Human Needs Chapter Notes | Science Olympiad Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Human Needs |

|
| Air |

|
| Water |

|
| Food |

|
| Shelter |

|
Human Needs
To ensure their survival, humans have fundamental requirements, including air, water, food, and shelter.
Air

What is Weather?
Weather refers to the day-to-day condition of a specific place, which can change frequently, even within hours. It may be sunny, cloudy, windy, or rainy, depending on the atmospheric conditions.
Seasons and Weather Patterns
When weather remains consistent for several months, it defines a season. 
Different seasons have distinct characteristics:
1. Summer Season: The weather is extremely hot.
2. Rainy/ Monsoon Season:
- Follows summer in most parts of India.
- Rainfall is frequent, almost daily, during this season.
3. Winter Season:
- In some regions of India, winters are very cold, while in others, the temperature remains moderate.
- In several parts of South India, woollen clothing is rarely needed during winter.
Water

Water holds significant importance for humans as it serves multiple crucial functions:
- Replenishing the water lost through activities such as breathing, sweating, and urination.
- Eliminating waste from the body.
- Facilitating digestion.
- Promoting overall health and well-being.
- Regulating body temperature.
- Enabling bathing, cleaning, and washing.
- The human body primarily consists of water, accounting for over half of its weight.
- Loss of water transpires through respiration, perspiration, and urination.
- In order to maintain a healthy body, it is recommended to consume seven glasses of water daily.
- Additionally, water is obtained through the consumption of water-rich foods, such as fruits and vegetables.
Food
Food is the source of essential nutrients our body needs to grow, stay healthy, and combat diseases.
The food we consume serves the following purposes:
- Provides energy for daily activities
- Protects against diseases
- Repairs and builds damaged body parts
- Supports growth
Nutrients in Food
To meet the body's demands, it is essential to consume a variety of foods that contain different nutrients. There are five key nutrients, each serving a specific purpose.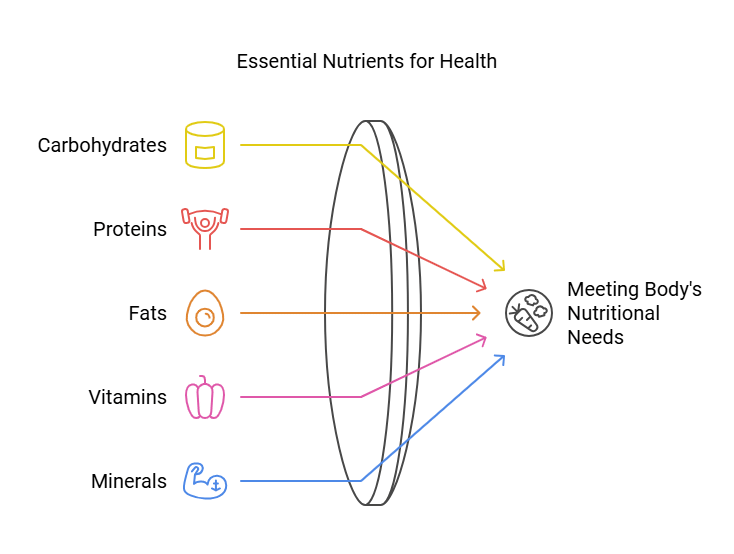
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy, enabling us to work, play, and carry out daily activities.  They are classified into two types:
They are classified into two types:
1. Starch: Found in potatoes, rice, wheat, and corn.
2. Sugar: Found in fruits like bananas, grapes, pineapples, oranges, peaches, and mangoes.
People engaged in intense physical activities, such as athletes and laborers, require higher amounts of carbohydrates to meet their energy needs.
2. Proteins
Proteins are essential for building, maintaining, and repairing body tissues, making them known as body-building foods. 
- Growth Needs: Children require more protein than adults due to higher cellular growth.
- Sources: Meat, fish, eggs, milk, curd, cheese, nuts, and pulses.
3. Fats
Fats provide more energy than carbohydrates and serve as the body’s energy reserve. They also:
- Protect vital organs by acting as a cushion.
- Help maintain body warmth in cold weather.
- Support healthy skin and hair.

Sources: Butter, ghee, oil, nuts, and cheese.
Caution: Excess fat consumption may lead to obesity and associated health issues, such as heart disease.
4. Vitamins and Minerals
These are protective nutrients vital for various body functions:
- Vitamins: For example, Vitamin D strengthens bones, and Vitamin C aids in healing.
- Minerals: Examples include calcium, iron, and iodine.

Sources: Green leafy vegetables, fruits, milk, and fish.
5. Fibre or Roughage
Fibre, though indigestible, plays a crucial role in digestion and waste elimination. 
Benefits:
- Promotes smooth digestion and prevents constipation.
- Aids in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Sources: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
6. Water
Water is indispensable for life, making up over half of our body weight. 
Functions:
- Carries oxygen to cells via blood.
- Assists in digestion and waste removal.
Sources: Drinking water, juices, milk, and water-rich fruits and vegetables like cucumbers, watermelons, and oranges.
Tip: Drink 6–8 glasses of water daily.
Balanced Diet
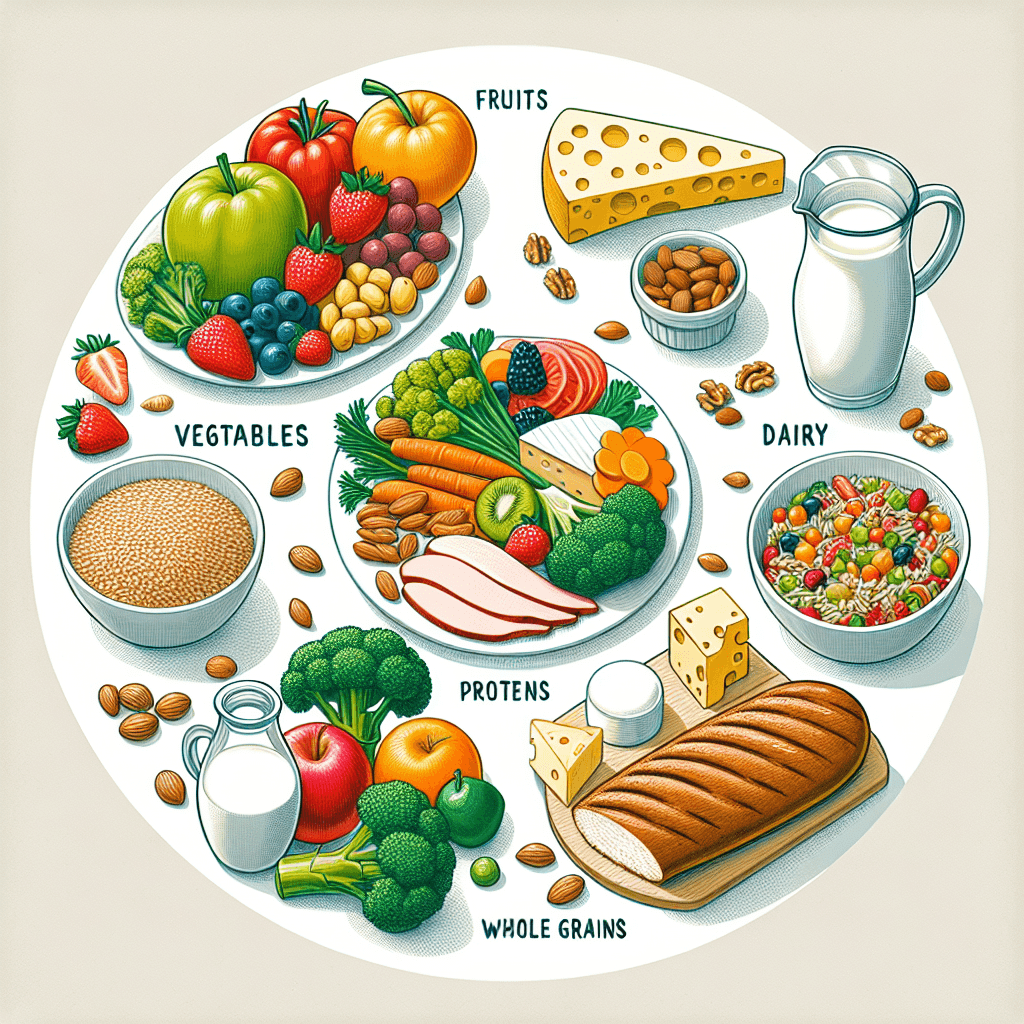 A balanced diet includes all essential nutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals—in the correct proportions, along with fibre and adequate water.
A balanced diet includes all essential nutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals—in the correct proportions, along with fibre and adequate water.
Shelter

What is a Shelter?
A shelter is a covered structure that provides protection to humans, animals, and birds from their surroundings.
- Animals: Create shelters by burrowing, building lodges, or using tree branches and mud.
- Birds: Build nests on trees using various materials.
- Humans: Construct houses using materials like wood, mud, bamboo, and stone, depending on environmental conditions and the availability of raw materials.
Why Do We Need a Shelter?
Shelters serve the following purposes:
- Protection: Safeguard from weather conditions (rain, wind, heat, cold) and dangerous animals.
- Rest and Activities: Provide a place to rest and perform daily tasks.
- Privacy and Storage: Offer private spaces and facilities to store belongings.
Types of Shelter
Permanent Shelter:
- Structures used for long durations or lifetimes.
- Examples: Houses, caves, bird nests.

Temporary Shelter:
- Structures used for short durations or specific purposes.
- Examples: Tents, caravans, houseboats, migratory bird nests.
Living Beings and Their Shelters
Animals and Their Shelters 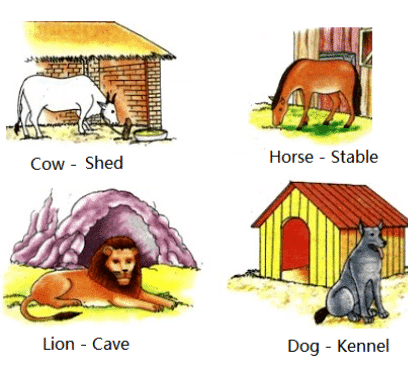
- Land and Forest Animals: Cow, dog, horse, lion, elephant, peacock.
- Tree Dwellers: Monkeys, birds, sloths.
- Burrowing Animals: Rats, ants, rabbits, snakes, earthworms.
- Land and Water Animals: Frogs, crocodiles, snakes.
Birds and Their Shelters: Birds build nests using materials like grass, twigs, wool, and leaves. The type and location of the nest vary by bird species. 
Insects and Their Shelters: Insects create diverse shelters, such as ant hills, beehives, and silk cocoons. 
Humans and Their Shelters 
- Human shelters, called houses, are of two main types:
1. Kutcha Houses: Made from mud, wood, and straw. Examples: Huts.
2. Pucca Houses: Built with cement, bricks, and steel. Examples: Apartments, bungalows.
Factors Influencing Shelter Choice
- Location and Geography: Desert homes differ from those in hilly areas.
- Environmental Conditions: Climate influences the materials and design of shelters.
- Raw Materials and Economic Status: Availability of materials and a person's financial resources affect the type of shelter built.
Types of Houses Based on Regions
Mud Houses: 
- Found in deserts (e.g., Rajasthan).
- Mud walls keep interiors cool in extreme heat.
Wood and Bamboo Houses: 
- Common in regions like Assam with heavy rainfall.
- Elevated structures protect against flooding.
Houseboats: 
- Found in Kashmir and Kerala.
- Floating wooden houses designed for water.
Igloos: 
- Found in cold regions.
- Made of ice blocks and shaped like domes.
Tents: 
- Temporary shelters for mountaineers and hikers.
- Made of plastic or fabric for portability.
|
48 videos|68 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Human Needs Chapter Notes - Science Olympiad Class 4
| 1. What are the basic human needs essential for survival? |  |
| 2. Why is clean water important for human health? |  |
| 3. How does food contribute to human well-being? |  |
| 4. What role does shelter play in human life? |  |
| 5. How do air quality and access to fresh air impact health? |  |















