Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Circular Motion
Circular Motion | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Circular Motion
- Velocity is a vector quantity, and the velocity of an object is its speed in a given direction
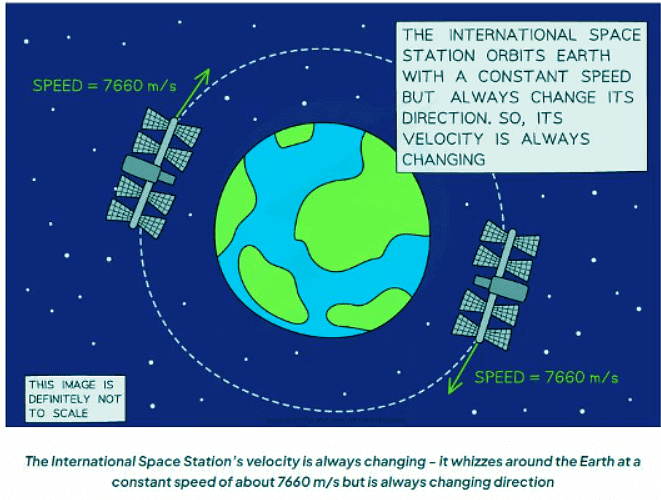
- When an object moves in a circular path, its velocity constantly changes.
- Even if the object's speed remains constant, it always changes direction as it follows the circular path.
- This means that an object in circular motion maintains a steady speed but experiences a varying velocity.
- An object moving in circular motion maintains a consistent speed but experiences altering velocity.
- The image depicted below provides an illustration of a well-known object following a circular path. Despite its steady speed, this object undergoes shifts in direction.
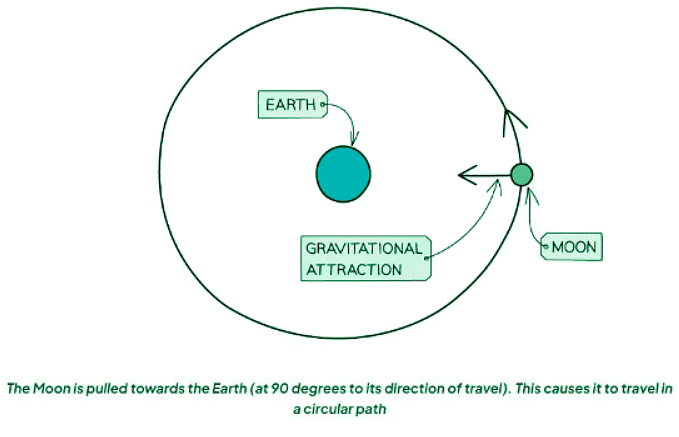
- When a force acts at 90 degrees to an object’s direction of travel, the force will cause that object to change direction

- If the force continues to act at 90 degrees to the motion, the object will keep changing its direction (whilst remaining at a constant speed) and travel in a circle
- This phenomenon is exemplified by the orbital motion of planets around stars or satellites around planets.

- The force required for an object to move in a circle is influenced by several factors:
- The mass of the object: A heavier object requires more force to maintain constant speed and radius.
- The speed of the object: Higher velocities demand greater force with constant mass and radius.
- The radius of the circle: A smaller circle necessitates more force to sustain speed and radius.
Question for Circular MotionTry yourself: What happens to the velocity of an object moving in a circular path?View Solution
The document Circular Motion | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Circular Motion - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is circular motion? |  |
Ans. Circular motion is the movement of an object in a circular path around a fixed point. This type of motion involves constant changes in direction but not necessarily in speed.
| 2. How does force play a role in circular motion? |  |
Ans. In circular motion, a centripetal force is required to keep an object moving in a circular path. This force acts towards the center of the circle and is necessary to prevent the object from moving in a straight line.
| 3. What are some key concepts to understand in circular motion? |  |
Ans. Some key concepts in circular motion include centripetal force, centripetal acceleration, angular velocity, and radius of the circular path. These concepts are essential in understanding the dynamics of objects moving in circular paths.
| 4. How does circular motion relate to real-life examples? |  |
Ans. Circular motion can be seen in various real-life scenarios, such as the motion of a car around a curve, the rotation of a Ferris wheel, or the orbit of planets around the sun. Understanding circular motion is crucial in explaining these everyday phenomena.
| 5. What are some common misconceptions about circular motion? |  |
Ans. One common misconception is that an object in circular motion experiences a centrifugal force pushing it outward. In reality, it is the centripetal force acting towards the center that keeps the object in its circular path. Understanding this distinction is important in grasping the dynamics of circular motion.
Related Searches