India, That Is Bharat Chapter Notes | Social Studies (SST) Class 6 PDF Download
Introduction to India's Past
India, as we know it today, is a modern country with clear borders, different states, and a large population. But if we go back in time—500 years, 2,000 years, or even 5,000 years ago—India was very different. The land we now call India was known by different names and had changing boundaries. This region, often called the 'Indian Subcontinent,' has a rich history that we can learn about from various sources.
Throughout history, India has been known by many names. These names were given by the people who lived here and by visitors from other countries. We find these names in ancient texts, stories written by travelers and pilgrims, and old inscriptions carved in stone. By exploring these sources, we can learn about the fascinating journey of India through time.

How Indians Named India
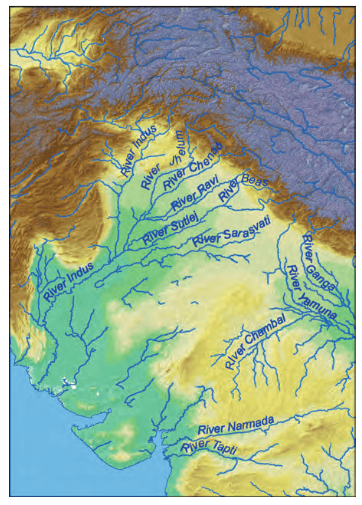
The Rig Veda and the Name 'Sapta Sindhava'
- The Rig Veda is India's oldest text, written several thousand years ago.
- In this ancient text, the northwest region of the Indian Subcontinent is called 'Sapta Sindhava,' which means the 'land of the seven rivers.'
- The word 'Sindhava' comes from 'Sindhu,' a term used for the Indus River or sometimes for rivers in general.
Names of Different Regions in Ancient Literature
As time passed, more names for different parts of India began to appear in literature. One of the most famous Indian texts, the Mahabharata, lists many regions that are familiar to us today.
For example:
- 'Käshmira' refers to what is now Kashmir.
- 'Kurukshetra' is part of today's Haryana.
- 'Vanga' corresponds to parts of Bengal.
- 'Prägjyotisha' is roughly today's Assam.
- 'Kaccha' is today's Kutch region.
- 'Kerala' is more or less the same as the present-day state of Kerala.
The Names 'Bhäratavarsha' and 'Jambudvipa'
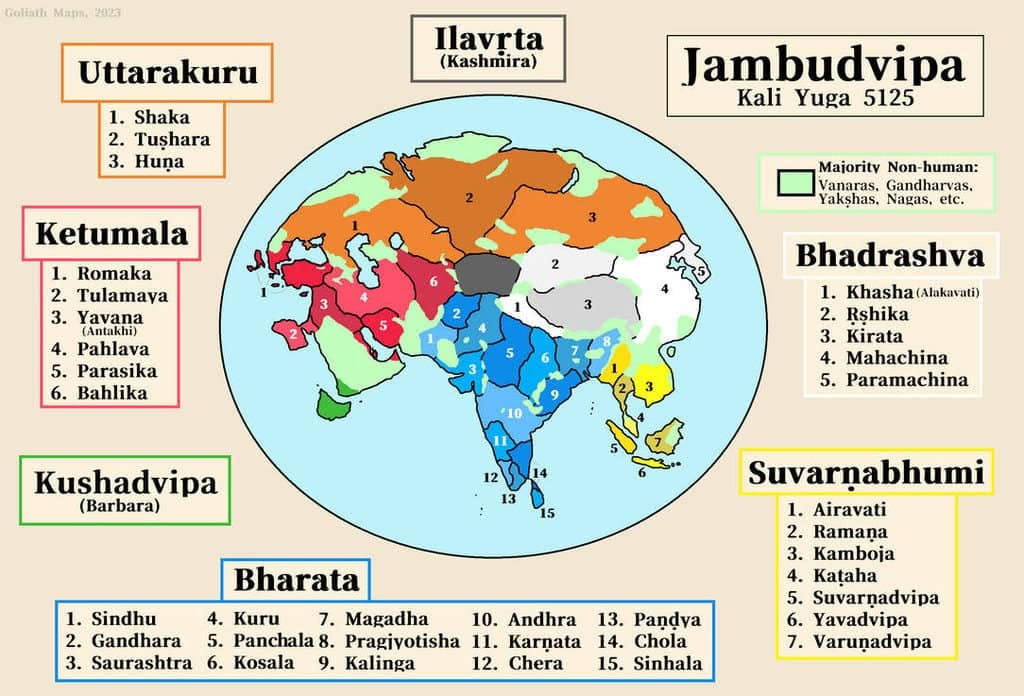
When did the entire Indian Subcontinent get a name? This is a tricky question because ancient texts are hard to date. However, in the Mahabharata, we come across the terms 'Bhäratavarsha' and 'Jambudvipa.' Scholars believe that this poem was written a few centuries before the Common Era (BCE).
- Bhäratavarsha: This term refers to the entire Subcontinent. It means 'the country of the Bharatas.' The name 'Bharata' first appears in the Rig Veda and refers to one of the main Vedic groups of people. Later literature mentions several kings named Bharata.
- Jambudvipa: This term means 'the island of the jamun tree fruit.' The jamun tree, also called the jambul tree or Malabar plum tree, is native to India. Over time, 'Jambudvipa' came to represent the Indian Subcontinent.
Emperor Ashoka and the Name 'Jambudvipa'
- A big clue about the use of 'Jambudvipa' comes from Emperor Ashoka, who ruled around 250 BCE.
- Ashoka left many inscriptions, and in one of them, he used 'Jambudvipa' to describe the whole of India.
- During his time, this included areas that are now Bangladesh, Pakistan, and parts of Afghanistan.
'Bhärata' Becomes the Name for the Subcontinent

- A few centuries later, 'Bhärata' became the widely used name for the Indian Subcontinent.
- For example, in an ancient text called the Vishnu Purana, the name 'Bhärata' is used to describe the region.
- This name is still in use today. In North India, it is generally written as 'Bharat,' while in South India, it is often 'Bharatam.'
Ancient Tamil Literature and the Idea of India
- Interestingly, different parts of ancient India shared a similar understanding of the country's geography.
- For example, a poem from ancient Tamil literature, about 2,000 years old, praises a king whose fame spread "from [Cape] Kumari in the south, from the great mountain in the north, from the oceans on the east and on the west..." This shows that ancient Indians knew their geography well and had a clear idea of the land that made up India.
The Indian Constitution: 'India, that is Bharat'
In the very beginning of the Indian Constitution, which was originally written in English, the phrase "India, that is Bharat" is used to describe the nation. Similarly, in the Hindi version of the Constitution, this is written as "Bhärat arthäth India." This shows the dual identity of the country as both 'India' and 'Bharat'.
How Foreigners Named India
What did the Persians call the region around the Indus River?
The Persians called the region around the Indus River 'Hind,' 'Hidu,' or 'Hindu,' which was a geographical term, not related to the Hindu religion.

The Persians and the Name 'Hind'
- The Persians, ancient inhabitants of Iran, were the first foreigners to mention India. In the 6th century BCE, a Persian emperor led a military campaign and gained control over the region around the Indus River, which was earlier called 'Sindhu.'
- The Persians adapted this name in their language, referring to the region as 'Hind,' 'Hidu,' or 'Hindu.' It's important to note that in ancient Persian, 'Hindu' was a geographical term and had no connection to the Hindu religion.
The Greeks and the Name 'Indoi' or 'Indike'
- Based on Persian sources, the ancient Greeks referred to the region as 'Indoi' or 'Indike.'
- They altered the name by dropping the initial 'h' from 'Hindu' since the letter 'h' did not exist in the Greek language.

The Chinese and the Name 'Yintu' or 'Yindu'
- The ancient Chinese also had interactions with India and referred to the region as 'Yintu' or 'Yindu.' This name, like others, was derived from 'Sindhu.'
- Another Chinese word derived from 'Sindhu' was 'Tianzhu,' which could also be interpreted as 'heavenly master.' This term reflects the respect the ancient Chinese had for India as the land of the Buddha.

The Term 'Hindustan'
- You might be familiar with the term 'Hindustan,' but it was first used in a Persian inscription around 1,800 years ago.
- Over time, 'Hindustan' became the common term used by many invaders to describe the Indian Subcontinent.
Xuanzang's Journey to India
- Xuanzang, a Chinese scholar (previously spelled as Hiuen Tsang or Hsuan Tsang), traveled from China to India in the 7th century CE. During his 17-year journey, he visited various parts of India, met with scholars, and collected numerous Buddhist texts.
- Upon his return to China, Xuanzang translated these manuscripts from Sanskrit into Chinese. Over the centuries, several other Chinese scholars also made similar journeys to India.
India's Ancient Names
- India is a very old land with a rich history, and throughout this history, it has been known by many different names.
- The ancient people of India called their land 'Jambudvipa' and 'Bhärata.' Over time, 'Bhärata' became widely used and is now the name for India in most Indian languages.
- Foreign visitors and invaders often based their names for India on the Sindhu or Indus River, leading to names like 'Hindu,' 'Indoi,' and eventually 'India.'
|
67 videos|386 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on India, That Is Bharat Chapter Notes - Social Studies (SST) Class 6
| 1. How did Indians name India? |  |
| 2. How did foreigners name India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the name "Bharat" for India? |  |
| 4. How has the name "India" evolved over time? |  |
| 5. How do the names "India" and "Bharat" reflect the diversity of the country? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|



















