Economic Activities Around Us Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
Understanding Economic Activities
Every day, people engage in various types of work to make a living, such as farming, teaching, driving buses, and manufacturing machines. These are called economic activities as they help communities and generate income.
In the past, work mainly focused on basic activities like farming, animal rearing, crafting, and weaving.
Today, economic activities are more diverse and includes activities like manufacturing computers, phones, and drones, working in banks, schools, and hotels, driving vehicles for transport, etc.

The Classification of Economic Activities into Economic Sectors
Do the three main economic sectors include primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors?
Yes, the three main types of economic sectors are primary, secondary, and tertiary economic sectors.
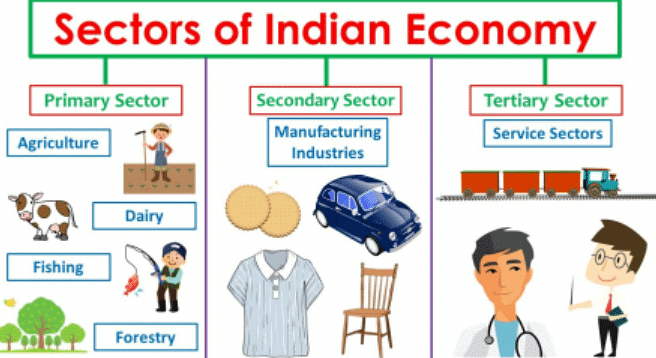
Economic activities that share similar characteristics can be grouped into larger categories called economic sectors. The primary sector focuses on obtaining raw materials from nature, the secondary sector changes these raw materials into products, and the tertiary sector offers services that support both the primary and secondary sectors.
A. Primary Activities
Economic activities that rely directly on nature to produce goods are termed primary activities or primary sector economic activities. Jobs in this sector depend directly on nature for essential resources. These primary activities involve:
- Growing grains and vegetables on farms
- Collecting wood from forests
- Mining coal
- Catching fish
- Gathering eggs from poultry farms

The most common primary activities include:
- Agriculture
- Mining
- Fishing
- Raising livestock
- Forestry
The connection between these sectors is essential; if one activity stops, it significantly affects the others.
B. Secondary Activities
The secondary activities involve taking raw materials from the primary sector and changing them into products that can be sold or used. These jobs take natural resources and transform them into usable items.
What Does the Secondary Sector Do?
- It includes building construction, roadwork, and providing essential services like water, electricity, and gas.
- It covers the manufacturing of goods in factories, where raw materials are processed into items that can be sold or consumed.
 Examples of Secondary Activities:
Examples of Secondary Activities:
- Processing Food: Grains are milled into flour.
- Woodworking: Timber is crafted into furniture and paper.
- Making Clothes: Cotton is woven into fabric for clothing.
- Making Cars: Steel from iron ore is shaped into vehicles like cars and trucks.
C. Tertiary Activities
The economic activities that assist those involved in primary and secondary sectors are known as tertiary activities. These include various services that, while often unseen, are essential to our daily lives.
Examples of Tertiary Activities:
- Transportation Services: Truck drivers transport grains and vegetables from farms to markets and factories.
- Retail Services: Individuals selling fruits and vegetables at shops or markets.
- Professional Services: Doctors, teachers, nurses, lawyers, and pilots provide crucial assistance.
- Repair and Maintenance Services: Technicians fix mobile phones and televisions, while mechanics repair vehicles like cars and tractors.
- Communication Services: Mobile phones and the internet allow us to stay connected.
- Other Services: This sector is often referred to as the service sector.
Interdependence Among Sectors
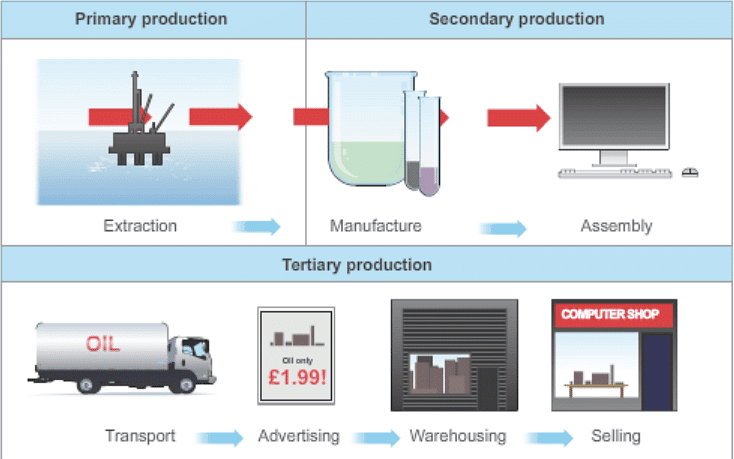
The three types of economic activities or economic sectors are essential for transforming natural resources into final products for consumption. Let’s take a virtual trip to a village in Anand district of Gujarat to see how these sectors are connected and support one another.
Example from Anand District, Gujarat
In a village in Anand district, Gujarat, you can observe how these sectors work together:
- Primary Sector: Farmers are involved in tasks like growing grains and vegetables, gathering wood from forests, mining coal, fishing, and raising poultry for eggs.
- Secondary Sector: The harvested crops are taken to factories where they are turned into food products.
- Tertiary Sector: After processing, these products are distributed to various shops for consumers to buy. This sector also includes services that assist both primary and secondary sectors, such as transportation and business management.
Dairy Cooperative: From Farm to Plate
In Gujarat, farmers begin their day by milking their cows, which are vital to their livelihoods. The milk helps support their families, and they sell it to AMUL. At the end of each month, they receive payment based on the quantity and quality of their milk. This was not always the case, especially 50 years ago.

Life Before AMUL
In the past, farmers had to travel to nearby villages on foot or by bicycle to sell their milk. Since milk spoils quickly, they needed to sell it quickly. They relied on middlemen who bought milk at low prices and resold it in the market. Many farmers felt cheated and mistreated by these middlemen, often receiving unfair payments.
The Start of AMUL
Farmers came together to speak with Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, a respected leader, who advised them to work together and create a cooperative. Following his guidance, they formed the cooperative to reduce their dependency on middlemen.
AMUL was established in 1946 under the leadership of Tribhuvandas Patel and Dr. Varghese Kurien. They began managing their own milk collection, processing, and sales. By forming a cooperative, farmers could buy and sell milk collectively, handling all aspects of milk collection, processing, and distribution. This collaboration allowed farmers to earn more and become self-sufficient.
How AMUL Grew
AMUL expanded rapidly, producing so much milk that they started making other products like butter and milk powder. They built a factory in Anand to meet the growing demand.
Today, AMUL manufactures a wide variety of dairy products in factories throughout India, which are sold in shops across the country and even exported abroad.
How the Sectors Work
- Primary Sector Activity: Farmers milk their cows, which is the primary sector as it is sourced from nature.
- Secondary Sector Activity: The milk is transformed into products like milk powder, butter, and cheese in factories.
- Tertiary Sector Activity: AMUL transports the products via trucks, trains, planes, and ships, selling them in stores across India.
What is a Cooperative?
- A cooperative is a group of individuals who join forces to accomplish tasks they cannot achieve individually.
- For instance, farmers may create a cooperative to sell their milk straight to shops.
- This approach eliminates the need for middlemen, allowing them to function like a large family.
- The milk producers together make decisions regarding:
1. Production
2. Pasteurisation
3. Sale of milk - By collaborating, they can earn more and have greater control over their products.
- Middlemen: Individuals who acquire goods from producers and sell them to consumers, charging a fee for this service.
What is Pasteurization?
- Pasteurisation is a technique that ensures milk and other liquids are safe to consume.
- This process involves:
1. Heating the liquid to a set temperature for a brief duration.
2. Then, it cools quickly.- This method helps preserve milk by heating it to eliminate harmful bacteria.
Similar to AMUL, there are numerous other milk cooperatives in India that create and market milk and dairy products using various brand names. Some of these cooperatives include:
- Nandini from Karnataka
- Mother Dairy from Delhi-NCR
- Aavin from Tamil Nadu
- Vijaya from Andhra Pradesh
- Kevi from Nagaland
- Sudha from Bihar
- Verka from Punjab
 1. This movement brought farmers, including women, together. They were given control over making and selling milk. The farmers worked as a team to make important decisions about milk production, pasteurisation, and sales. By sharing the work, they earned more money. They didn’t need middlemen anymore and felt like one big family!
1. This movement brought farmers, including women, together. They were given control over making and selling milk. The farmers worked as a team to make important decisions about milk production, pasteurisation, and sales. By sharing the work, they earned more money. They didn’t need middlemen anymore and felt like one big family!
2. One day, the farmers spoke to Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, an important national leader, about their problems. He told them to form a cooperative so they could manage everything on their own and stop depending on middlemen. A cooperative would help them handle all steps: collecting milk, processing it, and selling it. The farmers listened to Sardar Patel and followed his advice.
3. AMUL was started in 1946 by Tribhuvandas Patel (a lawyer and freedom fighter) and Dr. Varghese Kurien (an engineer working in a dairy factory in Mumbai).
This kind of work is called a primary sector activity because the milk comes directly from cows or animals.
4. As more farmers saw the benefits of the cooperative, it grew. They collected so much milk that they decided to make other products too. They built a factory in Anand to make butter and milk powder.
5. Today, AMUL makes many different products in factories across India. These products are sold in small and large shops all over the country. AMUL also sells its products in many other countries. They use trucks, trains, planes, and ships to send their goods. They have set up stores and supply milk and dairy products to shops in towns, cities, and villages across Gujarat and other states. This kind of work is called a tertiary activity, which means it's part of the service and selling process.
Recycling Used Paper
Recycling paper involves processing old paper to create new paper products. Nowadays, used paper is repurposed to produce fresh paper.
Benefits of Recycling Paper:
- Recycling one tonne of paper can save 17 trees.
- It helps conserve 2.5 cubic metres of landfill space.
- It requires 70 per cent less energy and water to recycle paper compared to making new paper from wood pulp.

Conclusion
Recycling paper is essential for saving natural resources and significantly impacts the interconnectedness of economic sectors. Recognising how recycling integrates into the larger economic framework enhances our understanding of sustainable practices.
Key Words
- Monetary value: The worth of something expressed in terms of money.
- Economic Sectors: Broad groups that include various activities that help with the economic prosperity of a nation.
- Primary sector: Activities focused on extracting raw materials from nature, such as farming, fishing, forestry, greenhouse farming, mining, fish farming, and raising animals.
- Secondary sector: Activities that process raw materials from the primary sector into products for sale or use, including constructing buildings and roads, and providing essential services like water, electricity, and gas.
- Tertiary Sector: Activities that offer services that support both primary and secondary sectors, like transport, banking, and business management. These services are vital for the functioning of the other sectors.
- Warehouses: Large buildings used for storing products before they are sold, used, or rented out to shops.
- Dairy:. facility where milk is collected and stored.
- Cooperative:. group of individuals who come together voluntarily to meet their economic and social needs in a formal manner. They jointly own the cooperative and collectively make decisions to improve their economic activities.
- Middlemen: Individuals who purchase goods from producers and sell them to consumers, charging a fee for their service.
- Pasteurisation:. method of preserving milk by heating it to a certain temperature to eliminate harmful bacteria.
- Factory:. building or complex where goods are manufactured or assembled into final products.
- Retail: The sale of products in small quantities to end consumers rather than for resale.
- Export: Goods and services produced in one country and sold to buyers in another country.
FAQs on Economic Activities Around Us Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are the main economic sectors classified in economic activities? |  |
| 2. How do the economic sectors interdepend on each other? |  |
| 3. What role does the tertiary sector play in economic development? |  |
| 4. How can the classification of economic activities help in policy-making? |  |
| 5. What factors can influence the interdependence among economic sectors? |  |


















