Sound Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| How Sound Travels |

|
| Echoes |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
- Sound is energy that travels as waves through air, water, or solids when an object vibrates.
- These vibrations create sound waves that travel to our ears, allowing us to hear.
- Sound waves travel at different speeds: fastest in solids, slower in liquids, and slowest in gases.

- Sound can be loud or soft, high-pitched or low-pitched, depending on its frequency and amplitude.
- We use sound for communication, music, warning signals, and entertainment.
- Understanding sound helps us design better communication systems and enjoy music and movies.
How Sound Travels
Sound travels as energy in the form of waves. Here's how it works:
- Vibration: Sound is produced when an object vibrates, creating vibrations in the surrounding medium (air, water, or solids).
- Compression and Rarefaction: These vibrations create sound waves, which consist of compressions (areas of high pressure) and rarefactions (areas of low pressure).
- Propagation: Sound waves travel from the source of the vibration outward in all directions.
- Medium Dependence: Sound travels fastest through solids, slower through liquids, and slowest through gases due to differences in the density and elasticity of the medium.
- Reception: When sound waves reach our ears, they cause our eardrums to vibrate, which our brain interprets as sound.
How Sounds Are Made
Sounds are produced in various ways:
- Clapping : Clapping your hands creates a sound due to the rapid collision of your hands.
- Elastic : Pulling and releasing an elastic band causes it to vibrate, producing sound.
- Wind Instruments : Blowing into or across a tube causes the air inside to vibrate, creating sound.

Sounds are made by vibrations. When an object vibrates, it causes the surrounding air to vibrate. These vibrations travel through the air to our ears, where they are detected as sound.
Making Air Vibrate
When you pull an elastic band, it moves through a series of positions:
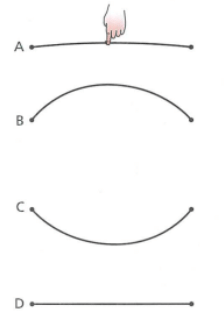
- Position A: The elastic is stretched.
- Position B: The elastic moves to this position.
- Position C: The elastic springs back and moves to this position.
- Position D: The elastic returns to its original position.
As the elastic moves, it causes the air particles surrounding it to also move. These air particles vibrate backwards and forwards along with the elastic.
Sound Waves
When we make sounds:
 How sound travels through air
How sound travels through air
- Some air particles are pushed closer together at first and then spring apart again.
- Others are pulled further apart and then spring back until they are closer together again.
- These vibrations in the air particles create sound waves.
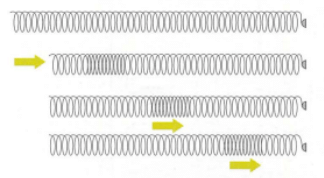 A Wave moves along a slinky spring
A Wave moves along a slinky spring
This process results in the creation of a sound wave.
Echoes
Echoes occur when sound is reflected:
- Sometimes you can hear the echo of your own voice.
- This happens when you shout near a large, hard object like a cliff or a wall.
- The sound waves you produce reflect off the wall and return back to you.
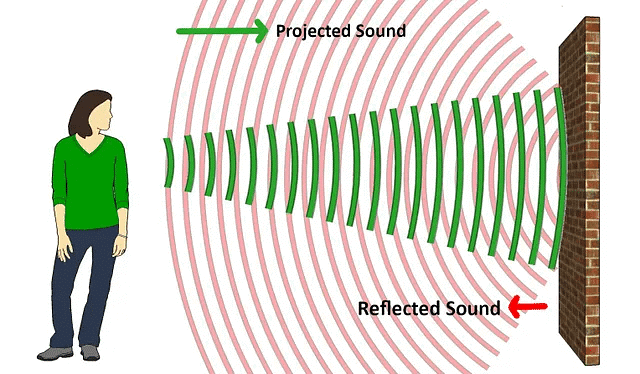
This reflection of sound waves creates an echo.
Using Echoes
Echoes have practical uses:
- Echoes can be used to measure the speed of sound.
- If you know the speed of sound through a medium, you can use echoes to measure the distance between the source of a sound and an object that reflects it.
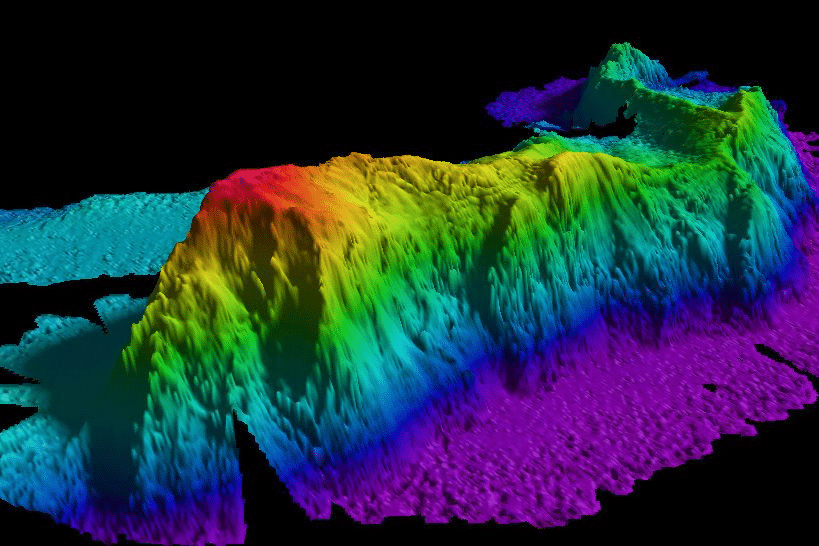 Underwater mountains and volcanoes have been found in the South China Sea using sonar.
Underwater mountains and volcanoes have been found in the South China Sea using sonar.
- This is done by timing how long it takes for an echo to return to the source after hitting the object.
- Ultrasound scans use this principle where special sound waves are sent into the body and reflected back to create images.
- Some animals with poor eyesight, like bats, use echoes to judge distances.
Reducing Echoes
Echoes can sometimes cause problems:
- Rooms with bare walls and tiled floors can make people's voices echo, making it difficult to hear conversations.
- Theatres and concert halls may also have similar problems with echoes.
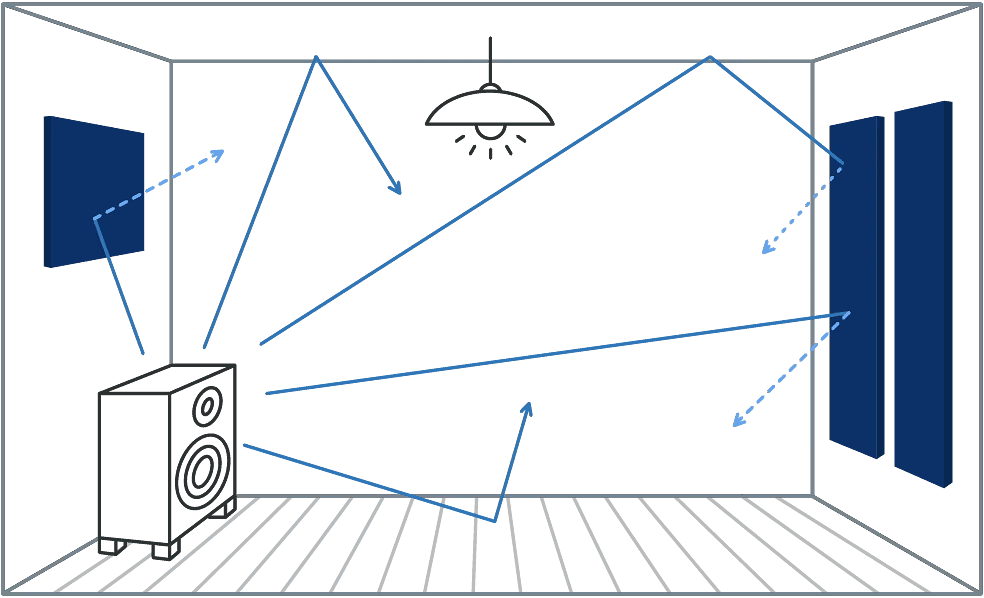
Some materials are good at absorbing energy from sound waves and reducing echoes:
- Hard materials reflect sound better and create stronger echoes.
- Materials that absorb sound energy, like soft materials or special acoustic materials, can help reduce echoes.
Conclusion
- Definition: Sound is a form of energy that travels in waves through mediums such as air, water, and solids.
- Production of Sound: Sound is produced by vibrating objects.
- Propagation: Sound waves require a medium to travel; they cannot travel through a vacuum.
- Types of Waves: Sound waves are longitudinal waves where particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of the wave.
- Properties of Sound:
- Pitch: Determined by the frequency of the sound wave; higher frequency means higher pitch.
- Volume: Determined by the amplitude of the sound wave; larger amplitude means louder sound.
- Speed: Sound travels at different speeds in different mediums; fastest in solids, slower in liquids, and slowest in gases.
- Reflection and Absorption:
- Echo: Sound waves reflecting off surfaces create echoes.
- Absorption: Some materials absorb sound, reducing its intensity.
- Hearing: Humans detect sound using their ears, which convert sound waves into signals that the brain interprets.
|
64 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Sound Chapter Notes - Science for Grade 7
| 1. What is an echo? |  |
| 2. How is the distance of an object calculated using an echo? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the formation of echoes? |  |
| 4. How can echoes be used in everyday life? |  |
| 5. How does the phenomenon of echoes contribute to the understanding of sound waves? |  |















