Organisms and Cells Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Characteristics of living things |

|
| Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems |

|
| Comparing plant and animal cells |

|
| Specialised cells |

|
Characteristics of living things
All living things carry out certain activities to stay alive. This chapter looks at those life processes, the tiny building blocks called cells, and how cells are specially designed for specific jobs.
Working as a Scientist
- Role of Hypotheses: Scientists generate hypotheses as testable ideas to answer their questions.
- Prediction and Testing: Before experimenting, predictions are made based on these hypotheses.
- Data Collection: Experiments provide data that serve as evidence.
- Drawing Conclusions: Scientists use data to support or refute their hypotheses. Conclusions explain how the evidence supports or contradicts the hypothesis.
Organisms
 Organisms
Organisms
Living organisms carry out certain life processes that keep them alive and allow their existence. These seven life processes are:
Movement: The ability to move parts or the entire body.
Reproduction: Creating new organisms similar to themselves (offspring).
Sensitivity: Detecting and responding to changes in the environment through senses.
Respiration: Releasing energy from food through a chemical process, often requiring oxygen.
Excretion: Eliminating waste substances that can be harmful.
Nutrition: Obtaining necessary substances for survival and growth.
To remember the life processes, make up a sentence using the first letter of each one. Or create a word or phrase using those letters.
An example is: MRS GREN
Movement
- All organisms can move.
- Plants only move some parts of themselves, like their roots move towards the water under soil.
- Animals move their whole bodies to find food, shelter, and escape danger.
Reproduction
- Organisms reproduce to make new organisms like themselves, called offspring.
- Scientists study organism and offspring numbers, especially for rare species, presenting data in tables and bar charts.
Sensitivity
- Organisms sense changes in their surroundings through sensitivity, allowing them to react.
- Many animals use smell and hearing to find food and detect danger for survival.
- Humans have senses like taste, touch, hearing, smell, sight, etc.
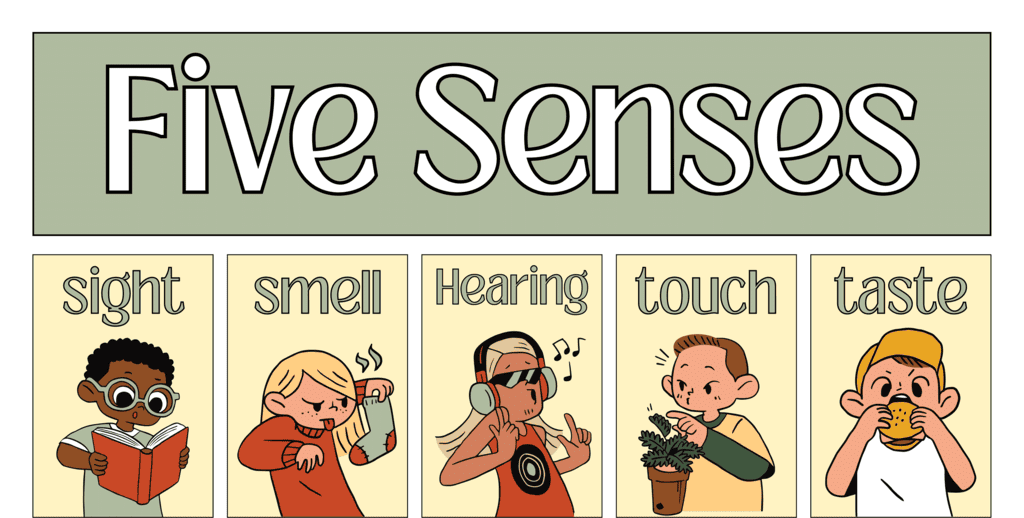 Senses
Senses
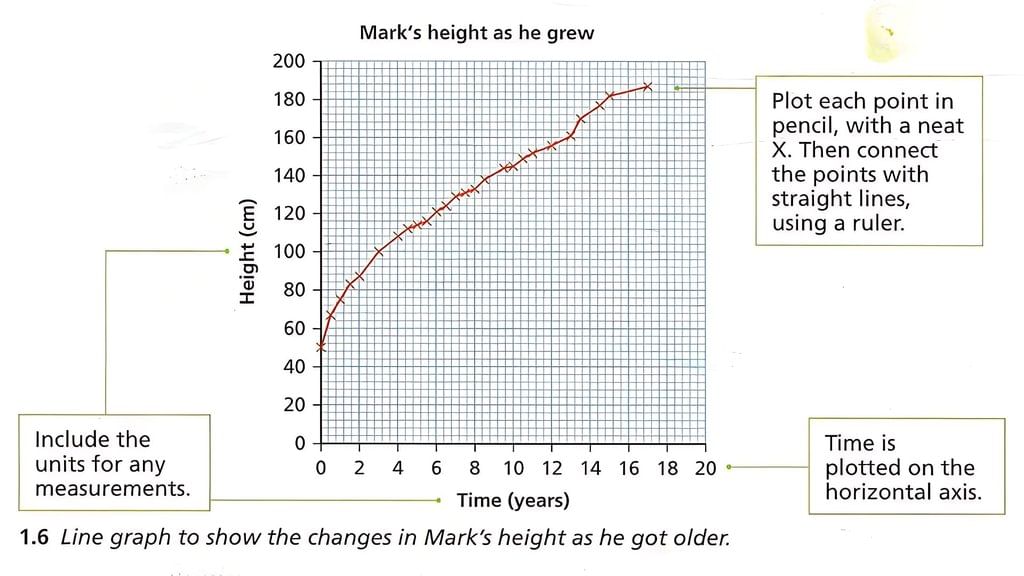
Growth
- All organisms go through a period of growth as they get older.
- Some organisms stop growing but others continue to grow their whole lives.
- We show how something changes with time using a line graph. Line graphs help us to see patterns in data.
Respiration
- All organisms undergo respiration to release energy from food.
- Respiration often needs oxygen and produces waste carbon dioxide gas.
Excretion
- Organisms excrete (eliminate) toxic waste substances that can damage them.
- Many animals excrete liquid wastes like urine.
Nutrition
- Organisms require specific nutrients (substances) to survive, stay healthy, and grow.
- Animals and humans get nutrition from food
- Plants make their own but need small soil nutrients.
- Certain plants like Venus flytraps obtain nutrients from insects in nutrient-deficient soils.
Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems
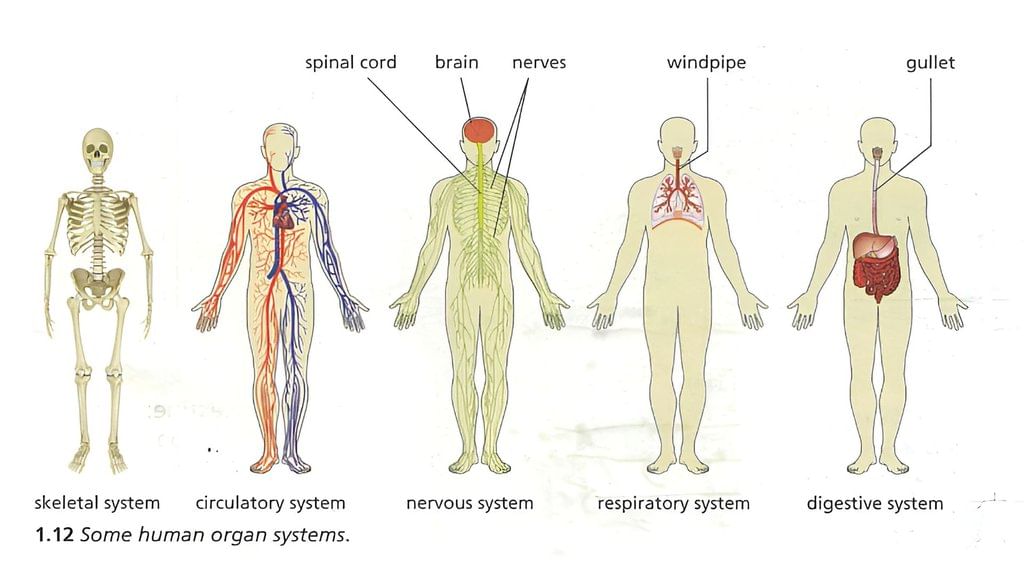
Human Organs:
The body has organs (body parts) with important functions or jobs. Some main human organs and their functions are shown
- Skin: Protects and helps sense things.
- Lungs: Oxygenate the blood and remove carbon dioxide.
- Liver: Synthesizes and breaks down substances.
- Heart: Pumps blood through the circulatory system.
- Stomach: Aids in digesting food.
- Small Intestine: Digests food and absorbs nutrients.
- Large Intestine: Removes water from undigested food.
- Kidneys: Filter blood and produce urine.
- Bladder: Stores urine.
Human Organ Systems
Organs work together in organ systems like the- Circulatory System: Circulates blood throughout the body.
- Nervous System: Controls sensory and motor functions.
- Respiratory System: Manages breathing and gas exchange.
- Digestive System: Breaks down food and absorbs nutrients.
- Skeletal System: Provides structure and facilitates movement.
Plant Organs and Systems
Main Plant Organs:
- Roots: Absorb water and nutrients.
- Stem: Transports substances and supports the plant.
- Leaves: Conduct photosynthesis.
- Flower: Contains reproductive structures.
- Plant Organ Systems: These systems help in the transport of water and nutrients. If a plant lacks water, it wilts.
In flowering plants, roots, stem, and leaves form the water transport system, absorbing, transporting, and distributing water throughout the plant.
Organs and Tissues
- Organs are made of different tissues, which are groups of similar cells performing specific functions.
Comparing plant and animal cells
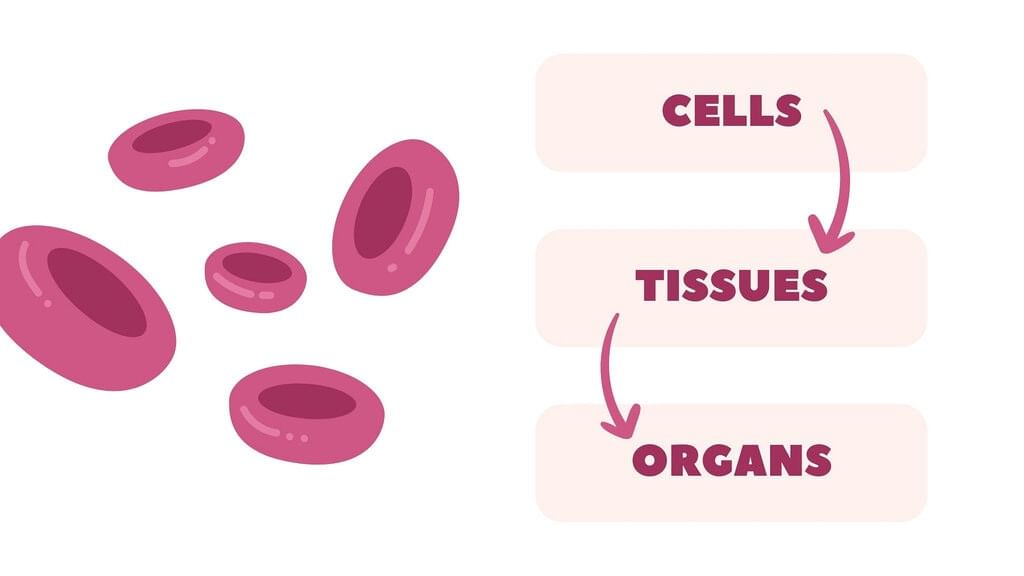
Tissues and Cells:
- Tissues are made of smaller units called cells, the smallest living parts of organisms.
- Groups of cells form tissues, tissues form organs, and organs form systems in large organisms like plants and animals.
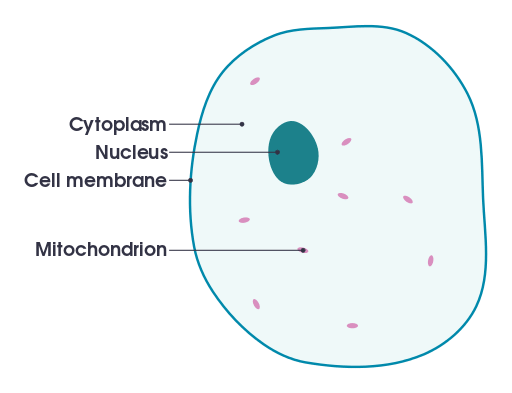
Cell Structure
Animal cells contain a nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and mitochondria (for respiration). Plant cells also have chloroplasts (photosynthesis), a cell wall, and a vacuole.
- Nucleus: Acts as the control center of the cell, dictating various functions and processes.
- Cell Membrane: Serves as a barrier controlling what enters and exits the cell.
- Cytoplasm: A gel-like substance within the cell where new substances are synthesized.
- Mitochondria: Known as the powerhouse of the cell, they are responsible for generating energy through respiration.
- Chloroplasts: Where photosynthesis occurs, allowing the plant to convert sunlight into energy.
- Cell Wall: Provides structure and protection to the cell.
- Sap Vacuole: Stores nutrients and maintains cell structure by exerting pressure on the cell wall.
 Cell Diagram
Cell Diagram
Discovery and Study of Cells
Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665 while studying cork bark under a microscope, calling the box-like structures "cells".
Microscopes
- A light microscope uses light and lenses to magnify objects placed on slides. It is essential not to expose the microscope to direct sunlight as it can cause damage.
Components of a Microscope include:
- Objective Lenses: Increase the magnification of the specimen.
- Stage: Holds the slide in place.
- Light Source and Mirror: Illuminate the specimen.
- Eyepiece Lens: Where you view the magnified image.
Using a Microscope
To use a microscope, the specimen is placed on the stage, and light passes through lenses (objective and eyepiece) to magnify the view.
Unicellular and multicellular organisms
- Multicellular organisms like plants and animals consist of many cells
- Unicellular microorganisms like bacteria and protists are single-celled.
Specialised cells
Plant Cells
- Plant cells contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, except root cells (no light underground).
- Leaves have a layer of palisade cells with many chloroplasts to produce food using light energy (photosynthesis).
- The outer root layer has root hair cells with hair-like projections, increasing surface area for quick water absorption.
Specialized Animal Cells
Animals have specialized cells adapted for specific functions, such as
- Muscle cells muscle cells contain special fibres that allow them to get bigger and smaller.
- Red blood cells carry oxygen it contains haemoglobin (a substance that carries oxygen), and its biconcave shape increases its
surface area, so that it can absorb oxygen quickly
- White blood cells A white blood cell has a very flexible shape allowing it to squeeze into all the different parts of the body. White blood cells fight disease by finding and destroying invading microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses that get inside the body.
- Neurons A neurone (nerve cell) carries signals from one part of the body to another. It is very long, to help carry these signals quickly.
|
64 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Organisms and Cells Chapter Notes - Science for Grade 7
| 1. What are the characteristics of living things? |  |
| 2. What are the components of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems in living organisms? |  |
| 3. How do plant and animal cells differ from each other? |  |
| 4. What are specialised cells in living organisms? |  |
| 5. How do cells contribute to the overall function of an organ system in living organisms? |  |















