Movements of Earth Class 5 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Rotation? |

|
| Days and Nights |

|
| What is Revolution of Earth? |

|
| Seasons |

|
| Important Facts |

|
Long ago, people thought that the Earth didn't move and everything else moved around it. But Nicolaus Copernicus, who was from Poland and studied the stars, said something different. He said that the Earth spins like a top and moves around the Sun. So, the Earth has two types of movements – it spins around like when you spin around in a circle and it moves around the Sun like when you walk around something.
What is Rotation?
Rotation is when something turns around like a spinning top. For example, when you spin a toy top, it rotates. Similarly, the Earth rotates around its own center, which makes the Sun appear to rise in the east and set in the west.
 Rotation
Rotation
Days and Nights
The Earth's rotation creates periods of day and night. Because the Earth is shaped like a ball, only one side receives sunlight at a time, creating daytime. The other side, which is facing away from the Sun, is in darkness, creating nighttime. Days and Nights
Days and Nights
What is Revolution of Earth?
As the Earth spins on its axis, it also moves around the Sun in a circular path. This movement is known as revolution. The Earth follows a fixed path around the Sun called an orbit, which is shaped like an oval. It takes the Earth approximately 365 days, or one year, to complete one revolution around the Sun.
Seasons
The Earth's revolution around the Sun is responsible for the occurrence of the four seasons: summer, autumn (fall), winter, and spring. This phenomenon occurs due to two main factors: the tilt of the Earth's axis and its orbit around the Sun.
Let us now understand how the seasons change?
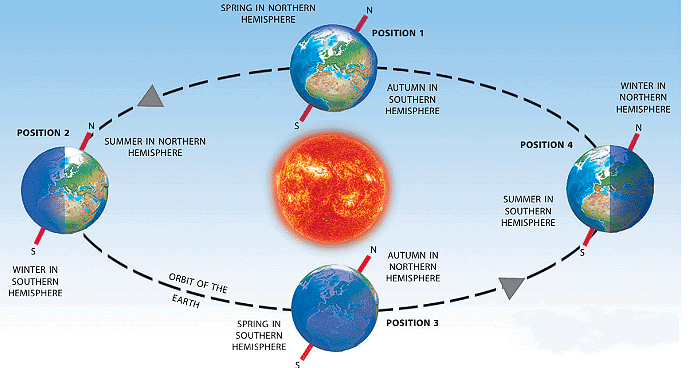
The revolution and tilt of the Earth on its axis cause the four seasons: summer, autumn (fall), winter, and spring. Here's an explanation of the key points:
Note: Revolution of the Earth: The Earth revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit, taking approximately 365.25 days to complete one orbit. This revolution causes the change of seasons.
Tilt of the Earth's Axis: The Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbit around the Sun. This tilt is approximately 23.5 degrees. This tilt is responsible for the varying lengths of daylight and darkness experienced at different times of the year in different parts of the world.
(a) Position 2 (Summer in Northern Hemisphere)
- When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun (Position 2), it receives more direct sunlight, resulting in longer daylight hours and warmer temperatures.
- This leads to summer in the Northern Hemisphere. Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere experiences winter because it is tilted away from the Sun, receiving less direct sunlight and shorter daylight hours.
(b) Position 4 (Summer in Southern Hemisphere)
- When the Southern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun (Position 4), it experiences summer .
- Meanwhile, the Northern Hemisphere experiences winter because it is tilted away from the Sun.
(c) Position 1 and Position 3 (Equinoxes)
- When the Earth is in these positions, the Sun's rays fall directly on the Equator. This results in equal length of days and nights worldwide, known as equinoxes.
- During these times, neither hemisphere is tilted towards or away from the Sun significantly. This results in milder temperatures, neither too hot nor too cold.
- The Northern Hemisphere experiences spring in Position 1 and autumn in Position 3, while the Southern Hemisphere experiences autumn in Position 1 and spring in Position 3.
Note : Leap Year- The Earth actually takes approximately 365.25 days to complete one orbit around the Sun. To accommodate this fractional day, we add an extra day to the calendar every four years, creating a leap year with 366 days instead of the usual 365. This adjustment helps to keep our calendar synchronized with the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
Important Facts
- On June 21, the Northern Hemisphere encounters the longest day and most brief night and the Southern Hemisphere encounters the longest night and most brief day.
- On December 21, the Northern Hemisphere encounters the longest night and most brief day and the Southern Hemisphere encounters the longest day and most brief night.
- Earth finishes its unrest around the Sun in 365 days and 6 hours (365.242199 mean sun based days). Earth's orbital speed midpoints about 29.8 km/s.
- We experience various seasons as the inclined Earth rotates around the Sun. On January 3, the Earth is nearest to the Sun (147.3 million km) known as Perihelion.
- Earth is the farthest from the Sun at 152.1 million km on July 4, known as Aphelion.
 Rotation vs Revolution
Rotation vs Revolution
Conclusion
Earth is the main planet which underpins life. The earth has two sorts of movements, specifically pivot and upheaval. Revolution is the development of the earth on its pivot. The development of the earth around the sun in a fixed way or circle is called Revolution.
Pivot is slanted at a point of 23.5° from the vertical plane or a point of 66.5° from the orbital plane. Earth takes roughly 24 hours to finish one turn. The time of turn is known as Earth day.
|
29 videos|226 docs|48 tests
|
FAQs on Movements of Earth Class 5 Notes SST
| 1. What is the difference between rotation and revolution of the Earth? |  |
| 2. How does the rotation of the Earth affect the length of days and nights? |  |
| 3. How does the revolution of the Earth impact the occurrence of seasons? |  |
| 4. Why do we experience longer days in summer and shorter days in winter? |  |
| 5. How do the movements of the Earth contribute to the concept of time zones? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|

















