Class 6 Geography Notes - India-Climate Vegetation and Wildlife
| Table of contents |

|
| Seasons in India |

|
| Natural Vegetation |

|
| Why are Forests Necessary? |

|
| Wildlife |

|
In this chapter we will be learning about the following topics:
- Seasons in India
- Cold Weather Season (Winter) December to February
- Hot Weather Season
- Southwest Monsoon Season (Rainy) June to September
- Season of Retreating Monsoon (Autumn) October and November
- Natural Vegetation
- Why are Forests Necessary?
- Wildlife

The day to day changes in atmosphere is called weather. Weather includes changes in temperature, sunshine and rainfall.
Seasons in India
In India the Four Major Seasons Are:
- Cold Weather Season (Winter) December to February
- Hot Weather Season
- Southwest Monsoon Season (Rainy) June to September
- Season of Retreating Monsoon (Autumn) October and November
 4 Seasons in India
4 Seasons in India1.1 Cold Weather Season or "Winter"
- In the cold weather, the rays coming from the sun do not fall directly on the region.
- Due to this, the temperatures remain quite low in northern India.
- The winter season continues from December to February in India.

1.2 Hot Weather Season or Summer
- In the hot weather season, these rays coming from the sun are more or less directly falling on this region.
- This causes an increased temperature.
- The hot and dry winds blowing is referred as loo, during the day.
- The summer season continues from March to May in India.
1.3 South-West Monsoon Season or Rainy Season
- This season starts with the onset and advance of the monsoon.
- The direction of the wind is from the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal towards the land.
- These winds carry moisture with them.
- Once these winds strike the mountain barriers, rainfall occurs.
- The rainy season falls from June to September.

1.4 Season of Retreating Monsoon or Autumn
Winds start to come back from the land area to the Bay of Bengal. This season is referred to as the retreating monsoons. The southern parts of India, mainly Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh receive rainfall in this season.
This season falls in October and November.
The climate is the average weather condition over a place, which has been measured over many years. The climate of India is described as Monsoon type.
Since India’s is present in the tropical region, most of the rain falling is brought in by monsoon winds.
In India, agriculture is dependent on rain. Good monsoons bring adequate rain for crops. The climate of any place is affected by some factors like its location, altitude, and distance from the sea. Hence, regional differences can be experienced in the climate of India.

Natural Vegetation
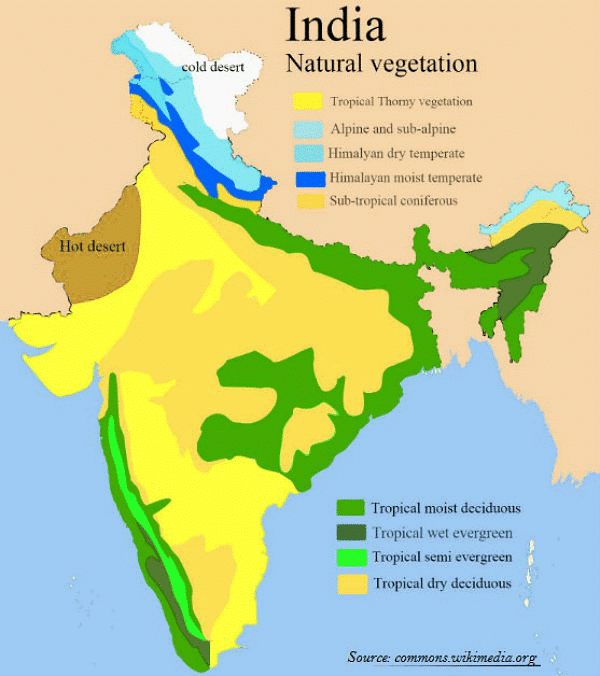 1. Tropical Rain Forest:
1. Tropical Rain Forest: - Tropical rainforest is found in those areas which receive heavy rainfall.
- The tropical rainforest is so dense that sunlight does not reach the ground.
- The trees of the tropical rainforest shed their leaves at different times of the year.
- These are also called monsoon forests.
- The trees of a deciduous forest shed their leaves at a particular time of the year.
- Hence, such a forest is called a deciduous forest.
- This type of vegetation is found in dry areas.
- The leaves are in the form of spines.
- This helps the plant to reduce the loss of water.
- Different types of species are found in the mountains at different altitudes.
- Most of the trees are conical in shape at a height of between 1500 m and 2500 m.
- Due to this, they are called coniferous trees.
- Mangrove plants can survive in saline water.
- They are mainly found in the Sunderbans in West Bengal and in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Sundari is a well-known tree in the mangrove forest of Sunderban.
Loss of Natural Vegetation
- Humans have destroyed a large tract of forest by recklessly cutting trees for various purposes.
- Forests are cleared to make way for agriculture and to make townships and factories. This is creating environmental problems for us.
- Van Mahotsav is being organized to educate people about the importance of forests.

Why are Forests Necessary?
- Plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Oxygen is utilized by us for breathing.
- The roots of plants bind the soil. Thus, plants prevent soil erosion.
- Forests provide us with timber for furniture and firewood. They also provide fodder, medicinal plants and herbs. We also get lac, honey, and gum from forests.
- Forests are the natural habitat of wildlife.
Wildlife

- Forests are home to a number of species of animals and a large number of reptiles, amphibians, mammals, birds, insects and worms living there.
- The tiger is India's national animal. Tiger can be seen in various parts of the country.
- Gir forest in Gujarat is referred as the home of Asiatic lions.
- One-horned rhinoceroses and elephants could be seen in the forests of Assam.
- Elephants can also be seen in Kerala and Karnataka.
- Camels and wild asses can be seen in the Great Indian desert and the Rann of Kuchchh.
- Peacock is the national bird of India. Some other birds commonly found are parrots, pigeons, mynah, geese, bulbul and ducks. The bird sanctuaries which are created to provide a natural habitat for these birds.
- Due to the cutting of forests ( Known as deforestation) and hunting, some of the species of India are declining at a faster rate. Some of the species have become extinct.
Extinct Species: A species which no longer exists is called and extinct species.
Endangered Species: A species which is in danger of becoming extinct is called endangered species.
- In order to protect these species national parks, sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves have been made. The Government has also initiated Project Tiger and Project Elephant in order to protect these animals.
FAQs on Class 6 Geography Notes - India-Climate Vegetation and Wildlife
| 1. What are the different seasons in India? |  |
| 2. What is natural vegetation? |  |
| 3. Why are forests necessary? |  |
| 4. What is wildlife? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of studying climate, vegetation, and wildlife in India? |  |




















