Staffing Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
- Staffing is the process of filling various positions in an organization.
- It involves workforce planning, recruitment, selection, training, development, promotion, compensation, and performance appraisal.
- Staffing is important as it recognizes the value of each individual employee.
- It is the managerial function of filling and maintaining positions in the organization structure.
- In a new enterprise, staffing follows planning and organizing functions.
- In an existing enterprise, staffing is a continuous process.
Importance of Staffing
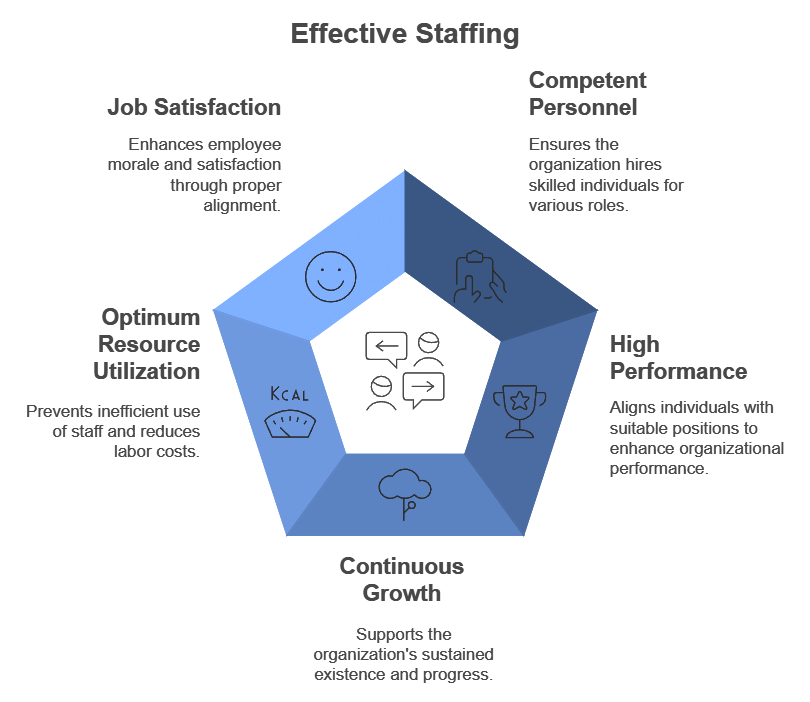
- Obtaining Competent Personnel: Effective staffing facilitates the identification and acquisition of skilled individuals for diverse job roles.
- High Performance: Optimal staffing leads to enhanced performance through the appropriate alignment of individuals with suitable job positions.
- Continuous growth: Effective staffing is crucial for the sustained existence and progress of the organization.
- Optimum utilization of human resources: Proper staffing prevents the inefficient utilization of staff and excessive labour expenses.
- Improves job satisfaction: Proper staffing enhances job satisfaction and boosts employee morale.
Staffing as a part of Human Resource Management
- Staffing is a critical function of Human Resource Management that all managers need to perform.
- It involves filling positions in the organization and ensuring they are occupied by qualified individuals.
- Staffing is closely linked to organizing, as positions are determined and then people are required to work in those positions.
- The staffing function deals with managing the human element of an organization, which is crucial for its success.
- Managers have the responsibility of selecting, training, motivating, and developing employees.
- In small organizations, managers may handle all responsibilities related to employees' salaries, welfare, and working conditions.
- As organizations grow, a separate Human Resource department is formed with specialists managing people.
- The size of the Human Resources department indicates the size of the business, with larger companies having specialists for each function within the department.
Human Resource Management involves a range of specialized activities and duties as follows:
- These include recruitment to find qualified individuals, job analysis to prepare job descriptions, and developing compensation and incentive plans.
- It also involves training and development for employee performance and career growth.
- Maintaining labour relations, handling grievances and complaints, and providing social security and welfare for employees are also important responsibilities.
- Lastly, HR is responsible for defending the company in legal matters and avoiding legal complications.
Evolution of Human Resource Management
- The concept of human resource management (HRM) has replaced traditional labour welfare and personnel management.
- The emergence of trade unions created a need for a link between owners and workers, leading to the role of a labour welfare officer.
- The labour welfare officer's role was limited to basic welfare activities and was not highly regarded by workers or owners.
- The introduction of the factory system led to the need for personnel officers who were responsible for recruitment, selection, and placement of employees.
- The human relations approach recognized the importance of the human factor in an organization's success.
- Technological developments required new skill development and employee training, leading to the recognition of people as a valuable resource.
- The increased scope of work led to the replacement of personnel managers with human resource managers.
- Staffing is an inherent part of HRM, involving the practice of finding, evaluating, and establishing relationships with people for a purpose.
- Staffing is both a function of management (like planning, organizing, directing, and controlling) and a distinct functional area of management (like marketing and financial management).
- Staffing is referred to as both a line and staff activity, meaning it is an essential function of managers and an advisory role played by the HR department.
Staffing Process
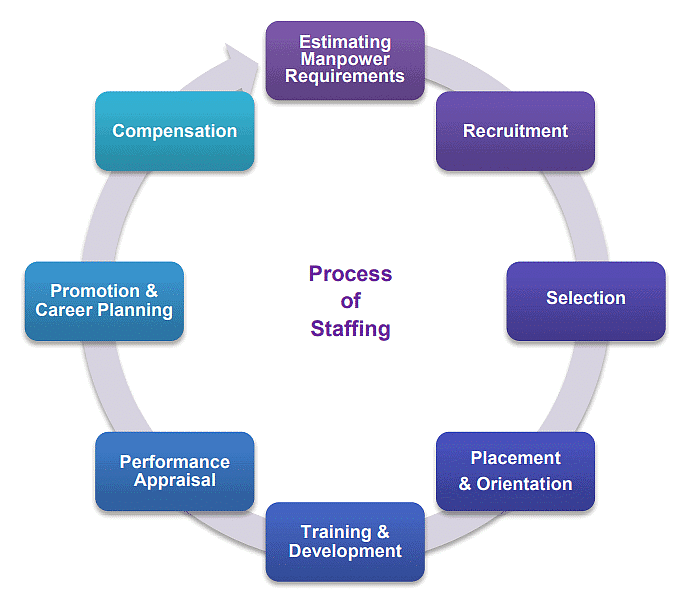
- Estimating the Manpower Requirement: It involves the following:
(a) Making an inventory of current human resources regarding qualification, training & skills
(b) Assessing future human resource needs of all departments.
(c) Developing a program to provide human resources. Job Analysis is an intensive way of finding details related to all jobs. - Recruitment: It refers to identifying the sources of manpower availability and making efforts to secure applicants for the various job positions in an organization.
- Selection: It is the process of choosing and appointing the right candidates for various organizational jobs through various exams, tests &interviews.
- Placement and Orientation: When a new employee reports for duty, he is to be placed on the job for which he is best suited. Placement is very important process as it can ensure “Right person for right job”. Orientation/Induction is concerned with the process of introducing a new employee to the organization. The new employees are familiarized with their units, supervisors and fellow employees. They are also to be informed about working hours, procedure for availing leave, medical facilities, history and geography of organization and rules/regulations relating to their wages etc.
- Training and Development: Systematic training helps in increasing the skills and knowledge of employees in doing their jobs through various methods. Development involves growth of an employee in all respects. It is the process by which the employees acquire skills and competence to do their present jobs and increase their capabilities for higher jobs in future.
- Performance Appraisal: It is concerned with rating or evaluating the performance of employees. Transfers and promotions of the staff are based on performance appraisal.
- Promotion and Career Planning: Organizations need to address career development and promotional opportunities for their employees. Managers should design activities that help employees grow and reach their full potential. Promotions involve being placed in positions of increased responsibility, often resulting in higher pay and job satisfaction.
- Compensation: Organizations must establish wage and salary plans for their employees. Different pay plans can be prepared based on the value of the job. Compensation refers to all forms of pay or rewards given to employees, including direct financial payments (wages, salaries, incentives) and indirect payments (insurance, vacations). Direct financial payments can be time-based (salary/wages paid regularly) or performance-based (pay based on productivity). Various methods can be used to calculate compensation under incentive plans. Pay plans can be a combination of time-based pay and performance-based incentives. Other factors that influence pay plan design include legal, union, company policy, and equity considerations.
Recruitment
Recruitment may be defined as the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization.
Sources of Recruitment
- Recruitment aims to attract potential employees who have the necessary qualifications and characteristics for the available jobs.
- The process of recruitment occurs before the selection of the right candidate for the organization.
- The process of recruitment includes identifying labor sources, evaluating their validity, selecting appropriate sources, and requesting applications from prospective candidates for job openings.
- The two main sources of recruitment are internal (filling positions from within the organization) and external (hiring candidates from outside the organization).
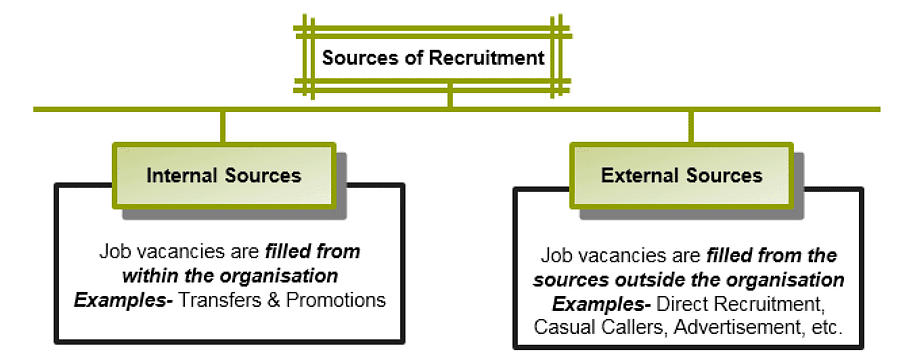
Internal Sources of Recruitment
Internal sources refer to inviting candidates from within the organization. The following are important sources of internal recruitment:
- Transfers: Transfers involve moving an employee from one job, department, or shift to another without changing their responsibilities or status. Transfers can result in changes in duties, responsibilities, and working conditions, but not necessarily salary. Transfers can be used to fill vacancies in over-staffed departments or branches. Job transfers can help avoid termination and resolve individual problems and grievances. Employees being transferred should be capable of performing their new job. Transfers can also be used for employee training and learning different jobs.
- Promotions: Promotions involve promoting employees from lower positions to higher positions. Promotions lead to higher responsibilities, facilities, status, and pay for the employee. Promotions improve employee motivation, loyalty, and satisfaction. Promotions can have a psychological impact, as they can lead to a chain of promotions at lower levels in the organization.
Advantages of Internal Sources Recruitment:
- Motivation and Performance Improvement: Promotions and internal transfers motivate employees to improve their performance. This can lead to a chain of promotions at lower levels, encouraging employees to work with commitment and loyalty.
- Simplified Selection and Placement: Candidates already working in the organization can be evaluated accurately and economically. It is a more reliable way of recruitment since the candidates are already known to the organization.
- Training and Development: Transfers serve as a tool for training employees and preparing them for higher jobs. People recruited from within the organization do not require induction training.
- Workforce Management: Transfers allow for the shifting of the workforce from surplus departments to those with staff shortages.
- Cost-effectiveness: Filling jobs internally is cheaper compared to recruiting candidates from external sources.

Limitation of Internal Sources
- Reduced scope for fresh talent: When vacancies are filled through internal promotions, the organization may miss out on the opportunity to bring in new and diverse perspectives, limiting the infusion of fresh talent into the company.
- Potential employee lethargy: If employees are guaranteed time-bound promotions through internal recruitment, they may become complacent and lack motivation to perform at their best.
- Incompatibility with new enterprises: Internal sources of recruitment may not be suitable for new organizations that require a significant number of new hires to establish their workforce.
- Impaired spirit of competition: Relying solely on internal recruitment may hinder healthy competition among employees, as they may feel less motivated to compete for promotions or advancements.
- Reduced productivity due to frequent transfers: Frequent transfers of employees within the organization can disrupt workflow and reduce productivity, as employees may need time to adjust to new roles and responsibilities.
External Sources of Recruitment
When candidates from outside the organization are invited to fill the vacant job position, then it is known as external recruitment. The common methods of external sources of recruitment are:
- Direct Recruitment:
1. Notice placed on notice-board specifying job details
2. Job-seekers assemble on specified dates and selection is done on the spot
3. Suitable for filling casual vacancies of unskilled or semi-skilled jobs - Casual Callers:
1. Reputed organizations maintain a database of unsolicited applicants
2. List of job-seekers screened to fill vacancies as they arise
3. Reduces cost of recruiting workforce - Advertisement:
1. Used when wider choice is required
2. Senior positions filled through this method
3. Provide more information about the organization and job
4. Brings in a flood of response, which may include unsuitable candidates - Employment Exchange:
1. Good source of recruitment for unskilled and skilled operative jobs
2. Compulsory notification of vacancies required by law
3. Helps match personnel demand and supply - Placement Agencies and Management Consultants:
1. Private agencies and professional bodies assist in technical and professional areas
2. Provide nationwide service in matching personnel demand and supply
3. Charge fee for services, useful for extensive screening
4. Management consultancy firms assist in recruiting middle and top-level executives - Campus Recruitment:
1. Colleges and management institutes are popular sources for technical, professional, and managerial jobs
2. Recruitment from educational institutions with well-established practice - Recommendations of Employees:
1. Applicants introduced by current employees or their friends and relatives
2. Known background of applicants, preliminary screening takes place - Labour Contractors:
1. Maintain close contact with labourers and provide unskilled workers at short notice
2. Workers recruited through labour contractors who are employees of the organization - Advertising on Television:
1. Telecasting vacant posts over television gaining importance
2. Detailed job requirements and organization profile publicized - Web Publishing:
1. The Internet is becoming a common source of recruitment
2. Specific websites provide information about job seekers and job openings
3. Visited by prospective employees and organizations searching for suitable candidates.
Merits of External Sources
- Qualified Personnel: By using external sources of recruitment the management can attract qualified and trained people to apply for the vacant jobs in the organization.
- Wider Choice: The management has a wider choice in selecting the people for employment.
- Fresh Talent: It provides wider choices and brings new blood to the organization.
- Competitive Spirit: If a company taps external sources, the staff will have to compete with the outsiders.

Limitations of External Sources of Recruitment:
- Dissatisfaction among existing employees: Recruitment from outside may cause dissatisfaction among the employees. They may feel that their chances of promotion are reduced.
- Costly process: A lot of money has to be spent on advertisements therefore this is a costly process.
- Lengthy Process: It takes more time than internal sources of recruitment.
Selection
Selection is the process of choosing from among the candidates from within the organization or from outside the most suitable person for the current position or for the future position.
Process of Selection
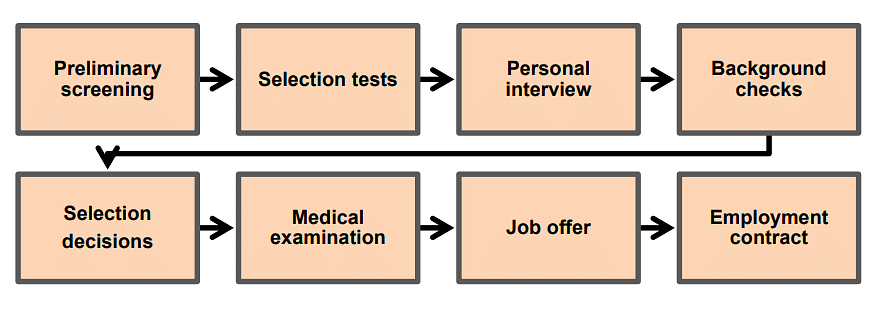
The successive stages in the selection process are:
1. Preliminary Screening: After applications have been received, they are properly checked as regarding qualification etc. by the screening committee. A list of candidates to be called for employment tests is made and unsuitable candidates are rejected altogether.
2. Selection Tests: These tests include:
(a) Psychological tests are based on the assumption that human behaviour at work can be predicted by giving various tests like aptitude, personality tests, etc.
(b) Employment test for judging the applicant’s suitability for the job.
3. Employment Interviews: The main purpose of interview is:
(a) to find out the suitability of the candidates.
(b) to seek more information about the candidate.
(c) to give the candidate an accurate picture of the job with details of terms and conditions.
4. Reference Checks: Prior to final selection, the prospective employer makes an investigation of the references supplied by the applicant. He undertakes a thorough search into the candidate’s family background, past employment, education, police records etc.
5. Selection Decisions: A list of candidates who clear the employment tests, interviews and reference checks is prepared and then the selected candidates are listed in order of merit.
6. Medical/Physical Examination: A qualified medical expert appointed by the organisation should certify whether the candidate is physically fit to the requirements of a specific job. A proper physical exam will ensure a higher standard of health & physical fitness of employees thereby reducing absenteeism.
7. Job Offer: After a candidate has cleared all hurdles in the selection procedure, he is formally appointed by issuing him an Appointment Letter. The broad terms and conditions, and pay scale are integral parts of the Appointment Letter.
8. Contract of Employment: After getting the job offer, the candidate has to give his acceptance. After acceptance, both employer and employee will sign a contract of employment which contains terms & conditions, pay scale, leave rules, hours of work, mode of termination of employment etc.
Training and Development
Training is the act of increasing the knowledge and technical skills of an employee to do a particular job efficiently. Both existing employees and new employees get acquainted with their jobs and this increases job-related skills.
Benefits to the Organization:
1. It enhances employees' productivity and quality.
2. Training increases employees' morale.
3. Employees get new technical knowledge.
4. Efficient use of machines.
Benefits to the Employee:
1. Improved skills and knowledge of employees.
2. Increased performance by the individual helps him to earn more.
3. Less accidents.
4. Training increases the satisfaction and morale of the employee.
 Benefits of Training
Benefits of Training
Training Methods
On-the-Job Method
It refers to the methods that are applied at the workplace, where the employee is working. It means learning while doing.
The following are the methods of On-the-job training:
- Apprenticeship Training: Under this, the trainee is placed under the supervision of an experienced person (master worker) who imparts him necessary skills and regulates his performance. The trainee is given a stipend while learning so that he/she can enjoy the “earn while you learn” scheme.
- Internship Training: Under this method, an educational institute enters into an agreement with industrial enterprises to provide practical knowledge to its students by sending them to business organizations to gain practical experience.
- Induction training is a type of training given to help a new employee settle down quickly into the job by becoming familiar with the people, the surroundings, the job and the business. The duration of such type of training may be from a few hours to a few days. The induction provides a good opportunity to socialize and brief the newcomer on the company’s overall strategy, performance standards etc. If carefully done, it saves time and cost (in terms of effectiveness or efficiency etc.)
Off-the-Job Methods
Off-the-job training refers to the training where the subordinates learn by doing at a place away from the workplace. It includes:
- Classroom Lectures/ Conference: It is a method of training where information is conveyed through lectures for conferences.
- Films: It is a method of training where important information or skills are demonstrated using films, televisions, videos or presentations.
- Case study: It is a method of training where actual work situations of the past are discussed to identify problems, analyse their causes, and develop alternative solutions to solve problems
- Computer Modelling: It is a method of training where the actual work environment is imitated by programming a computer.
- Vestibule Training: It is a method of training where a duplicate work environment called a 'vestibule" is created to train employees with technical and operating skills.
- Programmed instructions: It is a method of training where specific skills or knowledge are broken into units and arranged in a logical and sequential learning package.
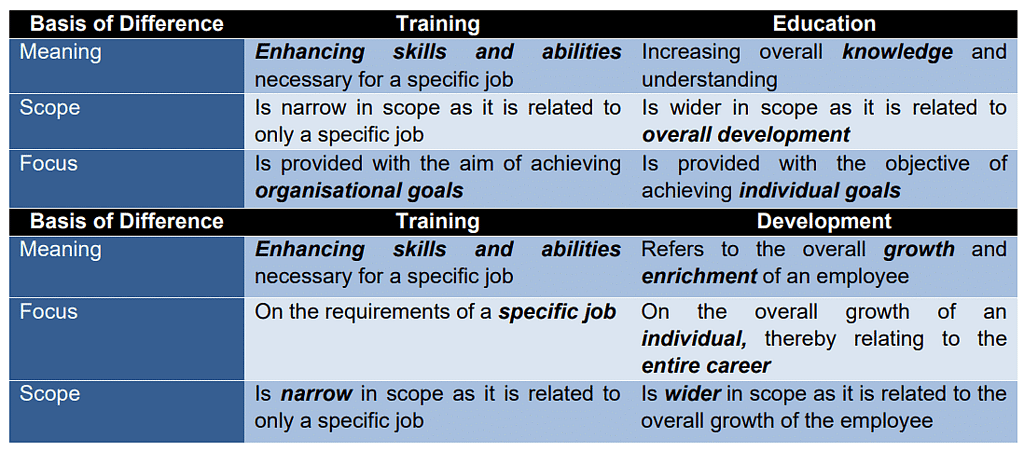
Training, Education and Development
|
53 videos|208 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Staffing Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the significance of staffing in an organization? |  |
| 2. What are the key steps in the staffing process? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using internal sources for recruitment? |  |
| 4. What are some effective training methods used in organizations? |  |
| 5. How does training, education, and development contribute to employee performance? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|


















