- If grains aren't stored correctly, they can get ruined by moisture, bugs, rats, and germs.
- Right after harvesting, grains still have a lot of moisture. If they're stored without drying first, they can spoil or become infested with pests, making them unusable.
- To prevent this, grains are spread out in the sun to dry before being stored. This helps keep away insects, bacteria, and fungi.
- Farmers usually store grains in jute bags or metal bins.
- For bigger amounts, they use large storage buildings called silos, which protect the grains from pests like rats and insects.
- At home, dried neem leaves can be used to help keep food grains fresh. For very large quantities, special chemical treatments are used to keep the grains safe from pests and germs.
- Proper storage keeps the grains in good condition until they're needed!
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 1
Introduction
During the summer vacation, Paheli and Boojho visited their uncle, who is a farmer.- They observed various farming tools like khurpi, sickle, shovel, and plough in the fields.
- This experience made them curious about agriculture and the tools used in it.
- To provide food for a large population, it is essential to ensure regular production, proper management, and distribution of food.
 Sickle, Khurpi & Plough
Sickle, Khurpi & Plough
Agricultural Practices
- Before 10,000 B.C.E., people were nomadic, wandering in groups in search of food and shelter.
- They consumed raw fruits and vegetables and relied on hunting animals for food.
- Eventually, people learned to cultivate land and produce crops like rice and wheat, marking the beginning of agriculture.
What is a Crop?
Plants of the same kind that are grown and cultivated as a source of food in a large cultivable land is called a crop.
 Wheat Crop
Wheat Crop
- For example, if you see a field full of wheat plants, that's a wheat crop.
- Crops can be different types like cereals (e.g., wheat, rice), vegetables (e.g., carrots, beans), and fruits (e.g., apples, bananas).
Types of Crops
Different types of crops like cereals, vegetables and fruits etc., can be classified on the basis of the season in which they grow.
 Types of Crops
Types of Crops
- India is a vast country. Here climatic conditions like temperature, humidity and rainfall vary from one region to another. Hence, a rich variety of crops can be grown in different parts of India.
- Despite this diversity, two broad cropping patterns can be identified: Kharif Crops & Rabi Crops
1. Kharif Crops
Plants that are planted during the rainy season are called Kharif crops.
 Kharif Crops
Kharif Crops
- The rainy season in India is generally from June to September.
- The rain provides them with the necessary moisture for growth.
- Examples: Paddy, Maize, Soybean, Groundnut, Cotton, etc.
Crops that are grown in the winter season are called rabi crops.
 Rabi Crops
Rabi Crops
- The time period for Rabi crops is generally from October to March.
- The cooler temperatures and gentle sunlight create just the right conditions for these crops to grow.
- Examples: Wheat, Gram, Pea, Mustard and Linseed
Question: What is the difference between Kharif crops and Rabi crops?
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:Listed below are the differences between Kharif & Rabi Crops
Basic Practices of Crop Production
The several activities undertaken by the farmers for the cultivation of crops over a period of time are referred to as agricultural practiceswhich are listed below:
1. Preparation of soil
2. Sowing
3. Adding manure and fertilisers
4. Irrigation
5. Protecting from weeds
6. Harvesting
7. Storage
1. Preparation of Soil
Thepreparation of soil is the first and most important step before growing a crop. Turning and loosening the soil helps the roots penetrate deeper and allows them to breathe easily.

Importance of Loosening and Turning Soil
- Loosened soil allows plant roots to penetrate deeper and breathe easily, even at greater depths.
- It promotes the growth of earthworms and microbes, which are beneficial to farmers as they help further loosen the soil and add humus (organic matter).
- Soil contains minerals, water, air, and living organisms that support plant growth.
- Decomposed plants and animals release nutrients back into the soil, which are absorbed by plants.
- Only a few centimetres of the top layer of soil support plant growth, so turning and loosening the soil brings nutrient-rich soil to the surface for plants to use.
 Levelling of soil
Levelling of soil
Tilling or Ploughing
- The process of loosening and turning the soil is called tilling or ploughing.
- Ploughs, made of wood or iron, are used for this purpose. If the soil is dry, it may need to be watered before ploughing.
- After ploughing, the field may have large soil clumps called crumbs, which must be broken down.
- Levelling the soil helps with sowing and irrigation and is done with a leveller.
Before sowing, it is necessary to break soil clumps using various tools. Agricultural Implements
Some commonly used implements include:
1. Plough
2. Hoe
3. Cultivator
Plough
A plough is a device that is used by farmers for different purposes such as adding fertilizers, tilling, and loosening the soil.

- Used since ancient times for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers, removing weeds, and turning the soil.
- Made of wood or iron, it has a ploughshare (a strong triangular iron strip) and a ploughshaft (a long log of wood).
- Operated by a pair of bulls or other animals like horses and camels.
Hoe
The hoe is like a gardener’s multi-tool. It’s simple but super useful.
- A simple tool used for removing weeds and loosening the soil.
- It has a long rod of wood or iron, with a broad, bent iron plate fixed at one end for easy soil management.

Cultivator
Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor-driven cultivator. The use of cultivator saves labour and time.
 Cultivator Driven by Tractor
Cultivator Driven by Tractor
2. Sowing
Sowing is the most important part of crop production. Before sowing, good-quality seeds are selected. These are clean and healthy seeds of a good variety.
Selection of Seeds
- Farmers prefer to use seeds that give a high yield.
Seed Test: Using water to test seeds is a smart way to separate good seeds from damaged ones. Healthy seeds sink, while damaged seeds float. This helps farmers ensure that only the best seeds are planted.
Tools for Sowing
Before sowing, one of the important tasks is to know about the tools used for sowing seeds:
(a) Traditional Tool: It is the tool-shapedliked funnel used traditionally for sowing seeds. The seeds are filled into the funnel, passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends. These ends pierce the soil and place seeds there.
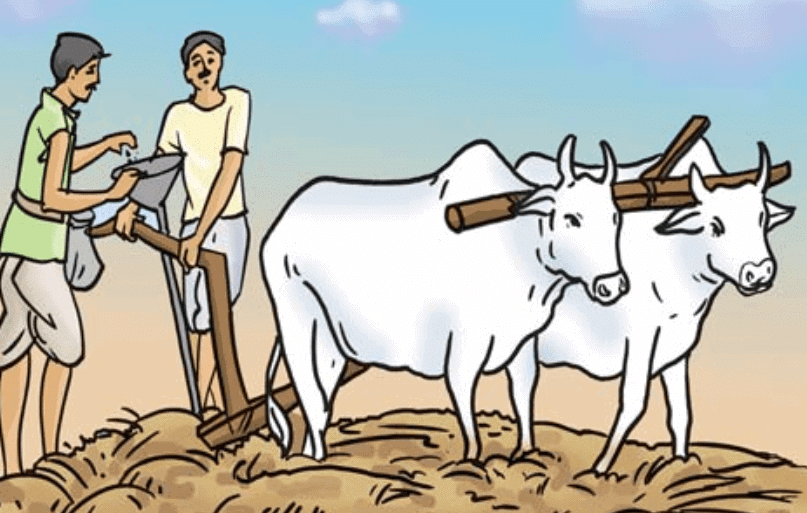 Traditional Tool
Traditional Tool
b) Seed Drill: Nowadays, the seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This tool sows the seeds uniformlyat proper distances and depths. It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing and prevents damage caused by birds. It saves time and labour.
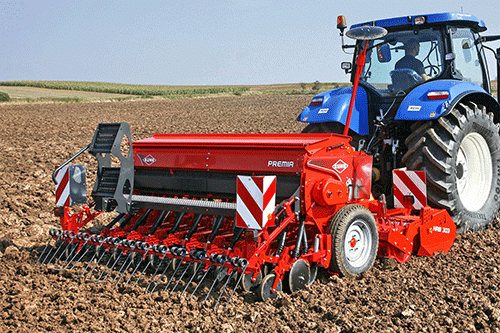 Seed Drill
Seed Drill
While sowing seeds, it is essential to make sure that:
 (a)Seeds are healthy and of high quality.
(a)Seeds are healthy and of high quality.
(b)They are planted at the correct distance from each other so that they can get proper light, water, and nutrients from the soil.
(c) They must be sown deep enough to protect them from animals and birds (which might eat them) and wind (which might blow them away) but not so deep that they may not get enough air to germinate.
3. Adding Manure and Fertilizers
Manure and fertilisers are essential substances added to soil to provide nutrients for healthy plant growth.
 Manure
Manure
Role of Nutrients in Soil
- Soil provides mineral nutrients to crops, which are necessary for plant growth.
- Continuous farming without leaving the field fallow depletes these nutrients, making the soil poor.
- To replenish soil nutrients, farmers add manure, a process known as manuring. Without proper manuring, plants become weak.
Manure
- Manure is an organic substance made from decomposed plant or animal waste.
- The decomposition process is carried out by microorganisms.
- Farmers create manure by allowing plant and animal waste to decompose in open pits.
Adding Fertilizers to soil :
- Fertilisers are chemical substances rich in specific nutrients and are produced in factories.
- Examples include urea, ammonium sulphate, super phosphate, potash, and NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium).
- Fertilisers help increase crop yields for crops like wheat, paddy, and maize.
- However, overuse of fertilisers can reduce soil fertility and cause water pollution.
Manure has several advantages over fertilisers, including:
- Improving water retention of the soil.
- Making the soil porous, allowing better air exchange.
- Increasing the population of beneficial microbes.
- Enhancing the texture of the soil.
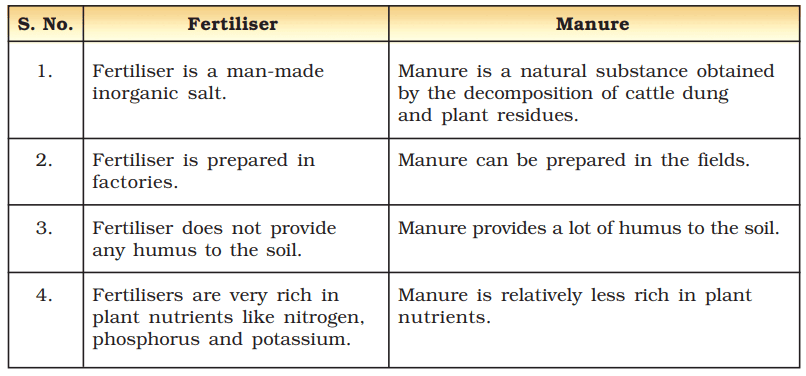
Question: What is the difference between Manure and Fertilizer?
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Listed below are the differences between Manure & Fertilizer
Crop Rotation:
- Another method to replenish soil nutrients is crop rotation, which involves growing different crops alternately.
- For example, earlier farmers in northern India grew legumes as fodder in one season and wheat in the next. This practice enriched the soil with nitrogen.
4. Irrigation
The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is known as irrigation.
- Irrigation depends on factors like crop type, soil type, and season.
- In summer, irrigation frequency is higher due to increased evaporation.
Importance of Water for Plants
- Absorption of nutrients: Water allows plants to absorb minerals and fertilisers through their roots.
- Seed germination: Seeds cannot germinate in dry conditions.

- Transportation of nutrients: Water helps transport nutrients to various parts of the plant.
- Protection: Water protects crops from frost and hot air currents.
- Soil moisture: Regular watering maintains the soil's moisture, promoting healthy crop growth.
Sources of Irrigation:
Water for irrigation is obtained from various natural and man-made sources, including:
- Wells
- Tubewells
- Ponds
- Lakes
- Rivers
- Dams
- Canals
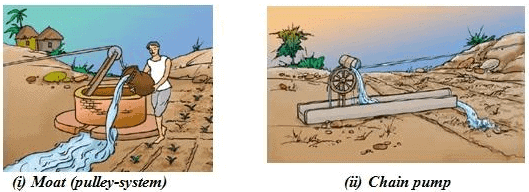
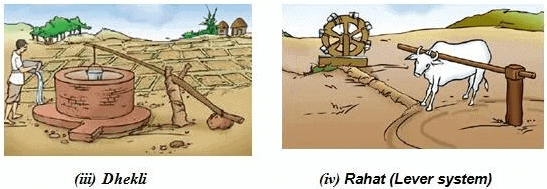
Traditional Methods of Irrigation
Traditional irrigation methods involve lifting water from wells, lakes, and canals using simple mechanisms. These methods are economical but less efficient and include:
- Moat (Pulley-system): A pulley system to draw water.
- Chain Pump: A rotating chain with buckets to lift water.
- Dhekli: A lever system to draw water manually.
- Rahat (Lever system): A lever-operated water lifting system.
These methods often rely on human or animal labor.
Modern Methods of Irrigation
Modern irrigation methods aim to conserve water and increase efficiency.
(i) Sprinkler System
- Ideal for uneven land with limited water availability.
- Perpendicular pipes with rotating nozzles are connected to a main pipeline.
- Water is sprayed over crops through rotating nozzles, simulating rainfall.
- Widely used in lawns, coffee plantations, and other crops.
 Sprinkler System
Sprinkler System
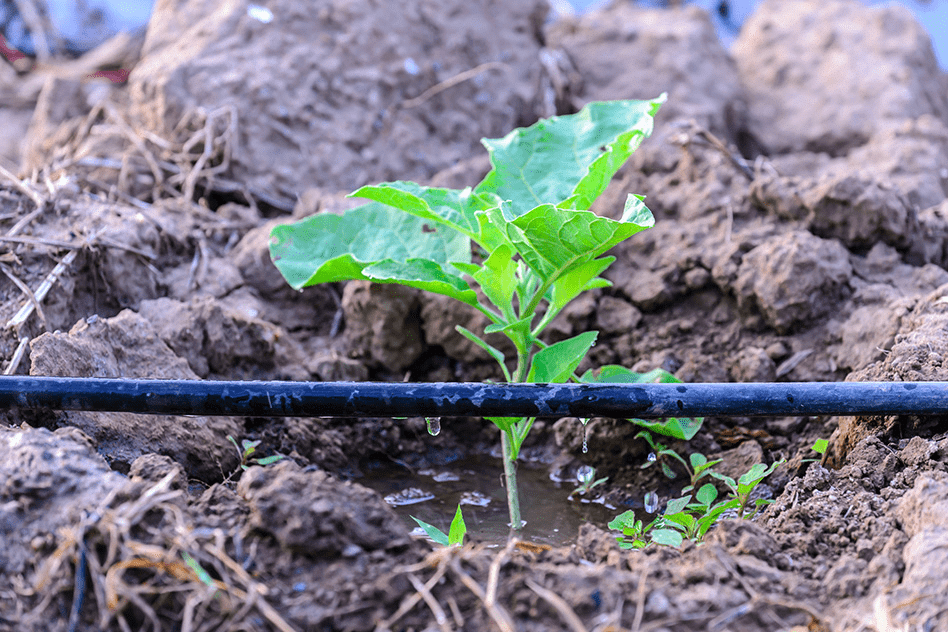
(ii) Drip System
- Water is delivered drop by drop directly to the plant's roots.
- This method is best suited for fruit plants, gardens, and trees.
- It conserves water and is particularly effective in water-scarce regions.
 Drip System
Drip System
5. Protection from Weeds
In a crop field, many unwanted plants, known as weeds, often grow along with the main crops. These weeds are undesirable as they compete with the crop for essential resources like water, nutrients, space, and light, hindering the growth and yield of the crop.
What are Weeds?
- Weeds are unwanted plants that grow alongside crop plants in a field.
- They are not purposely planted and compete with crops for resources, affecting crop growth and yield.
- Some weeds can interfere with harvesting and may even be poisonous to animals and humans
Weeding (Removal of Weeds)
- Weeding is the process of removing weeds from the crop fields.
- It is important to prevent weeds from competing with crops for essential nutrients, water, space, and light.
- Best time to remove weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds
Methods of Weed Control
To keep crops healthy, farmers need to remove weeds, a process known as weeding.
There are a few ways to do this:
(I) Tilling
- Tilling before sowing helps in uprooting and killing weeds.
- The uprooted weeds dry up and mix with the soil, adding organic matter.

(ii) Manual Removal
- Physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground is a common practice.
- This is done using tools like a khurpi or a seed drill.
(iii) Use of Weedicides
- Weedicides are chemical substances used to kill weeds.
- Common weedicides include 2,4-D, which is diluted with water and sprayed on the fields.
- These chemicals do not harm the crops but specifically target weeds.
- Weedicides are usually sprayed during the vegetative growth phase of weeds, before they flower and produce seeds.
 Spraying Weedicide
Spraying Weedicide
Safety Measures during Weedicide Application
- Spraying weedicides can be harmful to farmers' health.
- Farmers should take precautions like covering their nose and mouth with a cloth during the application to avoid inhaling harmful chemicals.
6. Harvesting
Cutting down a crop once it has reached maturityor once the crop has ripenedis called Harvesting.
- Harvesting refers to the process of cutting or pulling out the mature crops.
- The crops are either pulled out or cut close to the ground.
- For cereal crops, it typically takes 3 to 4 months to reach maturity.
Methods of Harvesting
- Manual Harvesting: Done using a sickle (a curved blade used for cutting crops).
- Machine Harvesting: Done using a machine called a harvester.
- Winnowing:Farmers with small holdings of land do the separation of grain and chaff by winnowing
Winnowing is a process to separate grain from chaff by tossing the mixture into the air, where the wind blows away the lighter chaff, leaving the heavier grains to fall back down.
 Winnowing
Winnowing
Threshing
- Threshing is the process of separating grain seeds from the chaff (outer husks).
- It can be done using a machine called a combine, which acts as both a harvester and thresher.
A combine machine is a combination of a thresher and a harvester.
 Combine machine
Combine machine
7. Storage
Storing harvested grains properly is really important to keep them fresh and safe.
Question: What are Granaries?
 View Answer
View AnswerGranaries are the place where freshly obtained food grains are stored.
 Granary
Granary
Food from Animals
- Food comes from many sources, and it's not just plants that provide it. For example, people living near the coast often eat fish (cod liver oil from fish which is rich in vitamin D) as a big part of their meals.
- Animals also play a big role in providing us with food, and they need proper care too. When we take care of animals by giving them good food, shelter, and attention, it's called animal husbandry.
Animal husbandry is like farming, but for animals. It involves making sure they are healthy and well-cared for, so they can provide us with things like milk, eggs, and meat. Just like crops, animals need the right conditions to thrive!
 Animal Husbandary
Animal HusbandaryFrequently Asked Questions
Q.1. What do you mean by the term crop? Explain briefly the types of crops.
Ans:Crop is the term used to describe a plant that is grown in a field on a large scale. For example, cereal crops, pulses, and fruit crops.
- The crops grown in India can be classified as kharif and rabi.
- Kharif crops are sown in the rainy season by June/July and are harvested by September/October.
- Thus, they are also known as summer season crops. For example, rice, maize, etc.
- Rabi crops are sown in the winter season in October or November and are harvested by March/April. Thus, they are also called winter season crops. For example, mustard, wheat, potato, etc.
Q.2. What is irrigation? Name the two main methods of irrigation and define them briefly.
Ans:The artificial method of watering the plants for assisting in the growth of the plants is called irrigation. The two main methods of irrigation are:
- Traditional method:The traditional method of irrigation is very less expensive and they often lead to wastage of water. The traditional method of irrigation involves a chain pump, dhekli, moat (the pulley system), and rahat (lever system).
- Modern method:Modern methods of irrigation are more inclined towards the use of diesel, bio¬gas, solar energy, and electricity for lifting water.
- The two most important modern systems of irrigation are: Sprinkler irrigation system & Drip irrigation system
Q.3. Write a short note on the terms:
Ans:
- Storage: Storage of produce is an important task. If the crop grains are to be kept for a longer time, they should be safe from moisture, insects, rats, and microorganisms. Before storing, the grains are properly dried in the sun to reduce the moisture in them. This prevents the attack by insect pests, bacteria, and fungi. Grains are stored by farmers in jute bags or metallic bins. However, large-scale storage of grains is done in silos and granaries to protect them from pests like rats and insects.
- Harvesting: After the maturation of crop, harvesting is an important task. In harvesting, crops are pulled out or cut close to the ground. It usually takes 3 to 4 months for a cereal crop to mature. Harvesting in our country is either done manually by sickle or by a machine called harvester.
|
90 videos|273 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Crop Production and Management Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 1
| 1. What are the main steps involved in crop production? |  |
| 2. Why is soil preparation important in crop production? |  |
| 3. How do manure and fertilizers affect crop yield? |  |
| 4. What are the methods of irrigation used in agriculture? |  |
| 5. How can farmers protect their crops from weeds? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|



















