disciplined in their activities. Under the guidance of superiors, the workers follow a fixed or strict timetable and execute the plans in the right direction.
5. Feedback: The supervisors are directly dealing with the subordinates. As a result, feedback in the form of suggestions, and grievances keeps coming to the management. It improves quality management decisions and revision of plans & policies.

6. Improved Motivation:A supervisor with good leadership qualities can build up high morale among workers. The relationship with the supervisor is a very good incentive to improve the motivation level of the employees while guiding the employees, the supervisors encourage the subordinates to perform to their best capacities.
7. Optimum utilization of resources: All the activities are under the observation of the supervisor so less wastage and optimum utilization of resources is possible.
What is Motivation?
- It is the process of stimulating people to act to their best ability to accomplish desired goals.
- Motivation means inspiring the employees to work with greater enthusiasm and more efficiency for the accomplishment of the objectives of the enterprise.
- It involves arousing needs and desires in people so as to initiate and direct their behaviour in a purposive manner.

When talking about motivation, we need to understand three related terms:
- Motive: An internal drive that directs behaviour toward a goal. Motives arise from needs (like hunger or recognition) and create restlessness, prompting action to satisfy them.
- Motivation: The process of encouraging people to act in order to achieve specific goals by meeting their needs.
- Motivators: Tools or techniques used by managers to inspire people, such as pay, promotions, recognition, or praise.
Features of Motivation
1. Psychological Phenomenon
Motivation is an internal feeling which means it cannot be forced on employees. Internal feelings such as need, desire, aspiration etc. influence human behaviour to behave in a particular manner.
2. Goal-Directed Behaviour
It induces people to behave in such a manner so that they can achieve their goals. A motivated person works towards the achievement of desired goals.
3. Motivation can be either positive or Negative
Positive motivation means inspiring people to work better and appreciating work that is well done e.g., pay increase promotion recognition. Negative motivation means forcing people to work by threatening or punishing them. e.g., issue of memo, demotion, stopping increments etc.
4. Complex Process
It is a complex and difficult process. Individuals differ in their needs and wants and human needs change from time to time.
5. Continuous Process
Human needs are unlimited and so they keep on changing continuously, satisfaction of one need gives rise to another. As soon as one need is satisfied another need arises. So managers have to continuously perform the function of motivation. 
Importance of Motivation
Motivation plays a key role in improving employee performance and organizational success. Here are its key benefits:
Improves Performance: When employees' needs are met, they put in their best effort, leading to higher productivity for both employees and the organization.
Changes Attitude: Proper rewards and recognition can turn negative or indifferent attitudes into positive ones, encouraging employees to perform better.
Reduces Turnover: Motivated employees are less likely to leave, reducing the cost and effort of hiring and training new staff. It also helps retain talented employees.
Lowers Absenteeism: Motivation makes work enjoyable, leading to fewer absences. Problems like poor working conditions or lack of recognition can be solved with the right motivational efforts.
Eases Change Management: Employees are more open to change if they see benefits, like additional rewards. Motivation helps reduce resistance to new changes within the organization.
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy-Theory of Motivation
Maslow’s Theory focuses on the needs as the basis for motivation. It classified human needs into the following five categories. It helps managers to realize that the need level of employees should be identified to motivate them. It is based on the following assumptions:
(i) People’s behaviour is based on their needs.
(ii) People’s needs are in hierarchical order.
(iii) A satisfied need can no longer motivate a person.
(iv) A person moves to the next higher level of hierarchy only when the lower need is satisfied.


Financial and Non-Financial Incentives
Incentives are all measures that are used to motivate people to improve their performance.

Financial Incentives
- Pay and Allowances: Salary is the basic incentive, including pay, allowances, and regular increments.
- Productivity-Linked Wages: Wages tied to individual or group productivity levels.
- Bonus: Extra pay given beyond regular wages or salary.
- Profit Sharing: Employees receive a share of company profits, encouraging better performance.
- Stock Options: Employees get company shares at lower prices, fostering a sense of ownership.
- Retirement Benefits: Provident funds, pensions, and gratuities offer post-retirement security.
- Perquisites: Extra benefits like company cars, housing, or medical aid are provided in addition to salary.
Non-Financial Incentives
- Status: Higher ranks or roles satisfy the need for recognition and prestige.
- Organizational Climate: Positive work environments with autonomy and rewards improve employee satisfaction.
- Career Advancement: Skill development and promotion opportunities encourage better performance.
- Job Enrichment: Adding variety and responsibility to jobs makes work more meaningful.
- Employee Recognition: Acknowledging good work through awards, compliments, or public recognition boosts motivation.
- Job Security: Stable jobs reduce employee anxiety, promoting focus and productivity.
- Employee Participation: Involving employees in decision-making enhances engagement.
- Employee Empowerment: Giving employees autonomy makes them feel valued and improves job performance.
Leadership
- Leadership is the activity of influencing people to strive willingly for mutual objectives.
- Managers at all levels are expected to be the leaders of their subordinates.
- Leadership indicates the ability of an individual to maintain good interpersonal relations with followers and motivate them to contribute to achieving organizational objectives.
- It is a process of interaction between the leader and his followers.
- It helps in persuading employees to work cooperatively and enthusiastically towards common goals.

Importance of Leadership
- Influences Positive Behavior: A good leader inspires people to channel their efforts toward the organization’s success.
- Builds Strong Relationships: Leaders support their followers, boosting their confidence and creating a positive work environment.
- Facilitates Change: Leaders help employees accept changes by explaining, motivating, and reducing resistance.
- Manages Conflicts: A good leader resolves conflicts by listening to disagreements and providing clear solutions.
- Prepares Future Leaders: Leaders train and develop their teams, ensuring a smooth transition when successors take over.
Styles of Leadership
- Leadership styles refer to a leader’s behaviour.
- The behavioural pattern that the leader reflects in his role as a leader is often described as the style of leadership.
- A Leadership style is the result of the leader’s philosophy, personality, experience and value system.
- It also depends upon the type of followers and the atmosphere revealed in the organization.
Different types of leadership styles are:
1. Autocratic leadership
2. Participative leadership/Democratic
3. Free rein leadership/Laissez Faire
A leader may use all styles over some time but one style tends to predominate as his normal way of using power.
Autocratic or Authoritarian Leader
- An autocratic leader gives orders and insists that they are obeyed.
- He determines the policies for the group without consulting them.
- He does not give information about future plans but simply tells the group what immediate steps they must take.
- Under this style, all decision-making power is centralized in the leader.
- He does not give the subordinates any freedom to influence his decisions.
- It is like “bossing people around.”
- This style should normally be used on rare occasions.
- It is best applied to situations where there is little time for group decision-making or where the leader is the most knowledgeable member of the group.

Democratic or Participative Leader
- A democratic leader gives orders only after consulting the group and works out the policies with the acceptance of the group.
- He never asks people to do things without working out the long-term plans on which they are working.
- He favours decision-making by the group as shown in the diagram.
- This improves the attitude of the employees towards their jobs and the organization thereby increasing their morale.
- Using this style is of mutual benefit - it allows them (subordinates) to become part of the team and helps leaders (seniors) to make better decisions.

When should participative/democratic leadership be applied?
- It works best in situations where group members are skilled and eager to share their knowledge.
- It is also important to have plenty of time to allow people to contribute, develop a plan and then vote on the best course of action.
- This style should NOT be used when: In situations where roles are unclear or time is of the essence, democratic leadership can lead to communication failures and incomplete projects.
Laissez Faire or Free Rein Leader
- A free-rein leader gives complete freedom to the subordinates.
- Such a leader avoids the use of power.
- He depends largely upon the group to establish its own goals and work out its own problems.
- Group members work themselves as per their own choice and competence.
- The leader exists as a contact man with the outsiders to bring information and the resources that the group requires to accomplish the job.
- Note: This is also known as laissez-faire which means no interference in the affairs of others (French word laissez means to let/allow and faire means to do).

When should laissez faire/free-rein leadership be applied?
- This is an effective style to use when followers are highly skilled, experienced and educated.
- Followers have pride in their work and the drive to do it successfully on their own.
- Outside experts, such as staff specialists or consultants are being used.
- Followers are trustworthy and experienced.
This style should NOT be used when:
Followers feel insecure about the non-availability of a leader. The leader cannot or will not provide regular feedback to his followers.
Communication
- It is the transfer of information from the sender to the receiver with the information being understood by the receiver.
- Communication plays a key role in the success of a manager.
- The directing abilities of a manager mainly depend upon his communication skills.
- That is why the organization always emphasizes improving the communication skills of managers as well as employees.
- Communication is important for the directing function because all other elements of directing become possible only when there is adequate communication.

Elements of Communication Process
1. Sender: Who conveys his thoughts or ideas.
2. Message: Ideas, feelings, suggestions, order etc.
3. Encoding: Converting the message into communication symbols such as words/pictures etc.
4. Media: Path/Channel through which encoded message is transmitted to receiver e.g., face to face, phone call, internet etc.
5. Decoding: Converting encoded symbols of the sender.
6. Receiver: Who receives communication from the sender.
7. Feedback: All those actions of the receiver indicating that he has received and understood the message of the sender.
8. Noise: Some obstruction or hindrance to communication like poor telephone connection, or inattentive receiver.
Importance of Communication
1. Facilitates Coordination: It facilitates coordination between interrelated departments and sections thus creating a unity of purpose and action.
2. Provides data necessary for decision-making: When information is effectively and efficiently communicated to management.
3. Increases managerial efficiency: Every individual in the organization is assigned a job or task. The employee must know clearly who has to report to whom, what part of the total job they are expected to perform and what are their decisions. The clarity comes only with the smooth flow of communication which keeps the organization at work with efficiency.
4. Promotes cooperation and Industrial Peace: The two-way communication promotes cooperation and mutual understanding between the management and workers and brings peace to the organization.
5. Establishes effective leadership: Effective communication helps to influence subordinates. while influencing, a leader should possess good communication skills. If there is a two-way information flow between the superior and subordinates, then there will be a positive reaction from employees.
Formal Communication
It refers to official communication that takes place following the chain of command. Classification of formal communication-
1. Vertical Communication: Flows vertically i.e., upwards or downwards through formal channels.
(i) Downward Communication: Higher to lower level like plans, policies, rules etc.
(ii) Upward Communication: Subordinate to superior like suggestions, grievances, reports etc.
2. Horizontal/lateral Communication: between persons holding positions at the same level of the organization e.g., the production manager may contact the marketing manager about product design, quality etc.
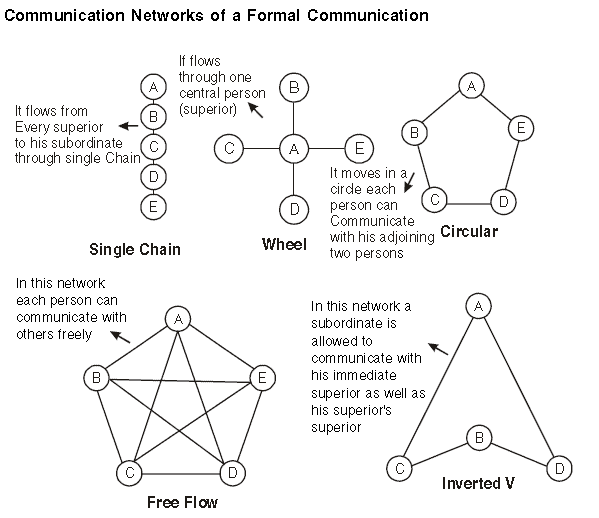
•Informal Communication: Communication that takes place without following the formal lines of communication is said to be informal communication. There is no fixed direction or path for the flow of information.
Grapevine or Informal Communication Networks:
1. Single Strand: Each person communicates with the other in a sequence.
2. Gossip: Each person communicates with all on a non-selective basis. A person shares the information with many other people in his social group.
3. Probability: The individual communicates randomly with other individuals.
4. Cluster: The individual communicates with only those people whom he trusts.


Barriers to Effective Communication Semantic Barriers
Concerned with problems and obstructions in the process of encoding or decoding the message into words or impressions.
A. Semantic barriers
Semantics is a branch of linguistics that focuses on the meaning of words and sentences. Semantic barriers occur when there are issues in encoding (sending) or decoding (receiving) messages, leading to misunderstandings. Some of these barriers are:
- Badly expressed message: Sometimes intended meaning may not be conveyed.
- Choice of words: Words or symbols with different meanings confuse the receiver.
- Translation errors: Faulty translations may transfer wrong messages.
- Unclarified assumption: Different interpretations may result in confusion.
- Technical Jargon: Technical words may not be understood by the workers.
- Body language and gesture decoding: If the words spoken don't align with the body movements or expressions, it can lead to misinterpretation or confusion in communication.
B. Psychological/Emotional barriers
Emotions and mental state can block effective communication. For example, a worried sender may struggle to convey the message clearly, and an angry receiver might misinterpret or ignore the message. The state of mind of both the sender and receiver directly affects how well the communication process works. These barriers include:
- Premature evaluation: judgement before listening leads to misunderstanding.
- Lack of attention: Lack of attention/poor listening may disappoint the employees.
- Loss by transmission and poor retention: When oral communication passes through various levels it destroys the structure of the message or leads to transmission of inaccurate message.
- Distrust: If the parties do not believe each other. They cannot understand each other’s message in its original sense.
Organizational Barriers
These arise from the structure, policies, and rules of an organisation. Key barriers include:
- Organisational Policy: If communication is restricted by policies (e.g., centralised control), it limits free flow.
- Rules and Procedures: Rigid rules can delay communication or make it complicated.
- Status Differences: Managers with high status may unintentionally discourage subordinates from speaking freely.
- Complex Structure: Many levels of management can delay and distort communication due to multiple filters.
- Lack of Facilities: Without tools like meetings, suggestion boxes, or transparent practices, communication can suffer.
Personal Barriers
These are individual factors that affect communication between people in an organisation:
- Fear of Authority Challenge: Superiors may withhold information if they feel it threatens their authority.
- Lack of Confidence in Subordinates: Managers may avoid seeking input if they doubt their team’s abilities.
- Unwillingness to Communicate: Subordinates might avoid communicating if they feel it could harm their interests.
- Lack of Incentives: If employees receive no recognition or rewards, they may hesitate to share ideas or suggestions.
Improving Communication Effectiveness
To ensure effective communication in organisations, the following strategies can be employed:
Clarify Ideas Before Communication:
- The communicator must understand the problem thoroughly before sharing it.
- A well-analyzed and clear message ensures better understanding by subordinates.
Communicate According to Receiver’s Needs:
- Adjust the message to match the education and comprehension level of the audience.
- This ensures the receiver can understand and respond appropriately.
Consult Others Before Communicating:
- Involving subordinates in planning communication fosters participation and cooperation.
- This can lead to smoother implementation and acceptance of the message.
Use Appropriate Language, Tone, and Content:
- Choose words carefully to avoid misunderstandings or offending listeners.
- Ensure the message stimulates interest and encourages a response.
Share Information of Value to the Listener:
- Align messages with the interests and needs of the audience to enhance engagement.
- Relevant information encourages a positive response from the receiver.
Ensure Proper Feedback:
- Ask questions to confirm understanding and encourage two-way communication.
- Feedback helps refine future communication and ensures clarity.
Communicate for Both Present and Future:
- Communication should address current needs and align with future organisational goals.
- This ensures continuity and consistency in decision-making.
Follow Up on Communication:
- Regularly review and monitor the implementation of instructions.
- Follow-ups help address issues promptly and ensure tasks are completed effectively.
Be a Good Listener:
- Active listening fosters trust and shows subordinates that their input is valued.
- Patient listening helps resolve issues and strengthens communication.
By adopting these measures, organisations can enhance the effectiveness of communication and create a more collaborative and responsive work environment.
|
52 videos|198 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Directing Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the role of directing in management? |  |
| 2. How does supervision differ from directing? |  |
| 3. What are effective methods of motivation in the workplace? |  |
| 4. What qualities make a good leader in a directing role? |  |
| 5. Why is communication important in the directing process? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|


















