Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Notes > Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) > Properties of Pure Substance
Properties of Pure Substance | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCE
- A pure susbtance is a substance of homogeneous chemical composition throughout its mass. It is one component system. It may exist in one or more phases.
- A saturation state is a state from where a change of phase may occur without a changes of pressure or temperature.
- Critical Point:
- Critical Temperature : At critical temperature a liquid completely changes to vapour and viceversa. Also above critical temperature a vapour cannot be liquified by any amount of pressure.
- Critical Pressure : At critical temperature the minimum pressure required to transform a vapour to liquid is called critical pressure.
- Transformation of solid to vapour directly is called sublimation.
- Transformation of vapour to solid directly is called ablimation.
- Triple point is the fixed point (fixed temperature and pressure) at which solid, liquid and vapour phase co-exist in equilibrium
- Following is the decreasing arrangement of substances triple point
- For water
- Critical pressure (pc) = 221.2 bar
- Critical temperature (tc) = 374.15ºC
- Critical volume (vc) = 0.00317 m3/kg
- Triple point (P) = 4.58 mm Hg
- Triple point (T) = 273.16 K
- The slope of vaporization and sublimation curve for all substance are positive. The slope of the fusion curve for most substances is positive but for water, it is negative.
- Water expands upon freezing while volume of other substances decreases upon freezing.
- Mollier diagram (or h-s diagram)
- The slope of constant pressure lines is given as
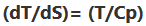
- Dryness fraction : It is indicates the mass fraction of vapour in a liquid.
mv = mass of vapour
ml = mass of liquid.
- For saturated liquid, x = 0
- For saturated vapour, x = 1
- Dryness quality lines originate from critical line in various diagrams (P–V, h–s diagram etc.).
- Various properties of pure substance based on dryness fraction.
- For given pressure and temperature
v, vf, vg = specific volume of moist vapour, liquid, vapour
vfg = vg – vf
h, hf, hg = specific enthalpy of moist vapour,liquid, vapour
hfg = hg – hf
s, sf, sg = specific entropy of moist vapour, liquid, vapour
sfg = sg – sf
- At triple point
| internal energy = 0 entropy = 0 enthalpy > 0 |
- A gas or a pure susbtance require two known properties (P, V, T, H etc.) to describe it completely i.e. it have two degrees of freedom.
- A liquid and vapour in equilibrium state (saturated state) has one degree of freedom.
- A liquid, vapour and solid in equillibrium (triple point) has zero degree of freedom.
- The difference between the temperature of the superheated vapour and that of saturated vapour at the same pressure is called degree of superheat.
- Throtting caloriemter
- It is used to measure dryness fraction of pure substance.
- Throttling is an irreversible and adiabatic but not isentropic.
- It is very difficult to measure quality of two phase system (liquid+vapour) so it is throttled to bring it to single phase that is vapour phase and then the measurment of pressure, temperature and other properties of two phase system can be done.
The document Properties of Pure Substance | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) is a part of the Mechanical Engineering Course Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical).
All you need of Mechanical Engineering at this link: Mechanical Engineering
|
6 videos|104 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Properties of Pure Substance - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What is a pure substance in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. A pure substance in mechanical engineering refers to a substance that has a constant chemical composition and distinct physical properties. It can exist in different phases, like solid, liquid, or gas, but its composition remains the same throughout.
| 2. What are the properties of a pure substance? |  |
Ans. The properties of a pure substance include specific volume, specific internal energy, specific enthalpy, specific entropy, and temperature. These properties are independent of the amount of substance present and can be used to describe its behavior.
| 3. How do specific volume and specific entropy relate to pure substances? |  |
Ans. Specific volume is the ratio of the volume of a substance to its mass, while specific entropy is the ratio of the change in heat to the absolute temperature. Specific volume provides information about the density of a substance, while specific entropy measures its disorder or randomness.
| 4. What is the significance of specific internal energy in pure substances? |  |
Ans. Specific internal energy represents the energy contained within a unit mass of a substance, including both its kinetic and potential energy. It is a crucial property in thermodynamics as it helps in understanding energy transfer and heat exchange processes in pure substances.
| 5. How does specific enthalpy differ from specific internal energy in pure substances? |  |
Ans. While specific internal energy includes the energy associated with the molecular structure of a substance, specific enthalpy also considers the energy involved in the pressure-volume work. It accounts for the heat transfer and work done during a process, making it a more comprehensive property for analyzing pure substances.
Related Searches






















