Ch 8 - Communication and Network Concepts, Computer Science, Class 12 Chapter Notes | COMPUTER SCIENCE for Class 12(XII) - CBSE & NCERT Curriculum PDF Download
Network
- The collection of interconnected computers is called a computer network.
 Network
Network - Two computers are said to be interconnected if they are capable of sharing and exchanging information.

Need
- Resource Sharing: Resource Sharing means to make all programs, data and peripherals available to anyone on the network irrespective of the physical location of the resources and the user.
- Reliability: Reliability means to keep the copy of a file on two or more different machines, so if one of them is unavailable (due to some hardware crash or any other) them its other copy can be used.
- Cost Factor: Cost factor means it greatly reduces the cost since the resources can be shared.
- Communication Medium: Communication Medium means one can send messages and whatever the changes at one end are done can be immediately noticed at another.
Evolution of Networking
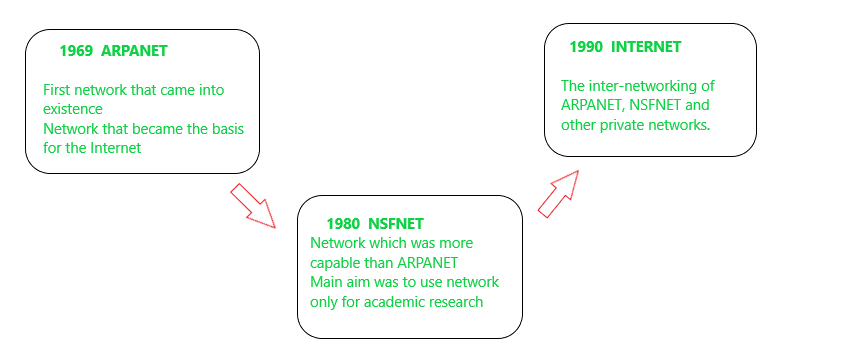
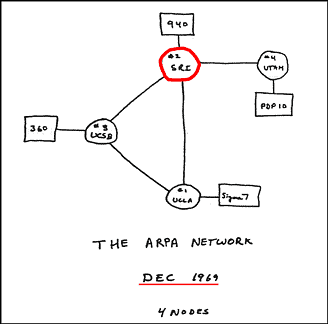
- ARPANET: In 1969, The US govt. formed an agency named ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) to connect computers at various universities and defense agencies. The main objective of ARPANET was to develop a network that could continue to function efficiently even in the event of a nuclear attack.

- Internet (INTERconnection NETwork): The Internet is a worldwide network of computer networks. It is not owned by anybody.
- Interspace: Interspace is a client/server software program that allows multiple users to communicate online with real-time audio, video and text chat in dynamic 3D environments.
Switching techniques
Switching techniques are used for transmitting data across networks.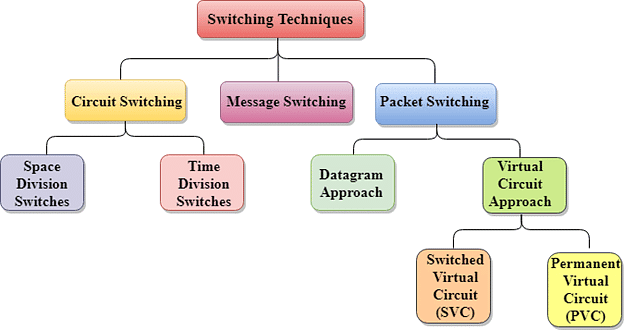
Different types are:
- Circuit Switching: In the Circuit Switching technique, first, the complete end-to-end transmission path between the source and the destination computers is established and then the message is transmitted through the path. The main advantage of this technique is guaranteed delivery of the message. Mostly used for voice communication.
- Message Switching: In the Message switching technique, no physical path is established between sender and receiver in advance. This technique follows the store and forward mechanism.
- Packet Switching: In this switching technique fixed size of packet can be transmitted across the network.
 Comparison between various switching techniques
Comparison between various switching techniques
Data Communication Terminologies
- Data channel: The information/data carry from one end to another in the network by channel. Baud & bits per second (bps): It’s used to measurement for the information carry of a communication channel.
- Measurement Units: bit
1 Byte= 8 bits
1 KBPS ( Kilo Byte Per Second)= 1024 Bytes
1 Kbps (kilobits Per Second) = 1024 bits
1 Mbps ( Mega bits Per Second )=1024 Kbps - Bandwidth: It is the amount of information transmitted or receives per unit time.
Transmission media
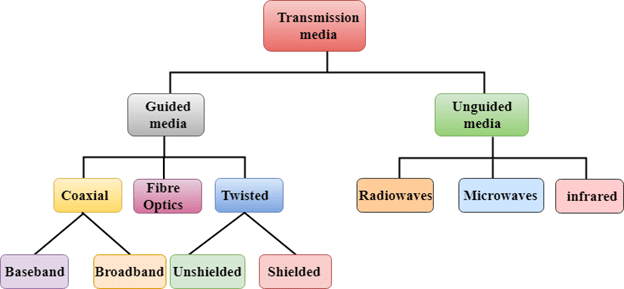
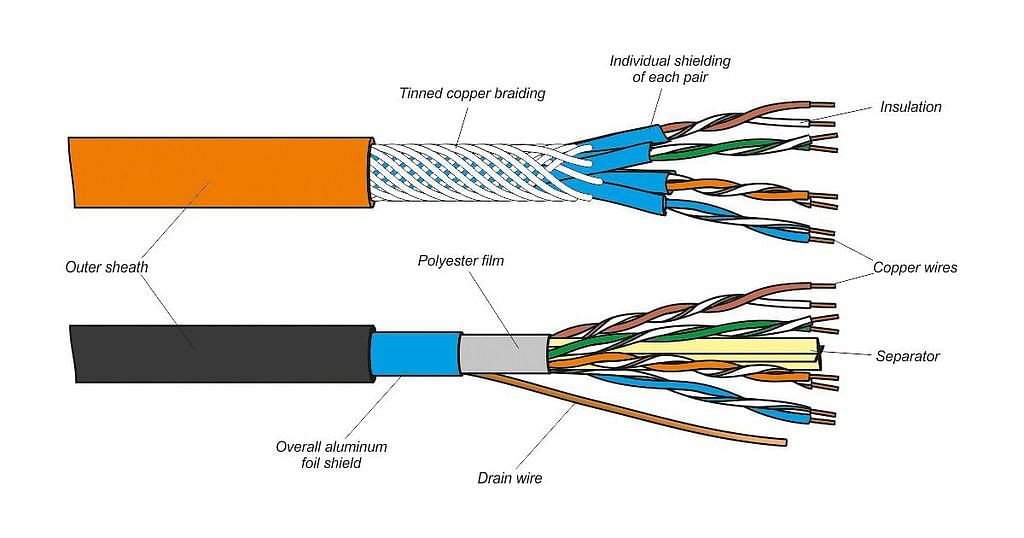
- Twisted pair cable: It consists of two identical 1 mm thick copper wires insulated and twisted together. The twisted-pair cables are twisted in order to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic induction.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
(i) It is easy to install and maintain.
(ii) It is very inexpensive
Disadvantages:
(i) It is incapable to carry a signal over long distances without the use of repeaters.
(ii) Due to low bandwidth, these are unsuitable for broadband applications. - Co-axial Cables: It consists of a solid wire core surrounded by one or more foil or braided wire shields, each separated from the other by some kind of plastic insulator. It is mostly used in the cable wires.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
(i) Data transmission rate is better than twisted-pair cables.
(ii) It provides a cheap means of transporting multi-channel television signals around metropolitan areas.
Disadvantages:
(i) Expensive than twisted-pair cables.
(ii) Difficult to manage and reconfigure. - Optical fiber: An optical fiber consists of thin glass fibers that can carry information in the form of visible light.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
(i) Transmit data over long distance with high security.
(ii) Data transmission speed is high
(iii) Provide better noise immunity
(iv) Bandwidth is up to 10 Gbps.
Disadvantages:
(i) Expensive as compared to other guided media.
(ii) Need special care while installation? - Infrared: The infrared light transmits data through the air and can propagate throughout a room, but will not penetrate walls. It is a secure medium of signal transmission.
The infrared transmission has become common in TV remotes, automotive garage doors, wireless speakers etc.
- Radio Wave: Radio Wave an electromagnetic wave with a wavelength between 0.5 cm and 30,000m. The transmission making use of radio frequencies is termed as
radio-wave transmission Radio waveAdvantages:
Radio waveAdvantages:
(i) Radio wave transmission offers mobility.
(ii) It is cheaper than laying cables and fibers.
(iii) It offers ease of communication over difficult terrain.
Disadvantages:
(i) Radio wave communication is insecure communication.
(ii) Radio wave propagation is susceptible to weather effects like rains, thunderstorms etc. - Microwave Wave: The Microwave transmission is a line of sight transmission. Microwave signals travel at a higher frequency than radio waves and are popularly used for transmitting data over long distances.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
(i) It is cheaper than laying cable or fiber.
(ii) It has the ability to communicate over oceans.
Disadvantages:
(i) Microwave communication is an insecure communication.
(ii) Signals from antenna may split up and transmitted in different way to different antenna which leads to reduce to signal strength.
(iii) Microwave propagation is susceptible to weather effects like rains, thunderstorms etc.
(iv) Bandwidth allocation is extremely limited in case of microwaves. - Satellite link: The satellite transmission is also a kind of line of sight transmission that is used to transmit signals throughout the world.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
(i) Area covered is quite large.
(ii) No line of sight restrictions such as natural mountains, tall building, towers etc.
(iii) Earth station which receives the signals can be fixed position or relatively mobile.
Disadvantages:-
(i) Very expensive as compared to other transmission mediums.
(ii) Installation is extremely complex.
(iii) Signals sent to the stations can be tampered by external sources
Network devices
- Modem: A MODEM (MOdulator DEModulator) is an electronic device that enables a computer to transmit data over telephone lines. There are two types of modems, namely, internal modem and external modem.
 Modem
Modem
- RJ45 connector: The RJ-45(Registered Jack) connectors are the plug-in devices used in the networking and telecommunications applications. They are used primarily for connecting LANs, particularly Ethernet.
- Ethernet Card: It is a hardware device that helps in connection of nodes within a network.
- Hub: A hub is a hardware device used to connect several computers together. Hubs can be either active or passive. Hubs usually can support 8, 12 or 24 RJ45 ports.
- Switch: A switch (switching hub) is a network device which is used to interconnect computers or devices on a network. It filters and forwards data packets across a network. The main difference between hub and switch is that hub replicates what it receives on one port onto all the other ports while switch keeps a record of the MAC addresses of the devices attached to it.
- Gateway: A gateway is a device that connects dissimilar networks.
- Repeater: A repeater is a network device that amplifies and restores signals for long distance transmission.
Network topologies and Types
- Topology: Topology refers to the way in which the workstations attached to the network are interconnected.
 Topologies
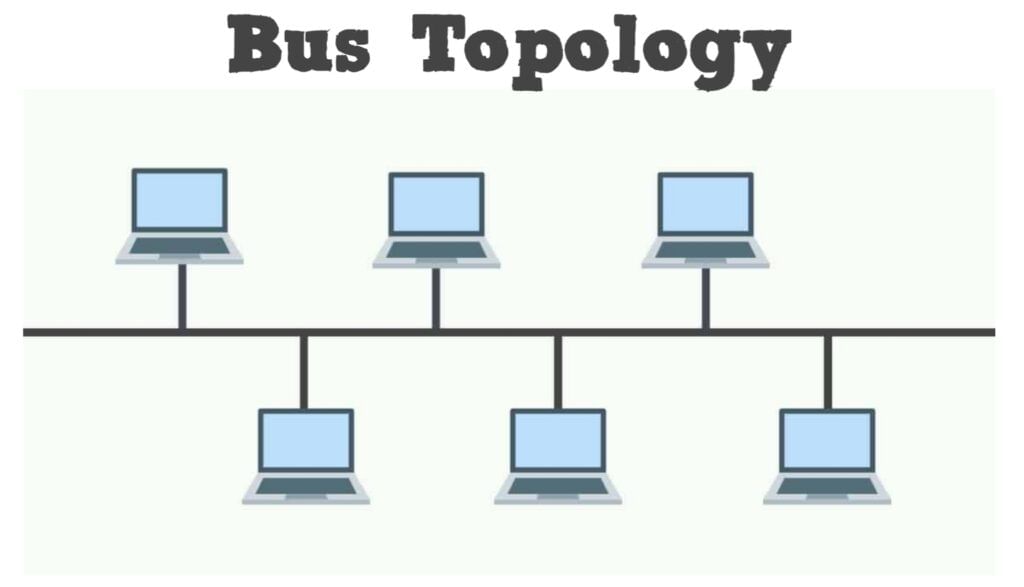
Topologies - The BUS Topology: The bus topology uses a common single cable to connect all the workstations. Each computer performs its task of sending messages without the help of the central server. However, only one workstation can transmit a message at a particular time in the bus topology.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
(i) Easy to connect and install.
(ii) Involves a low cost of installation time.
(iii) Can be easily extended.
Disadvantages:
(i) The entire network shuts down if there is a failure in the central cable.
(ii) Only a single message can travel at a particular time.
(iii) Difficult to troubleshoot an error. - The STAR Topology: A STAR topology is based on a central node which acts as a hub. A STAR topology is common in homes networks where all the computers connect to the single central computer using it as a hub.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
(i) Easy to troubleshoot
(ii) A single node failure does not affect the entire network.
(iii) Fault detection and removal of faulty parts is easier.
(iv) In case a workstation fails, the network is not affected.
Disadvantages:
(i) Difficult to expand.
(ii) Longer cable is required.
(iii) The cost of the hub and the longer cables makes it expensive over others.
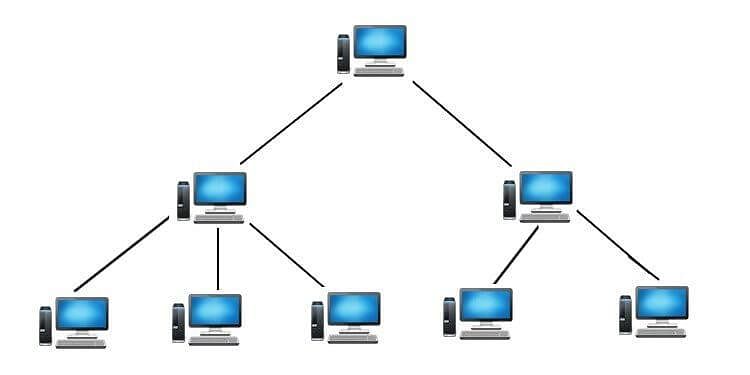
(iv) In case hub fails, the entire network fails. - The TREE Topology: The tree topology combines the characteristics of the linear bus and the star topologies. It consists of groups of star – configured workstations connected to a bus backbone cable.
 Tree TopologyAdvantages:
Tree TopologyAdvantages:
(i) Eliminates network congestion.
(ii) The network can be easily extended.
(iii) Faulty nodes can easily be isolated from the rest of the network.
Disadvantages:
(i) Uses large cable length.
(ii) Requires a large amount of hardware components and hence is expensive.
(iii) Installation and reconfiguration is very difficult.
Types of Networks
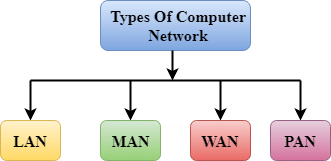
- LAN (Local Area Network): A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that is confined to a relatively small area. It is generally limited to a geographic area such as writing lab, school or building. It is generally privately owned networks over a distance not more than 5 Km.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): MAN is the networks cover a group of nearby corporate offices or a city and might be either private or public.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): These are the networks spread over large distances, say across countries or even continents through cabling or satellite uplinks are called WAN.
- PAN (Personal Area Network): A Personal Area Network is computer network organized around an individual person. It generally covers a range of less than 10 meters. Personal Area Networks can be constructed with cables or wirelessly.
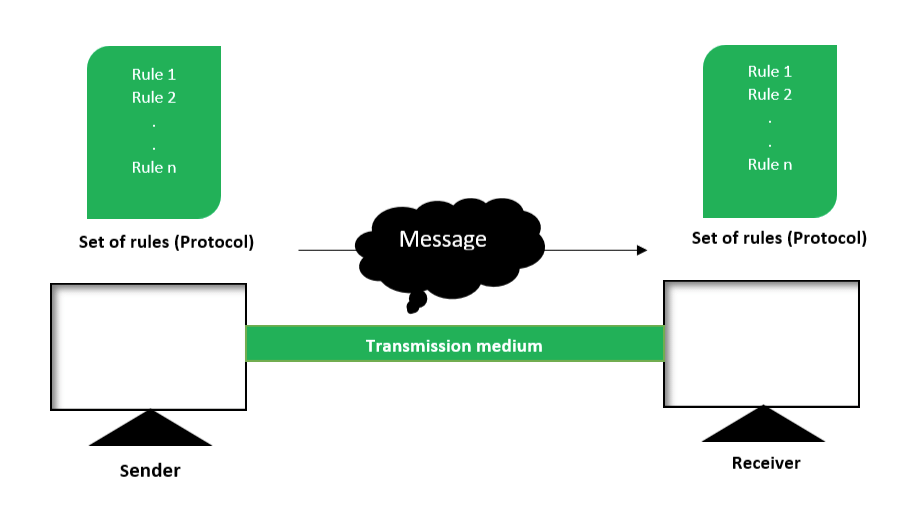
Network protocol
- A protocol means the rules that are applicable for a network.
- It defines the standardized format for data packets, techniques for detecting and correcting errors and so on.
- A protocol is a formal description of message formats and the rules that two or more machines must follow to exchange those messages.
- E.g. using library books.
Types of protocols are:
- HTTP
- FTP
- TCP/IP
- SLIP/PPP
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a communications protocol for the transfer of information on the intranet and the World Wide Web. HTTP is a request/response standard between a client and a server. A client is the end-user; the server is the web site.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is the simplest and most secure way to exchange files over the Internet.
The objectives of FTP are:- To promote sharing of files (computer programs and/or data).
- To encourage indirect or implicit use of remote computers.
- To shield a user from variations in file storage systems among different hosts.
- To transfer data reliably, and efficiently.
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol)
- TCP: is responsible for verifying the correct delivery of data from client to server. Data can be lost in the intermediate network. TCP adds support to detect errors or lost data and to trigger retransmission until the data is correctly and completely received.
- IP: is responsible for moving packet of data from node to node. IP forwards each packet based on a four byte destination address (the IP number). The Internet authorities assign ranges of numbers to different organizations. The organizations assign groups of their numbers to departments. IP operates on gateway machines that move data from department to organization to region and then around the world.
- Telnet: It is an older internet utility that lets us log on to remote computer system. It also facilitates for terminal emulation purpose. Terminal emulation means using a pc like a mainframe computer through networking.
Wireless/Mobile Computing
Wireless communication is simply data communication without the use of landlines. Mobile computing means that the computing device is not continuously connected to the base or central network. Mobile computing
Mobile computing
- GSM(Global System for Mobile communication): It is leading digital cellular system. In covered areas, cell phone users can buy one phone that will work any where the standard is supported. It uses narrowband TDMA, which allows eight simultaneous calls on the same radio frequency.
- CDMA(Code Division Multiple Access): It is a digital cellular technology that uses spreadspectrum techniques. CDMA does not assign a specific frequency to each user. Instead ,every channel uses the full available spectrum.
- WLL(Wireless in Local Loop) : WLL is a system that connects subscribers to the public switched telephone network using radio signals as a substitute for other connecting media.
- Email(Electronic Mail): Email is sending and receiving messages by computer.
- Chat: Online textual talk in real time is called Chatting.
- Video Conferencing: a two way video phone conversation among multiple participants is called video conferencing.
- SMS(Short Message Service): SMS is the transmission of short text messages to and from a mobile phone, fax machine and or IP address.
- 3G and EDGE: 3G is a specification for the third generation of mobile communication of mobile communication technology. 3G promises increased bandwidth, up to 384 Kbps when a device is stationary.
- EDGE(Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution) is a radio based high speed mobile data standard.
Network Security Concepts
- Viruses: Viruses are programs which replicate and attach to other programs in order to corrupt the executable codes. Virus enters the computer system through an external source and become destructive.
 Virus
Virus
- Worms: Worms are also self- replicating programs that do not create multiple copies of itself on one computer but propagate through the computer network. Worms log on to computer systems using the username and passwords and exploit the system.
- Trojan horse: Though it is a useful program, however, a cracker can use it to intrude the computer system in order to exploit the resources. Such a program can also enter into the computer through an email or free programs downloaded through the Internet.
- Spams: Unwanted e-mail (usually of a commercial nature sent out in bulk)
- Cookies: Cookies are the text messages sent by a web server to the web browser primarily for identifying the user.
- Firewall: A firewall is used to control the traffic between computer networks. It intercepts the packets between the computer networks and allows only authorized packets to pass.
- Cyber Law: Cyber law refers to all the legal and regulatory aspects of Internet and the World Wide Web.
- Cyber Crimes: Cyber crime involves the usage of the computer system and the computer network for criminal activity.
- Hacking: Hacking is an unauthorized access to computer in order to exploit the resources.
Web Services
- WWW: The World Wide Web or W3 or simply the Web is a collection of linked documents or pages, stored on millions of computers and distributed across the Internet.
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language): HTML is a computer language that describes the structure and behaviour of a web page. This language is used to create web pages.
- XML (eXtensible Markup Language): Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-language that helps to describe the markup language.
- HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol): A protocol to transfer hypertext requests and information between servers and browsers.
- Domain Names: A domain name is a unique name that identifies a particular website and represents the name of the server where the web pages reside.
- URL: The Uniform Resource Locator is a means to locate resources such as web pages on the Internet. URL is also a method to address the web pages on the Internet. There are two types of URL, namely, absolute URL and relative URL.
- Website: A collection of related web pages stored on a web server is known as a website.
- Web browser: A software application that enables to browse, search and collect information from the Web is known as Web browser.
- Web Servers: The web pages on the Internet are stored on the computers that are connected to the Internet. These computers are known as web servers.
- Web Hosting: Web Hosting or website hosting is the service to host, store and maintain the websites on the World Wide Web.
- Web Scripting: The process of creating and embedding scripts in a web page is known as Web
Scripting
 Types of Scripts
Types of Scripts
- Client-Side Scripts: - Client-side scripts supports interaction within a webpage. E.g. VB Script, JavaScript, PHP (PHP‟S Hypertext Preprocessor).
- Server-Side Scripts: - Server-side scripting supports execution at server–end. E.g. ASP, JSP, PHP
Open Source Terminologies
- Free Software: The S/W’s is freely accessible and can be freely used changed improved copied and distributed by all and payments are needed to make for free S/W.
- Open Source Software: S/w whose source code is available to the customer and it can be modified and redistributed without any limitation. OSS may come free of cost but nominal charges has to pay nominal charges (Support of S/W and development of S/W).
- FLOSS (Free Libre and Open Source Software): S/w which is free as well as open-source S/W. ( Free S/W + Open Source S/W).
- GNU (GNU’s Not Unix): GNU project emphasize on the freedom and its objective is to create a system compatible with UNIX but not identical with it.
- FSF (Free Software Foundation): FSF is a non–profit organization created for the purpose of the free s/w movement. Organization funded many s/w developers to write free software.
- OSI (Open Source Initiative): Open source software organization dedicated to cause of promoting open source software it specified the criteria of OSS and its source code is not freely available.
- W3C(World Wide Web Consortium): W3C is responsible for producing the software standards for World Wide Web.
- Proprietary Software: Proprietary Software is the s/w that is neither open nor freely available, normally the source code of the Proprietary Software is not available but further distribution and modification is possible by special permission by the supplier.
- Freeware: Freeware is the software freely available, which permit redistribution but not modification (and their source code is not available). Freeware is distributed in Binary Form (ready to run) without any licensing fees.
- Shareware: Software for which license fee is payable after some time limit, its source code is not available and modification to the software are not allowed.
- Localization: localization refers to the adaptation of language, content and design to reflect local cultural sensitivities.
Example: Software Localization: where messages that a program presents to the user need to be translated into various languages. - Internationalization: Opposite of localization.
FAQs on Ch 8 - Communication and Network Concepts, Computer Science, Class 12 Chapter Notes - COMPUTER SCIENCE for Class 12(XII) - CBSE & NCERT Curriculum
| 1. What is communication in the context of computer networks? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of computer network topologies? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of a network protocol? |  |
| 4. What is bandwidth in the context of computer networks? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a LAN and a WAN? |  |
|
9 docs
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|


 Advantages:
Advantages: Advantages:
Advantages: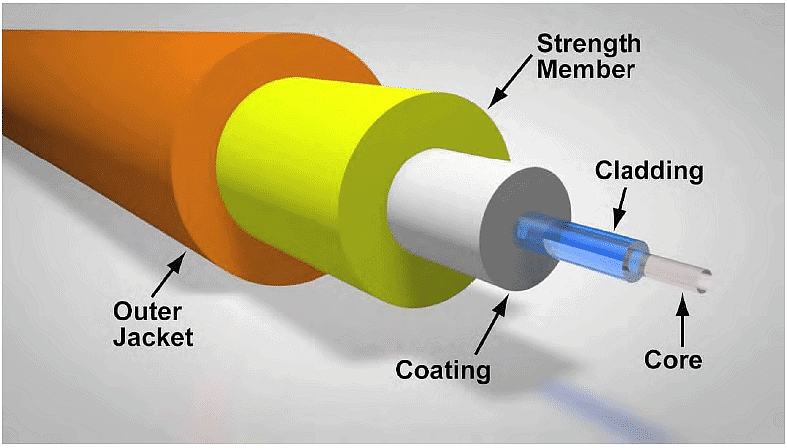 Advantages:
Advantages:
 Advantages:
Advantages: Advantages:
Advantages: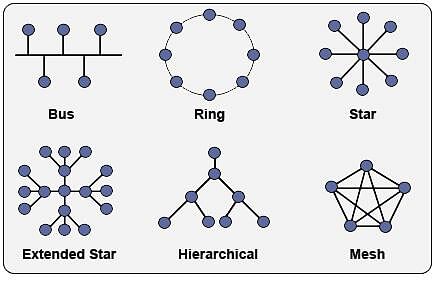
 Advantages:
Advantages: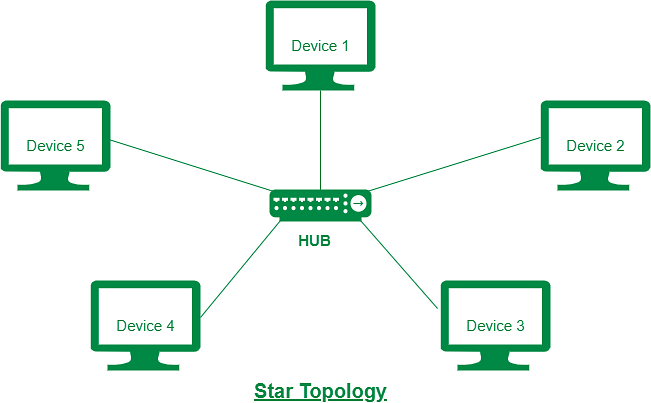 Advantages:
Advantages: