Local Self-Government in Cities Class 4 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| Levels of Government |

|
| Local Government |

|
| Types of Local Government |

|
| Roles in the Local Government and their Responsibilities |

|
| Taxes |

|
Everyone needs certain things to live comfortably, like clean water to drink, electricity for lights and appliances, roads to travel on, transportation like buses or trains, schools to learn, colleges for higher education, and hospitals for medical care.
 These things are called civic amenities or public services. In our country, the government makes sure people have access to these things.
These things are called civic amenities or public services. In our country, the government makes sure people have access to these things.
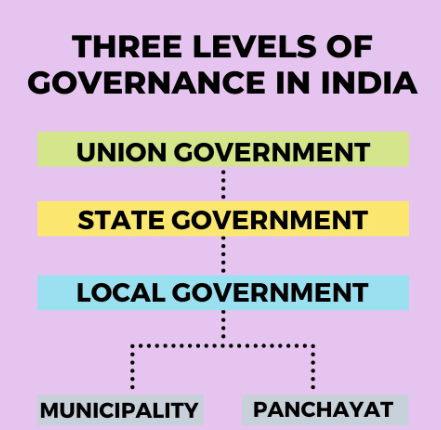
Levels of Government
The government works at three different levels:
- Central (National)
- State (Regional), and
- Local (In our Area).
(i) Central Government:
- The central government is based in New Delhi.
- It is responsible for matters that affect the entire country or multiple states, including defense, foreign affairs, currency, telecommunications, and interstate commerce.

- It consists of the President, the Parliament (comprising the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha), and the Prime Minister, who heads the executive branch.
(ii) State Government:
- India is divided into 28 states and 8 Union territories, each with its own elected government.
- State governments have jurisdiction over matters not exclusively reserved for the central government. This includes police, healthcare, education, agriculture, local infrastructure, and more.

- Each state has its own legislative assembly, headed by a Chief Minister, who is the head of the state government.
(iii) Local Government:
- Local governments are referred to as Panchayats in rural areas and Municipalities or Municipal Corporations in urban areas.

- They are responsible for local governance, including urban planning, local infrastructure development, waste management, water supply, and other essential services.
- Local bodies have elected representatives who serve on local councils. These representatives are elected by the people residing in the respective areas.
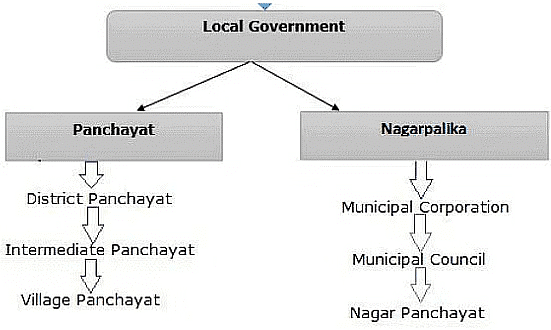
Local Government
The government that takes care of our area is chosen by the people living there. In villages, it's called the gram panchayat. In towns and cities, it's either the municipal committee or municipal corporation.
In India, local government means that people who live in a place choose leaders to take care of their area. These leaders manage things like water, roads, and other important services in villages, towns, and cities. They make sure everyone has what they need to live comfortably.
Types of Local Government
Municipal Committees
These are local governing bodies responsible for smaller cities or urban areas.- They handle the administration of various civic amenities and services within their jurisdiction.
- Municipal committees typically oversee functions such as sanitation, water supply, street lighting, public health, and maintenance of roads and parks.
Municipal Corporations
Municipal corporations are governing bodies for larger cities with significant populations, typically exceeding 1 million inhabitants.
- They have broader responsibilities compared to municipal committees due to the larger scale of urban infrastructure and services required.
- Municipal corporations handle a wide range of functions including urban planning, public transportation, education, healthcare, waste management, and more.
Election Process
- Members of the municipal committee or corporation are elected by the residents of the city through periodic elections, typically held every five years.
- These elections are conducted democratically, with eligible voters casting their votes to choose their representatives.
- Each geographical area within the city, known as a ward, elects one or more members to represent their interests in the local government body.
Roles in the Local Government and their Responsibilities
(i) Municipal Councillors
- Elected representatives who serve as the voice of the residents in the local government.

- They advocate for the needs and concerns of their constituents and participate in decision-making processes related to city governance.
(ii) Chairperson/President
- The leader of the municipal committee, responsible for presiding over meetings, setting agendas, and ensuring the efficient functioning of the committee.
- They often act as a liaison between the committee and other governmental bodies or stakeholders.
(iii) Mayor
- The head of the municipal corporation, elected by the citizens or sometimes appointed from among the elected councillors.
- The mayor serves as the chief executive officer of the city, overseeing its administration, implementing policies, and representing the city in various forums.
- The mayor is typically supported by a deputy mayor who assists in carrying out the duties and responsibilities of the office.
Taxes
Local governments need money to do their jobs. They get this money from taxes like property tax, road tax, and water tax.
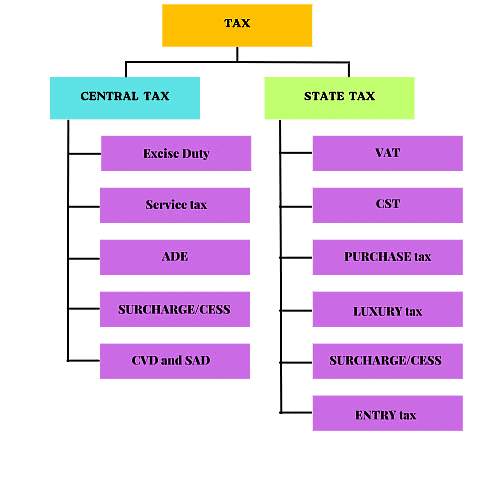
They also receive money from the state governments. It's important for us to work together with our local governments and support them however we can.
In summary, local self-government in cities is vital for democracy, effective services, and community involvement. By giving people a voice in decisions, cities can better meet their diverse needs.
Despite challenges, like limited resources, promoting local governance offers opportunities for transparency, accountability, and innovation. With everyone working together, cities can thrive as inclusive, resilient centers of growth and improvement.
|
47 videos|121 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on Local Self-Government in Cities Class 4 Notes SST
| 1. What is local self-government in cities? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of local self-government in cities? |  |
| 3. How does local self-government benefit cities? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges faced by local self-government in cities? |  |
| 5. How can citizens actively participate in local self-government in cities? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 4 exam
|

|






















