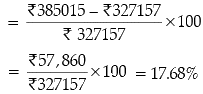Class 12 Economics: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term I (2021-22)- 2 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XIITime: 90Max. Marks: 40 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 90
Max. Marks: 40
General instructions:
- The Question Paper contains 3 sections.
- Section - A has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section - B has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section - C has 12 questions. Attempt any 10 questions.
- All questions carry equal marks.
- There is NO negative marking.
Section - A
Q.1: Who regulates money supply in India?
(a) Government of India
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) Commercial Banks
(d) Planning Commission
Correct Answer is Option (b)
RBI is the top monetary authority in the country who print currency and regulates money supply through its monetary policy.
Q.2: India entered the _________ stage of Demographic Transition after the year 1921.
(a) forth
(b) second
(c) third
(d) first
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The first stage of demographic transition was experienced in India, during the period of 1891-1921.
Q.3: Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: One of the worst impacts of fall in handicraft industry was the high level of unemployment.
Statement 2: Export of finished goods from India to Britain.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Due to decline of handicraft industry, unemployment level in the country increased. This decline was also caused because foreign goods were cheaper than Indian goods. Hence, it leads to import of finished goods from Britain.
Q.4: Fiscal Deficit equals:
(a) Interest payments
(b) Borrowings
(c) Interest payments less borrowing
(d) Borrowings less interest payments
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Fiscal deficit refers to the excess of total expenditure over total receipts excluding borrowings. It indicates borrowing requirements of the government.
Q.5: Identify the correct pair as given in Column B by matching them with respective concepts in Column A:
(a) 1 – a
(b) 2 – b
(c) 3 – c
(d) 4 – d
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Devaluation refers to fall in the value of domestic currency due to deliberate increase in foreign exchange rate by the government which follows fixed exchange rate system.
Q.6: Which of the following statements is true?
(a) M1 is the most liquid measure of money supply.
(b) M2 is the most liquid measure of money supply.
(c) M3 is the most liquid measure of money supply.
(d) All the statements are true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
M1 includes all forms of assets that are easily exchangeable as payment for goods and services. It consists of coin and currency in circulation and demand deposits, as payment for goods and services.
Q.7: Identify the correct matched pair from Column A to Column B: 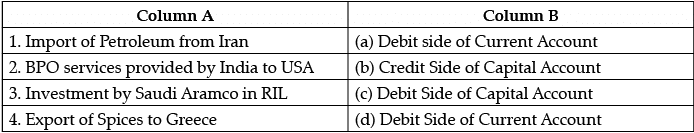
(a) 1 – a
(b) 2 – b
(c) 3 – c
(d) 4 – d
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Import of goods and services are recorded in current account as it is import of visible item. Import is recorded on the debit side as it leads to an outflow of foreign exchange in the country.
Q.8: Choose the correct pair of statements from the set of statements given in column I and column II:
(a) 1 – a
(b) 2 – b
(c) 3 – c
(d) 4 – d
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Subsistence farming is that farming in which crops are grown for own use rather than sale in the market. Commercial farming is that agriculture system in which crops are produced for sale in the market.
Q.9: Find out the revenue expenditure if revenue deficit is ₹ 50 crore, revenue receipts are ₹ 75 crore and capital receipts are ₹100 crore?
(a) ₹ 125 crore
(b) ₹ 100 crore
(c) ₹ 75 crore
(d) ₹ 50 crore
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Revenue deficit = Revenue expenditure – Revenue receipts
50 = Revenue expenditure – 75
Revenue expenditure = 75 + 50 = ₹125 crores
Q.10: Government uses _________ tax system to reduce inequalities in incomes.
(a) Progressive
(b) Proportional
(c) Regressive
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Government can intervene to promote equity and reduce inequality and poverty, through the tax and benefits system. Progressive tax system means more tax from those in higher levels of income and redistribute them through welfare benefits to those in lower levels of incomes.
Q.11: The teacher was discussing in the class with students “Foreign exchange transactions which are independent of other transactions in the balance of payment account.”
Identify the above statement about which type of foreign exchange transactions the teacher is talking about?
(a) Current transactions
(b) Capital transactions
(c) Autonomous transactions
(d) Accommodating transactions
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Autonomous transactions are independent of all other transactions in the BOP. These transactions are not influenced by the foreign exchange position of the country. Exports, imports, etc. are some example.
Q.12: On comparing data of graph, estimate whether the number of rural poor has declined or increased in the year 2011-12 as compared to 1973-74?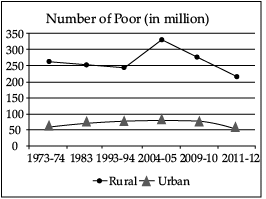
(a) increased
(b) decreased
(c) remained same
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The number of poor people has decreased from more than 320 million people in the year 1973-74 to more than 270 million people in the year 2011-12.
Q.13: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: The urban poor are largely the overflow of the rural poor.
Statement 2: Rural poor had migrated to urban areas in search of alternative employment and livelihood.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statements are true.
(b) Both the Statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The urban poor are largely the overflow of the rural poor who had migrated to urban areas in search of alternative employment and livelihood, labourers who do a variety of casual jobs and the self-employed who sell a variety of things on roadsides and are engaged in various activities.
Q.14: Ms. Anu, an economics teacher was discussing the concept of "the rate wherein loans are provided by central bank to commercial banks for their long-term needs."
Select the correct alternative from the following which explains the above concept.
(a) Repo rate
(b) Bank rate
(c) Open market operations
(d) Margin requirements
Correct Answer is Option (b)
It is the rate of interest at which Central Bank gives loan to the commercial banks without any security to cope with immediate cash crunch.
Q.15: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Growth of rural economy depends primarily on infusion of capital, from time to time.
Statement 2: Infusion of capital realises higher productivity in agriculture and non-agriculture sectors.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statements are true.
(b) Both the Statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Growth of rural economy depends primarily on infusion of capital, from time to time, to realise higher productivity in agriculture and nonagriculture sectors. As the gestation gap between crop sowing and realisation of income after production is quite long, farmers borrow from various sources (formal and informal) to meet their requirements on seeds, fertilisers, etc. and other family expenses of marriage, religious ceremonies, etc.
Q.16: The current account records exports and imports in _________ and _________ and _________. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
i. Goods
ii. Services
iii. Transfer payments
iv. International purchases
Identify the correct alternatives from the following:
Alternatives:
(a) i, ii and iv
(b) i, ii and iii
(c) iii, ii, and iv
(d) iv, i, and iii
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Current account contains the receipts and payments relating to all the transactions of visible items, invisible items and unilateral transfers.
Q.17: Calculate initial deposits if it is given that total deposits created by commercial banks is ₹ 20,000 and legal reserve requirements is 30%.
(a) ₹ 6,000
(b) ₹ 5,000
(c) ₹ 4,000
(d) ₹ 3,000
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Total deposit = Initial deposit × (1/LRR)
₹ 20,000 = Initial deposit × (1/30%)
₹ 20,000 = Initial deposit × (100/30)
Initial deposit = (₹20 000x30)/100
∴ Initial deposit = ₹ 6,000
Q.18: With which, disparity of income and its distribution are associated?
(a) Absolute Poverty
(b) Relative Poverty
(c) Chronic Poverty
(d) All of these
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Relative poverty means poverty defined in comparison to other people’s standing in the economy.
Q.19: Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Expenditure on Ujjwala Yojana launched by the Government is an example of capital expenditure.
(b) Expenditure on Ujjwala Yojana launched by the Government is an example of Revenue Expenditure.
(c) Expenditure on Ujjwala Yojana launched by the Government is an example of Deferred Revenue Expenditure.
(d) None of the statements are correct.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Expenditure on Ujjawala Yojana by the government is an example of revenue expenditure as it leads to neither creation of asset nor reduces liability.
Q.20: In how many categories industries were divided in Industrial Policy, 1956?
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 5
(d) 4
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Industries were divided into 3 categories in Industrial Policy, 1956:
Schedule A: Industries that are exclusively owned by the state.
Schedule B: In this, Industries can be under the private sector, but the starting of the new units will be under the public sector control.
Schedule C: Some industries will be under the private sector, but these have to take a license from the public sector.
Q.21: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: The government affects the personal disposable income of households.
Statement 2: Market Mechanism attempts to bring about a distribution of income.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statements are true.
(b) Both the Statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Through its tax and expenditure policy, the government attempts to bring about a distribution of income that is considered ‘fair’ by society. The government affects the personal disposable income of households by making transfer payments and collecting taxes and, therefore, can alter the income distribution. This is the distribution function.
Q.22: When was NABARD constituted?
(a) July, 1982
(b) June, 1982
(c) July, 1980
(d) July, 1984
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was set up in July 1982 as an apex body to coordinate the activities of all institutions involved in the rural financing system.
Q.23: Government uses _________ tax system to reduce inequalities in incomes.
(a) Progressive
(b) Proportional
(c) Regressive
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Government can intervene to promote equity and reduce inequality and poverty, through the tax and benefits system. Progressive tax system means more tax from those in higher levels of income and redistribute them through welfare benefits to those in lower levels of incomes.
Q.24: Suppose that there is a surplus in balance of trade of ₹ 10,000 crore. The import of goods is one-third of the export of goods to the rest of the world. The value of exports are ₹_________crore.
(a) ₹ 20,000 crore
(b) ₹ 15,000 crore
(c) ₹ 30,000 crore
(d) ₹ 25,000 crore
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Balance of trade = Exports – Imports
₹10,000 crores = Exports – Exports/3
₹10,000 crores = (3 Exports – Exports)/3
₹10,000 ×3 = 2 Exports
Exports = ₹30,000/2
Exports = ₹15,000 crores
Section - B
Q.25: Which of the following is false regarding SHGs?
(i) Self-Help Groups have emerged to fill the gap in the informal credit system
(ii) Improve rural’s poor access to formal credit system
(iii) Provide rural credit by mobilising their own resources
(iv) Small and informal association of poor persons
Choose the correct option:
(a) Only (i)
(b) Only (i) and (ii)
(c) Only (ii) and (iii)
(d) Only (iv)
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Self-Help Groups (SHGs) have emerged to fill the gap in the formal credit system because the formal credit delivery mechanism has not only proven inadequate but has also not been fully integrated into the overall rural social and community development.
Q.26: Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Income tax is a direct tax.
Statement 2: The burden of the direct tax can be shifted to others.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Direct tax is a tax whose burden cannot be shifted to others, i.e., the incidence and impact of the tax is imposed on the same person. For example, income tax.
Q.27: Choose the correct pair of statements from the set of statements given in Column I and Column II: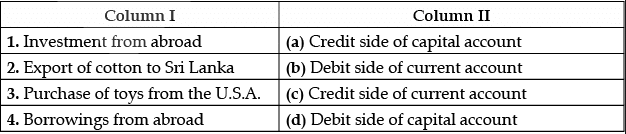
Alternatives:
(a) 1 – a
(b) 2 – b
(c) 3 – c
(d) 4 – d
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Self-Help Groups (SHGs) have emerged to fill the gap in the formal credit system because the formal credit delivery mechanism has not only proven inadequate but has also not been fully integrated into the overall rural social and community development.
Q.28: Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Building of Dam is a Revenue Expenditure of the government.
Reason (R): Revenue Receipts are receipts of the government which neither create any liabilities nor reduce any assets.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Building of Dam is a capital expenditure as it will result in the increase of the infrastructure of the country.
Q.29: Calculate the value of current account balance from the following data: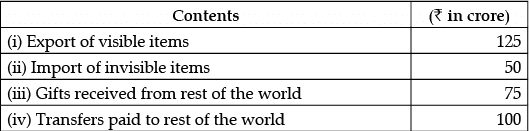
(a) ₹ 50 crore
(b) ₹ 100 crore
(c) ₹ 75 crore
(d) ₹ 80 crore
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Current account balance = Export of visible items – Import of invisible items + Gifts received from rest of the world – Transfers paid to rest of the world
= ₹ 125 – ₹ 50 + ₹ 75 – ₹ 100
= ₹ 50 crores
Q.30: Identify the correct statement from the following.
(a) British government developed air and water transport to the level of world-class infrastructure.
(b) Railways were introduced in India in 1848.
(c) The system of Electric Telegraph was introduced not to serve the purpose of maintaining law and order.
(d) Roads were constructed so that army could be mobilized within India and raw material could be moved to ports to be sent to England.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
As Britishers main motive behind construction of roads was to mobilize army within India and to move raw material to parts so that they can be sent to England.
Q.31: Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Borrowing from IMF in an accommodating item.
Reason (R): Accommodating item refers to transactions that take place because of other activities in Balance of Payment.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The government borrows from the IMF when it falls deficit in the Balance of Payment, thus it is an accommodating item as it took place due to excessive government spending.
Q.32: If in the government budget, revenue receipts are ₹ 75,000 crore and borrowings is equal to ₹ 90,000 crore. Calculate the fiscal deficit:
(a) ₹ 75,000 crore
(b) ₹ 80,000 crore
(c) ₹ 90,000 crore
(d) ₹ 15,000 crore
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Fiscal deficit = Borrowings = ₹90,000 crores
Q.33: Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Occupational structure can be defined as when working persons are distributed among different industries and sectors.
Statement 2: During the British rule, the agricultural sector share was low in workforce as compared to manufacturing and service sector.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statements are true.
(b) Both the Statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but Statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
During the British rule, the share of agriculture sector in workforce was high as compared to manufacturing and service sector. Hence, statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
Q.34: Rural development implies:
(a) Spread of agriculture among rural people
(b) Development of agriculture
(c) Providing health facilities in rural areas
(d) Everything that raises quality of life of rural people
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Rural development is a comprehensive term which essentially focuses on action for the development of areas that are lagging behind in the overall development of the village economy. It is a process whereby the standard of living of rural people, especially poor people, rises continuously.
Q.35: ______ can be defined as when the equity of public sector undertakings (PSUs) is sold to the private sector.
The above mentioned depicts the concept of:
(a) Globalisation
(b) Privatisation
(c) Liberalisation
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Privatisation can be defined as transfer of ownership from government to private sector.
Q.36: The industrial sector reform includes _________.
(a) Removal of industrial licensing
(b) Development of private banks
(c) Devaluation of rupee
(d) Reduction in taxes
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The industrial sector reform includes removal of industrial licensing, fall in role of public sector, and dereservation under small scale industries.
Q.37: Choose the correct alternative given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
Assertion (A): M3 and M4 are considered Broad Money.
Reason (R): M3 and M4 refers to currency held by public, demand deposits and time deposits.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Assertion(A) is true but reason (R) is false as M3 and M4 are considered as broad money but M3 and M4 are not only the currency held by the public, demand deposits and time deposits but also includes total deposits with the post office saving bank excluding National Saving Certificates.
Q.38: Identify the incorrect statement from the following:
(a) There was huge burden of debts before following the policy of economic reforms of 1991.
(b) India’s foreign exchange reserves were declining in 1991.
(c) There was surplus in Balance of Payments on the eve of independence.
(d) Price level was rising due to increase in money supply on the eve of independence.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
As statement given in option (C) is incorrect because in balance of payment before 1991, there was deficit.
Q.39: Refer to the following table for answering:
Which among the following statement is true from the given table?
(a) Life expectancy has increased over the years.
(b) Life expectancy has decreased over the years.
(c) Life expectancy remains same over the years.
(d) All of the above.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Life expectancy means the average number of years a person is expected to live and as the table shows that life expectancy has increased over the years of both males and females.
Q.40: Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Money Supply refers to the stock of money.
Reason (R): Money supply refers to volume of money held by public for transactions or settlement of debts.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Money supply can be defined as stock of money available with the public at a particular point of time. It means total volume of money held by public, used for transactions and for repaying debts.
Q.41: From the set of statements given in Column I and Column II, choose the correct pair of statements:
Alternatives:
(a) 1-ii, 2-iii, 3-i, 4-iv
(b) 1-ii, 2-i, 3-iv, 4-iii
(c) 1-iv, 2-ii, 3-i, 4-iii
(d) 1-ii, 2-iv, 3-i, 4-iii
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.42: Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Farmers did not have proper storage facilities to keep back their produce for selling laten at a better price.
Statement 2: Agricultural marketing needs to be improved through better infrastructural facilities.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statements are true.
(b) Both the Statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but Statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
When farmers sell their output to traders, they face the problem of faulty weighing and manipulation of their accounts. Farmers who did not have the required information on prices prevailing in markets were often forced to sell at low prices. Farmers also did not have storage facility. Thus, agricultural marketing need to be improved through better infrastructural facilities.
Q.43: MSP stands for _________.
(a) Maximum support price
(b) Minimum support price
(c) Maximum social price
(d) Minimum storage price
Correct Answer is Option (b)
MSP stands for minimum support price. MSP is decided by the government so that farmers' interest can be protected.
Q.44: Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Finished goods were exported from India during the Colonial Era.
Reason (R): India was a hub for raw materials for British Industries.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
From the time of Independence, India has been one of the important trading countries, exporting primary items like cotton, raw silk, sugar, wool, jute, and indigo, etc. and importer of finished consumer goods like woollen clothes, cotton, silk, and capital goods like light machinery manufactured in Britain.
Q.45: The imposition of education cess of _________ by the government of India on all Union taxes means that money so collected will be spent on elementary education only.
(a) 3 %
(b) 2 %
(c) 4 %
(d) 1 %
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The education cess of 2% was imposed by the government of India on all union taxes which means that money so collected will be spent on elementary education only.
Q.46: Choose the correct alternative given below for the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A) : To increase foreign trade, we should resort to reducing tariff rates, giving credit facilities to exporters from foreign markets and make available better infrastructural facilities to exporters.
Reason (R): Foreign trade boosts the economy of the country.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Foreign trade can be increased by resorting to reducing tariff rates, by giving credit facilities to exporters from foreign markets and thus make available better infrastructural facilities to said exporters. By this, it boosts the economy of the country.
Q.47: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: People spend to acquire information relating to the labour market and other markets like education and health.
Statement 2: People want to know the level of salaries associated with various types of jobs, whether the educational institutions provide the right type of employable skills and at what cost.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statements are true.
(b) Both the Statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
This information is necessary to make decisions regarding investments in human capital as well as for efficient utilisation of the acquired human capital stock.
Q.48: _____ is the important source of occupation for the women.
(a) Fishing
(b) Agriculture
(c) Livestock farming
(d) Horticulture
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Rural women perform numerous labour intensive jobs such as weeding, hoeing, grass cutting, picking, cotton stick collection, separation of seeds from fibre, keeping of livestock and its other associated activities like milking, milk processing, preparation of ghee, etc.
Section - C
Q.49: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data: (in ₹ Crores)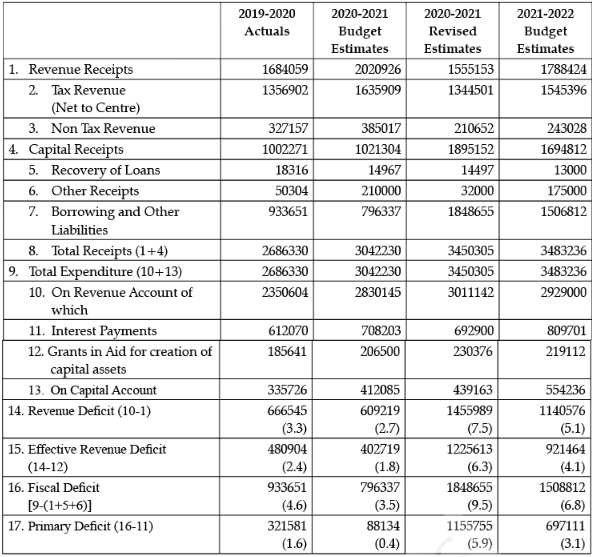
The value of recovery of loans has___________ crores between 2019-20 (Actual) and 2020-21 (Budgeted Estimate). (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
(a) fallen by ₹3349
(b) risen by ₹3349
(c) fallen by ₹3439
(d) risen by ₹3439
Correct Answer is Option (a)
2019-2020 (Actual) : ₹18316 crore
2020-2021 (Budgeted Estimates) : ₹ 14967 Crore
Change in Value = ₹ 14967 – ₹ 18316 = (–) ₹ 3349 crores
Q.50: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data: (in ₹ Crores)
The percentage change in the Non-tax Revenue, between 2019-20 (Actual) and 2020-21(Budgeted Estimate), taking the 2019-20 as base, would be ____________. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
(a) 15.02%
(b) 16.20%
(c) 17.68%
(d) 20.01%
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Non-Tax Revenue for :
2019-20 (Actual) = ₹ 327157 crore2020-21 (Budgeted Estimates) = ₹ 385017
Percentage Change
Q.51: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data: (in ₹ Crores)
Identify which of the following is not an example of tax revenue for the government: (Choose the correct alternative)
(a) Wealth Tax
(b) Special Assessments
(c) Income Tax
(d) Corporate Tax
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Tax revenue can be defined as receipts from taxes of the government. Tax revenue is of two types: Direct taxes and Indirect taxes.All other three options i.e. wealth tax, income tax, and corporate tax are a part of direct taxes under tax revenue. Whereas, special assessment is a part of non-tax revenue. Special assessment can be defined as payment made by owners of assets (like land, building) whose value has risen due to government developmental activities.
Q.52: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data: (in ₹ Crores)
Identify the correct formula to calculate Fiscal Deficit.
(a) Total expenditure-Total Receipt ( other than borrowings)
(b) Revenue Expenditure/Revenue Receipt
(c) Capital Expenditure/Capital Receipt
(d) Revenue Expenditure + Capital expenditure/Revenue Receipt
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Fiscal deficit is the difference between total expenditure and total receipts excluding borrowings. In other words, fiscal deficit is equal to borrowings by the government.
Fiscal deficit = Total expenditure – Total receipts excluding borrowings
Fiscal deficit = (Revenue expenditure + capital expenditure) – (Revenue receipts + capital receipts excluding borrowings)
Q.53: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data: (in ₹ Crores)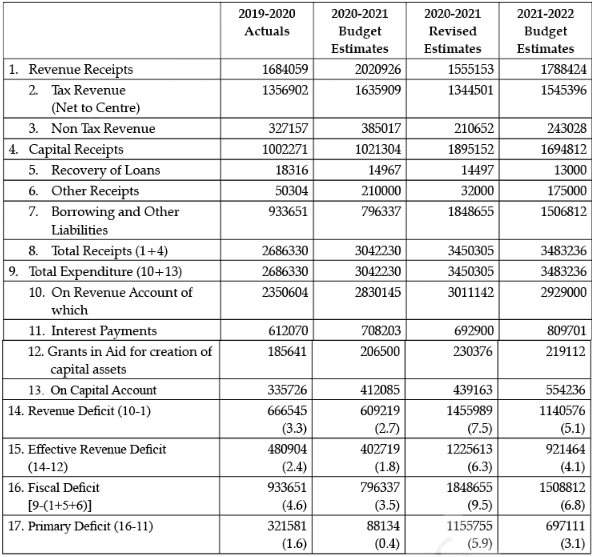
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1 : Revenue and Capital receipts are increasing but borrowings and other liabilities are reducing.
Statement 2 : Grants in aid for creation of capital assets decreased from 2019 to 2021.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Grants in aid for creation of Capital assets increased from 2019 to 2021 as it was ₹ 185641 crores in 2019 and ₹ 206500 crores as budgeted estimates for 2021.
Q.54: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data: (in ₹ Crores)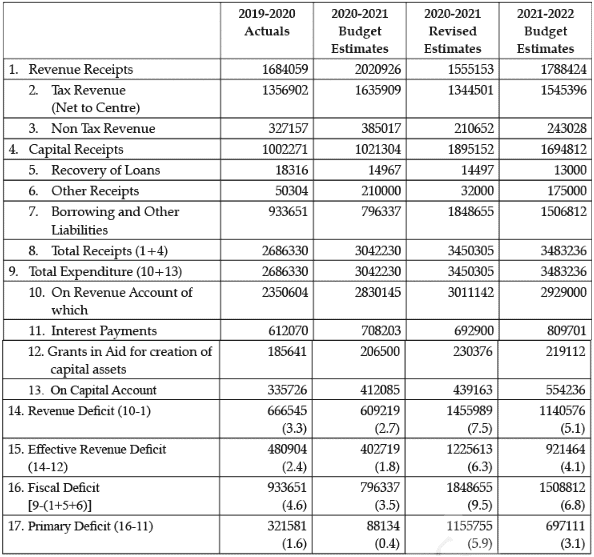
The value of Primary Deficit for the year 2020-21, would be ₹_____________ crores. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
(a) 88134
(b) 321581
(c) 96133
(d) 609219
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.55: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data:
India’s post-1990 economic strategy entailed three important breaks with the past:
- To dismantle the vast network of controls and permits that dominated the economic system.
- To redefine the role of the state as a facilitator of economic transactions and as a neutral regulator rather than the primary provider of goods and services.
- To move away from a regime of import substitution and to integrate fully with the global trading system.
The 1991 reforms unleashed the energies of Indian entrepreneurs and gave untold choice to the consumers and changed the face of the Indian economy. The reform agenda constituted a paradigm shift, and has defined the broad contours of economic policy making for three decades.
Liberalization was adopted as the guiding principle of governance and all governments since 1991, have broadly stuck to that path.
Today we don’t need a paradigm shift. We need to look at individual sectors and see which one of these needs, reforms to create a competitive environment and improve efficiency. The power sector, the financial system, governance structures and even agricultural marketing need reforms.
Today’s reforms also require much more discussion and consensus-building. The central government needs to work in tandem with state governments and consult different stakeholders impacted by reform decisions. Timing and sequencing are critically important in the new reforms’ agenda.
Source: Excerpts from ‘Like 1991, the 2021 crisis presents an opportunity, by C.Rangarajan, 22nd January 2021.
According to the given text, ________ was adopted as the guiding principle of governance and all governments since 1991.
(a) Modernization
(b) Liberalisation
(c) Privatization
(d) Globalization
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Liberalisation was adopted as the guiding principle of governance and all governments since 1991. Liberalisation means reducing government control and giving greater autonomy to private sector so as to increase competitiveness.
Q.56: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data:
India’s post-1990 economic strategy entailed three important breaks with the past:
- To dismantle the vast network of controls and permits that dominated the economic system.
- To redefine the role of the state as a facilitator of economic transactions and as a neutral regulator rather than the primary provider of goods and services.
- To move away from a regime of import substitution and to integrate fully with the global trading system.
The 1991 reforms unleashed the energies of Indian entrepreneurs and gave untold choice to the consumers and changed the face of the Indian economy. The reform agenda constituted a paradigm shift, and has defined the broad contours of economic policy making for three decades.
Liberalization was adopted as the guiding principle of governance and all governments since 1991, have broadly stuck to that path.
Today we don’t need a paradigm shift. We need to look at individual sectors and see which one of these needs, reforms to create a competitive environment and improve efficiency. The power sector, the financial system, governance structures and even agricultural marketing need reforms.
Today’s reforms also require much more discussion and consensus-building. The central government needs to work in tandem with state governments and consult different stakeholders impacted by reform decisions. Timing and sequencing are critically important in the new reforms’ agenda.
Source: Excerpts from ‘Like 1991, the 2021 crisis presents an opportunity, by C.Rangarajan, 22nd January 2021.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1 : 1991 was a landmark moment in India’s post-independence history as that changed the nature of the economy in fundamental ways.
Statement 2 : India’s economic establishment launched a multipronged reforms agenda to repair India’s macroeconomic balance sheet and ignite growth.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both the statements are true. Due to imposition of economic reforms since 1991, post-independence history of India changed the economy to more liberalized, privatization and more open towards the globalized world. This led to improvement in balance of payment situation of the country and thus increased growth rate.
Q.57: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data:
India’s post-1990 economic strategy entailed three important breaks with the past:
- To dismantle the vast network of controls and permits that dominated the economic system.
- To redefine the role of the state as a facilitator of economic transactions and as a neutral regulator rather than the primary provider of goods and services.
- To move away from a regime of import substitution and to integrate fully with the global trading system.
The 1991 reforms unleashed the energies of Indian entrepreneurs and gave untold choice to the consumers and changed the face of the Indian economy. The reform agenda constituted a paradigm shift, and has defined the broad contours of economic policy making for three decades.
Liberalization was adopted as the guiding principle of governance and all governments since 1991, have broadly stuck to that path.
Today we don’t need a paradigm shift. We need to look at individual sectors and see which one of these needs, reforms to create a competitive environment and improve efficiency. The power sector, the financial system, governance structures and even agricultural marketing need reforms.
Today’s reforms also require much more discussion and consensus-building. The central government needs to work in tandem with state governments and consult different stakeholders impacted by reform decisions. Timing and sequencing are critically important in the new reforms’ agenda.
Source: Excerpts from ‘Like 1991, the 2021 crisis presents an opportunity, by C.Rangarajan, 22nd January 2021.
Read the following statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A) : India’s pre-1990 economic strategy dismantles the vast network of controls and permits that dominated the economic system.
Reason (R) : The 1991 reforms unleashed the energies of Indian entrepreneurs, gave untold choice to consumers and changed the face of the Indian economy.
From the given alternatives choose the correct one:
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
After the economic reforms of 1991, various controls and restrictions in the form of licensing was removed and thus increasing competitiveness of private sector. By following these economic reforms, it increased consumerism and thus led to increase in the flow of goods and services in the economy.
Q.58: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data:
India’s post-1990 economic strategy entailed three important breaks with the past:
- To dismantle the vast network of controls and permits that dominated the economic system.
- To redefine the role of the state as a facilitator of economic transactions and as a neutral regulator rather than the primary provider of goods and services.
- To move away from a regime of import substitution and to integrate fully with the global trading system.
The 1991 reforms unleashed the energies of Indian entrepreneurs and gave untold choice to the consumers and changed the face of the Indian economy. The reform agenda constituted a paradigm shift, and has defined the broad contours of economic policy making for three decades.
Liberalization was adopted as the guiding principle of governance and all governments since 1991, have broadly stuck to that path.
Today we don’t need a paradigm shift. We need to look at individual sectors and see which one of these needs, reforms to create a competitive environment and improve efficiency. The power sector, the financial system, governance structures and even agricultural marketing need reforms.
Today’s reforms also require much more discussion and consensus-building. The central government needs to work in tandem with state governments and consult different stakeholders impacted by reform decisions. Timing and sequencing are critically important in the new reforms’ agenda.
Source: Excerpts from ‘Like 1991, the 2021 crisis presents an opportunity, by C.Rangarajan, 22nd January 2021.
In the light of the given text and common knowledge, identify the incorrect statement: -
(a) A severe balance of payments problem triggered an acute economic crisis in 1991.
(b) In 1991, the economic and political leadership launched a multipronged reforms agenda to repair the macroeconomic situation of the nation.
(c) In post 1991 situation, the state was given the role of primary regulator of the economy.
(d) Post pandemic, individual sectors should be looked closely. Sectors that need reforms should be identified and corrective action should be taken.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
After 1991, the role of the state was reduced. Privatisation led to transfer of ownership of enterprises under public sector to the private sector.
Q.59: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data:
India’s post-1990 economic strategy entailed three important breaks with the past:
- To dismantle the vast network of controls and permits that dominated the economic system.
- To redefine the role of the state as a facilitator of economic transactions and as a neutral regulator rather than the primary provider of goods and services.
- To move away from a regime of import substitution and to integrate fully with the global trading system.
The 1991 reforms unleashed the energies of Indian entrepreneurs and gave untold choice to the consumers and changed the face of the Indian economy. The reform agenda constituted a paradigm shift, and has defined the broad contours of economic policy making for three decades.
Liberalization was adopted as the guiding principle of governance and all governments since 1991, have broadly stuck to that path.
Today we don’t need a paradigm shift. We need to look at individual sectors and see which one of these needs, reforms to create a competitive environment and improve efficiency. The power sector, the financial system, governance structures and even agricultural marketing need reforms.
Today’s reforms also require much more discussion and consensus-building. The central government needs to work in tandem with state governments and consult different stakeholders impacted by reform decisions. Timing and sequencing are critically important in the new reforms’ agenda.
Source: Excerpts from ‘Like 1991, the 2021 crisis presents an opportunity, by C.Rangarajan, 22nd January 2021.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1 : Timing and sequencing are critically important in the post-economic reform agenda.
Statement 2 : Post pandemic reforms in India require a paradigm shift.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Timing and sequencing are critically important in the new reforms agenda. Also, central government works with the state government in tandem after discussion and consensus-building.
Q.60: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following data:
India’s post-1990 economic strategy entailed three important breaks with the past:
- To dismantle the vast network of controls and permits that dominated the economic system.
- To redefine the role of the state as a facilitator of economic transactions and as a neutral regulator rather than the primary provider of goods and services.
- To move away from a regime of import substitution and to integrate fully with the global trading system.
The 1991 reforms unleashed the energies of Indian entrepreneurs and gave untold choice to the consumers and changed the face of the Indian economy. The reform agenda constituted a paradigm shift, and has defined the broad contours of economic policy making for three decades.
Liberalization was adopted as the guiding principle of governance and all governments since 1991, have broadly stuck to that path.
Today we don’t need a paradigm shift. We need to look at individual sectors and see which one of these needs, reforms to create a competitive environment and improve efficiency. The power sector, the financial system, governance structures and even agricultural marketing need reforms.
Today’s reforms also require much more discussion and consensus-building. The central government needs to work in tandem with state governments and consult different stakeholders impacted by reform decisions. Timing and sequencing are critically important in the new reforms’ agenda.
Source: Excerpts from ‘Like 1991, the 2021 crisis presents an opportunity, by C.Rangarajan, 22nd January 2021.
Read the following statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A) : The 1991 reforms released the vitalities of Indian businesspersons.
Reason (R) : The reform agenda established a paradigm shift and defined the broad outlines of economic policy making for years to come.
From the given alternatives choose the correct one:
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The 1991 reforms gave more power to private sector. Hence, Indian Businesspersons along with government changed the structure of economic policy making for the future.
|
130 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Economics: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term I (2021-22)- 2 - Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce
| 1. What is the format of CBSE Class 12 Economics Term I exam? |  |
| 2. What is the syllabus for CBSE Class 12 Economics Term I exam? |  |
| 3. How many marks are allotted to each section in the CBSE Class 12 Economics Term I exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any choices in the CBSE Class 12 Economics Term I exam? |  |
| 5. How can I prepare effectively for the CBSE Class 12 Economics Term I exam? |  |