Chemical Reactions and Equations | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Physical and Chemical Change |

|
| Chemical Reactions |

|
| Types of Chemical Reactions |

|
| Oxidation and Reduction |

|
Physical and Chemical Change

- Physical Change: Changes that only affect physical properties like color, density, hardness, melting point, etc., without altering the chemical composition of the matter. These changes can be reversed by adjusting temperature and pressure.
- Examples include crystallization, sublimation, boiling, vaporization, cutting trees, dissolving salt in water, burning wax, and melting ice.
- Chemical Change: Changes that alter both the composition and chemical properties of matter, resulting in the formation of a new substance. Chemical changes are generally irreversible by changing temperature and pressure.
- Examples include burning a candle (producing gases), photosynthesis, ripening of fruits, electrolysis of water, digestion, burning paper, and souring of milk.
Chemical Reactions
- A chemical reaction involves a chemical change in which substances react to produce new substances.
- In our daily life, we come across many different types of chemical reactions. e.g. If milk is kept at room temperature for a few hours during summer, it becomes sour and turns into thick curdy mass.
- Iron articles when exposed to humid atmosphere, they get rusted.
- A freshed cut piece of apple turns brown after sometime. The cooking and digestion of food also involves chemical reactions.
- Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame and changes into a white powder. This powder is magnesium oxide. This is an example of a chemical reaction.
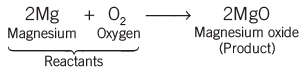
- A chemical reaction can be observed with the help of any of the following observations:
- Change in state
- Change in colour
- Evolution of a gas
- Change in temperature
- A chemical reaction involves bond breaking or bond formation between any two atoms to produce new substances.
Types of Chemical Reactions
Combination Reactions:
- Take a small amount of calcium oxide in a beaker and add water. Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water and produce slaked lime with the release of a large amount of energy.
- This is an example of combination reaction. In a combination reaction, two or more substances combine to form a single product.
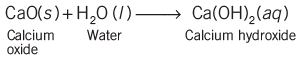
Decomposition Reactions:
In a decomposition reaction, a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.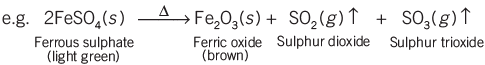
These reactions require energy in the form of heat, light, or electricity. Therefore, decomposition reactions come in three forms: thermal breakdown, light breakdown, and electrolysis.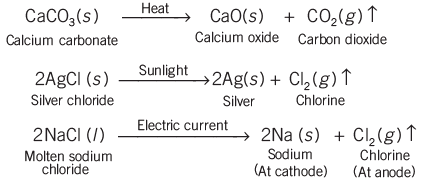
Below are examples of each:
- Thermal breakdown: Heat is used to break down the compound.
- Light breakdown (photolysis): Light energy is used to cause the breakdown.
- Electrolysis: Electricity is used to decompose the compound.
Dissociation Reactions:
Reversible reactions where a molecule dissociates into simpler molecules by heat or light.

Displacement Reactions:
- When an iron nail is placed in a copper sulphate solution, it turns brown, and the blue color of the solution fades. This shows that iron has replaced copper in the solution, which is a type of displacement reaction.
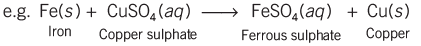
- Displacement reactions often involve a change in color, where a more reactive substance takes the place of a less reactive one in a solution.
- When sodium sulphate is mixed with barium chloride, a white substance that doesn't dissolve in water forms. This substance is known as a precipitate, and the reaction is termed a precipitation reaction, a type of double displacement reaction.
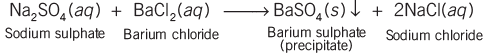
- In displacement reactions, ions are exchanged between the reacting substances to form new compounds.
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions:
- Exothermic Reactions: Heat is released along with product formation. Example: Burning fuel.
- Endothermic Reactions: Heat is absorbed during the reaction.
Reversible and Irreversible Reactions:
- Reversible Reactions: Occur in both forward and backward directions but never go to completion.
- Irreversible Reactions: Occur only in the forward direction and reach completion.
Redox Reactions:
Involve oxidation and reduction as two half-reactions. Examples include fuel combustion, electrochemical processes like sodium hydroxide manufacturing, photosynthesis, food digestion, battery functions, and metal corrosion. These reactions involve both oxidation and reduction processes.
Oxidation and Reduction
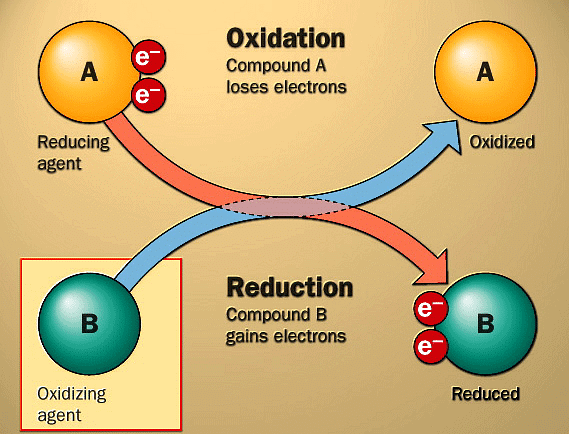
- Originally, when a substance gains oxygen, it was called oxidation.
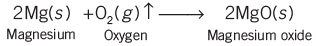
- Later, taking hydrogen away from a substance was also seen as oxidation.
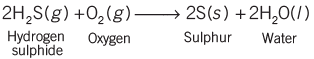
- The role of electrons in oxidation is crucial.
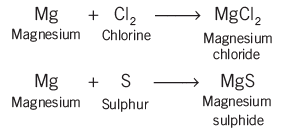
- In oxidation reactions, for example, magnesium changes into magnesium 2 ion and loses two electrons, showing that electrons are lost in oxidation.
- The concept of reduction was first used for processes turning metal oxides into metals using hydrogen, carbon, or carbon monoxide.
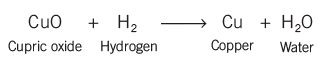
- Removing oxygen from a substance was considered as reduction.
- In reduction reactions, like when copper 2 changes into copper and gains two electrons, electrons are gained.
- Oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously and equally in a redox reaction.
- Oxidising agent (Oxidant): It's a substance that receives electrons in a chemical reaction, meaning electron acceptors are oxidising agents. All positively charged species act as oxidising agents, which are also Lewis acids.
- Reducing agent (Reductant): The substance that gives electrons in a chemical reaction is known as a reducing agent, so electron donors are reducing agents. All negatively charged species are reducing agents, which are also Lewis bases.
Rules for Determining Oxidation States
- The oxidation state of an element in its free or uncombined state is zero.
- The oxidation state of hydrogen is typically +1, but it is -1 in hydrides.
- The oxidation state of oxygen is usually -2, but it is -1 in peroxides.
- The oxidation state of elements in Group IA, IIA, and IIIA of the periodic table is +1, +2, and +3, respectively.
- The oxidation state of any ion equals its charge.
- The algebraic sum of oxidation states of all elements in a neutral molecule is zero.
- The algebraic sum of oxidation states of all elements in a polyatomic ion equals the charge of the ion.
- In halides (binary compounds with halogens), the oxidation state of halogens is -1.
- Oxygen exhibits a positive oxidation state in OF2.
|
478 videos|1421 docs|396 tests
|
FAQs on Chemical Reactions and Equations - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the difference between a physical and chemical change? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 3. How can oxidation and reduction be defined in the context of chemical reactions? |  |
| 4. Why are chemical reactions important in everyday life? |  |
| 5. How can chemical reactions be represented using chemical equations? |  |




















