Class 6 Civics Chapter 2 Notes - Diversity and Discrimination
| Table of contents |

|
| Difference and Prejudice |

|
| Creating Stereotype |

|
| Inequality and Discrimination |

|
| Striving for Equality |

|
Difference and Prejudice
Our world is full of diverse people with different ways of living, speaking, eating, dressing, and celebrating. This diversity is influenced by where we live and our history.
- For example, India is incredibly diverse, with eight major religions, 1600 languages, and over a hundred dance forms.

- Despite this rich diversity, people often feel more comfortable with those who are similar to them in appearance, dress, and thinking.
- This can lead to prejudices—negative judgments about people based on their background. For instance, people might unfairly judge rural folks as being old-fashioned or city dwellers as being money-minded and lazy.
Prejudice means making unfair judgments about others based on their appearance, beliefs, or where they come from.
- It prevents us from respecting and understanding people who are different from us.
- Recognizing and challenging these prejudices can help us treat everyone with fairness and kindness, and celebrate the wide variety of cultures and traditions present in our diverse world.
Creating Stereotype
Stereotypes are oversimplified ideas about a group of people. For example, people might believe that all boys are strong and never cry, while all girls are gentle and emotional. These ideas are not true for everyone, but they can influence how people think and act.
Why Are Stereotypes Problematic?
Unfair Generalizations: Stereotypes make unfair generalizations about people based on their country, religion, gender, race, or economic background. For example, saying all rich people are "stingy" or all poor people are "lazy" is not fair. These ideas ignore the fact that people are individuals with their own unique qualities.
Ignoring Individual Differences: By fitting people into one stereotype, we ignore their individual differences and personal qualities. This means we don’t see each person as they truly are, but only through the lens of the stereotype.
Limiting Opportunities: Stereotypes can stop people from trying new things or achieving their full potential. For example, if a stereotype suggests that girls should be soft and gentle, a girl who is assertive or enjoys sports might be discouraged from pursuing those interests.
Stereotypes and Gender:
Stereotypes About Girls: Some common stereotypes about girls include being soft, gentle, and well-behaved. However, these qualities are not something girls are born with. They are often learned from family, society, and cultural expectations. It is not fair to assume that all girls naturally have these traits, or that girls who are not gentle or who act differently are unusual or wrong.
Challenging Stereotypes: It's important to recognize that people do not fit into just one pattern. Boys and girls, like everyone else, have a wide range of qualities and skills. Girls who are not soft or gentle should not be judged harshly. Everyone should be encouraged to be themselves, rather than fitting into a stereotype.
The Impact of Stereotypes:
Preventing Fairness: Stereotypes can lead to unfair treatment and missed opportunities. For instance, if people believe that only boys can be good at sports, girls who enjoy sports might be overlooked or discouraged.
Encouraging Individuality: To combat stereotypes, we should focus on treating each person as an individual with their own unique abilities and interests. Recognizing and valuing differences helps everyone to reach their potential and promotes a fairer society.
Why Are Stereotypes Harmful?
- They Limit Us: Stereotypes can stop people from exploring their true interests and talents. For example, if someone believes that only boys can be good at sports, girls who are interested in sports might not be encouraged to pursue it.
- They Are Not True for Everyone: Just because a stereotype is common does not mean it applies to everyone. There are boys who cry, and there are girls who are strong and assertive. People should be seen for who they are individually, not just as part of a group.
- They Create Unfair Expectations: When people believe in stereotypes, they might expect everyone in a group to act in a certain way. This can lead to unfair treatment. For example, if people think all boys should be tough, a boy who is gentle might be teased or misunderstood.

The Importance of Challenging Stereotypes:
- Respect Individuality: It’s important to see people as individuals with their own unique qualities rather than just fitting them into a stereotype.
- Encourage Fair Treatment: By challenging stereotypes, we can make sure everyone is treated fairly and encouraged to pursue their own interests and strengths.

Children with Special Needs:
- Stereotypes About Disabilities: People sometimes have stereotypes about children with special needs, which might be unfair or limiting. For example, they might be seen as less capable, but each child has their own unique abilities.
- Inclusion in Schools: Many believe that children with special needs should be included in regular schools because it helps them learn and interact with others in a diverse environment. It also helps break down stereotypes and promotes understanding and acceptance.
Inequality and Discrimination
Discrimination occurs when people act unfairly based on their prejudices or stereotypes.
Examples:
- Stopping someone from participating in activities or jobs.
- Preventing people from living in certain neighborhoods.
- Not allowing certain people to use the same well, hand pump, or drink from the same cups as others.

Discrimination can deeply affect a person by making them feel unworthy and left out. When someone faces discrimination:
- Feeling Inferior: They might start to believe that they are not as good or as important as others because they are treated unfairly. This feeling can lower their self-esteem.
- Feeling Excluded: Discrimination often pushes people away from participating in normal activities, making them feel isolated. They may feel like they don't belong or aren't accepted in certain places or groups.
Reasons for Discrimination
1. Diversity:
- People often belong to different groups based on language, religion, or region, which is a natural part of human diversity.
- However, when these differences are seen as inferior or less valuable, it can lead to discrimination. For example, someone might be treated unfairly because they speak a different language or follow a different religion than the majority.
2. Economic Background:
- Poverty is another reason people face discrimination. Those who are poor might not have access to basic resources like good food, clothing, or shelter.
- Because of this, they may be treated unfairly in various places, such as being ignored in offices, receiving poor treatment in hospitals, or being looked down upon in schools, simply because they don’t have as much money as others.
3. Multiple Discriminations:
- Some individuals face discrimination on more than one front. For instance, someone might be discriminated against not only because they are poor but also because they belong to a certain cultural or religious group.
- Groups like tribals, some religious minorities, or people from specific regions may experience this dual discrimination, making their lives even more challenging as they are marginalized both economically and culturally.
Caste-Based Discrimination
Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar's Experience:
- Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar, one of India's most prominent leaders, was born into the Mahar caste, which was labeled "untouchable" by society. This meant that people from this caste were treated as outcasts and denied basic rights and dignity.
- As a child, Dr. Ambedkar, along with his siblings, experienced the harsh reality of caste discrimination firsthand. When they arrived at a train station, the stationmaster and cartmen initially treated them kindly, assuming they were from a higher caste. However, once they revealed their caste, the attitude towards them changed drastically. The stationmaster and cartmen refused to help them, leaving the children stranded simply because they belonged to the Mahar caste. This experience highlighted the severe prejudice and exclusion faced by those considered "untouchable."
 Dr. Ambedkar
Dr. Ambedkar
Dalits:
- The term "Dalit" is used by people from lower castes to describe themselves. The word means "broken," symbolizing the way social prejudices and discrimination have oppressed and marginalized them.
- The Indian government refers to Dalits as Scheduled Castes (SC), a term used to identify and provide special provisions for those who have historically been discriminated against.
 Dalits
Dalits
Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar's Contributions
- Dr. Ambedkar was the first person from his caste to attain higher education. He completed college and went on to become a lawyer, breaking barriers that were imposed by the rigid caste system.
- He strongly advocated for the education of Dalits, urging them to pursue schooling and government jobs. Dr. Ambedkar believed that education and economic independence were key to escaping the oppressive caste system and gaining dignity and respect.
- Dr. Ambedkar dedicated his life to fighting for the rights of Dalits. He led movements to allow Dalits entry into temples, which were often denied to them due to their caste.
- Later in life, Dr. Ambedkar converted to Buddhism, a religion that he believed offered equality to all its followers. This conversion was a powerful statement against the caste system, as he sought a faith that respected and treated everyone equally, regardless of their background.
Striving for Equality
- During India's fight for freedom, various groups like Dalits, women, tribals, and peasants also fought against the inequalities they experienced in their daily lives.
- Dalits, who were often denied entry into temples, organized themselves to fight for their right to worship freely.
- Women demanded that they should have equal rights to education, just like men, challenging the traditional norms that limited their opportunities.
- Peasants and tribals struggled to free themselves from the control of moneylenders, who charged them extremely high interest rates, trapping them in a cycle of debt.
- After independence in 1947, the leaders responsible for writing the Indian Constitution were keenly aware of the various forms of discrimination that had been practiced in society.
- Influential leaders like Dr. B.R. Ambedkar played a crucial role in advocating for the rights of Dalits, ensuring their voices were heard in the process of nation-building.
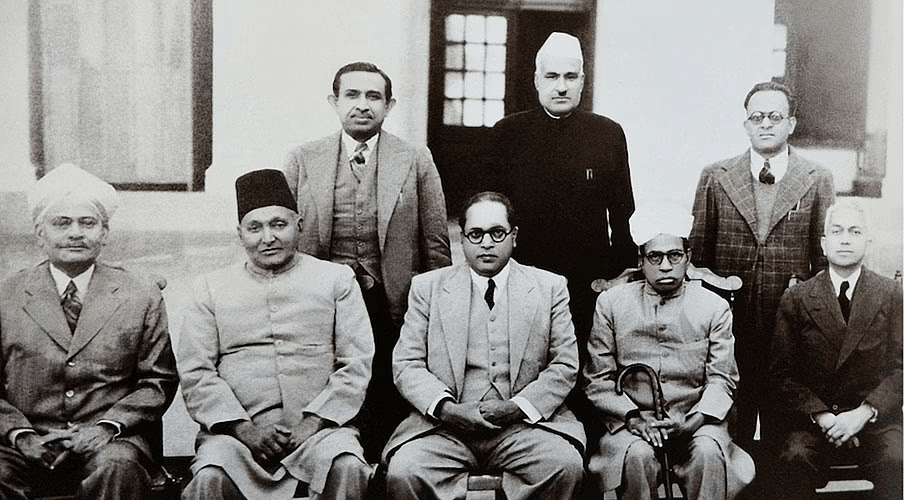
 Some of the members who wrote the constitution of India.
Some of the members who wrote the constitution of India. - The Constitution was crafted with the vision of treating all citizens of India equally, regardless of their background.
- It established that everyone in India has equal rights and opportunities, laying the foundation for a fair and just society.
- Untouchability, a practice that marginalized many communities, was declared a crime, and measures were taken to ensure that government jobs were accessible to all citizens.
- The Constitution also stressed the importance of allowing people the freedom to practice their own religion, speak their own language, and celebrate their own festivals without any fear of discrimination.
- India was established as a secular country, where no single religion, language, or festival was imposed on everyone, promoting unity in diversity.
- However, despite the ideals set forth in the Constitution, inequalities still persist in society today.
- Achieving true equality requires ongoing efforts from both individuals and the government to ensure that these constitutional values are upheld for all citizens.
|
65 videos|386 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 6 Civics Chapter 2 Notes - Diversity and Discrimination
| 1. What is the difference between prejudice and discrimination? |  |
| 2. How do stereotypes contribute to inequality and discrimination? |  |
| 3. What are some ways to strive for equality in society? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to address diversity and discrimination in society? |  |
| 5. How can individuals combat prejudice and discrimination in their daily lives? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|















