Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Outside Delhi Set-I) | Geography for Grade 12 PDF Download
Ques 1: State the two groups of factors which affect the profitability of mining.
Ans: Several factors affecting the profitability of mining operations are:
(i) Richness or Grade of the Ore,
(ii) Size of Deposit,
(iii) Method of Mining,
(iv) Accessibility,
(v) Stage of Industrial Development
Ques 2: Which country of the world has the highest road density?
Ans: Japan. With respect to country size/area, Japan has highest road density and is 327 km length of roads per 100 sq km area.
Ques 3: Name any two garrison (cantonment) towns of India.
Ans: Main Cantonment towns of India are:
(i) Ambala,
(ii) Jalandhar,
(iii) Mhow,
(iv) Babina
(v) Udhampur.
Ques 4: Why is West Asia the least developed in rail facilities? Explain one reason.
Ans: West Asia is the least developed in rail facilities because of vast deserts and sparsely populated regions.
Ques 5: Examine the twin environmental problems that have emerged in the 'Indira Gandhi Canal Command Area'.
Ans: Due to intensive irrigation arid excessive use of water has led to the emergence, of two problems of water logging and salinity and both these have adverse effect on soil fertility and agricultural productivity.
Ques 6: Classify minerals on the basis of chemical and physical properties.
Ans: Minerals are divided into groups on the basis of chemical and physical properties. These are:
(i) Metallic and
(ii) Non-Metallic minerals.
Examples of metallic minerals are iron, copper, gold, silver and non-metallic minerals are salt, coal, copper etc.
Ques 7: How can you help in improving the quality of water in your locality?
Ans: Quality of water suffers from large scale of pollution almost throughout the country. In the populated locality, we can avoid dumping all waste matter into water and into our rivers.
Ques 8: Study the map given below carefully and answer the questions that follow: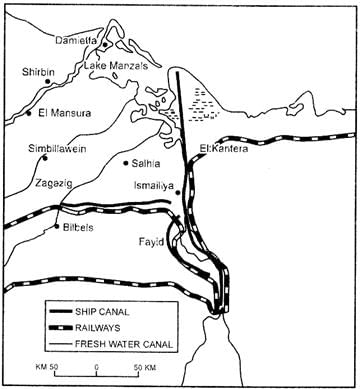 (1) Identify and name the canal shown in the map.
(1) Identify and name the canal shown in the map.
(2) Write any four characteristics of this canal.
Ans: (1) The canal shown in map is SUEZ CANAL, constructed in 1869 between Port Said and Port Suez in Egypt.
(2) The main characteristics of this canal are:
(i) It gives Europe a new gateway to the Indian Ocean and reduces sea-route distance between Liverpool and Colombo by 6400 km compared to Cape of Good Hope route.
(ii) It is a sea level canal without locks which is 130 km long and 11 to 15 meter deep.
(iii) About 100 ships travel daily and each ship takes around 10-12 hours to cross the canal.
(iv) A railway line follows along the canal.
(v) A navigable fresh canal also follows from Nile.
Ques 9: Describe any three characteristics of chain stores in the world.
Ans: The distinctive features oi multiple shops ate as under:
(1) Chain stores specialise m value based article. The articles are sold by all the similar shops charging uniform price.
(2) They operate on "cash and carry" principles and do not allow credit and free delivery services to customers. The goods are sold on cash basis.
(3) The main objective of the chain stores is to establish direct contact with the consumers by eliminating middlemen,
(4) They operate under centralised control and are horizontally integrated.
(5) The layout of these shops is simple and similar.
Ques 10: Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow: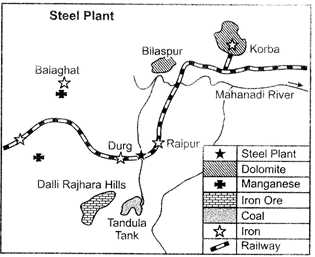 (i) Identify and name the steel plant given above. In which State this plant located?
(i) Identify and name the steel plant given above. In which State this plant located?
(ii) Which is the main source of power for this steel plant? Which rail route provides transport facilities to this plant?
(iii) What are the major sources of Iron-ore and water for this steel plant?
Ans: (i) Steel plant is BHILAI and located in Chhattisgarh State.
(ii) Main power source is KORBA THERMAL POWER STATION. The rail route connecting to this plant is KOLKATA-NAGPUR.
(iii) Major source of rich Hematite Iron Ore for this plant is Dalli-Rajhara Range of mines. The water source is TANDULA TANK?.
Ques 11: 'There is no consensus on what exactly defines a village or a town.? Analyse the statement by using different criteria.
Ans: We all live in cluster of houses which can be called as village or a town. It is widely accepted that settlements can be differentiated in terms of rural (village) and urban (town), but there is no consensus on what exactly defines a village or a town.
Although population size is an important criterion, it is not a universal criteria since many villages in densely populated countries in like India and China have population exceeding than some towns of Europe and USA.
In certain countries, urban settlements are defined on the economic basis. For example, In India, towns are called when it has 75% of its work force engaged in non-agricultural activities, whereas in some western countries an urban area is if more than 50% of the economically productive population are engaged in non-agricultural pursuits.
Ques 12: 'Nature provides opportunities and humans make use of these and slowly nature gets humanised and starts bearing the imprints of human endeavour.' Justify the statement.
Ans: When the human being make use of opportunities provided by nature, it starts bearing the imprints of human endeavour and this situation is known as humanisation of nature. Human beings interact with their physical environment with the help of technology. Technology indicates the level of cultural development of society. Knowledge about Nature is extremely important to develop technology and technology loosens the shackles of environment on human beings.
In the early stages of their interaction with their natural environment humans were greatly influenced by it. They adapted to the dictates of Nature. This is so because the level of technology was very low and the stage of human social development was also primitive. They create possibilities with the resources obtained from the environment. The human activities create the cultural landscape. The imprints of human activities are created everywhere; health resorts on highlands, huge urban sprawls, fields, orchards and pastures in plains and rolling hills, ports on the coasts, oceanic routes on the oceanic surface and satellites in the space.
Ques 13: 'Indiscriminate use of water by increasing population and industrial expansion has led to degradation of the water quality considerably in India.' Explain the values that can help in maintaining the quality of water.
Ans: Indiscriminate use of water by increasing population and industrial expansion has led to degradation of the quality of water considerably.
Values that can help in maintaining the quality of water are:
(1) Water pollution is a source of various water-borne diseases. The diseases commonly caused due to contaminated water are diarrhoea, intestinal worms, hepatitis etc., so water available from rivers, canals, lakes should be purified. Various health organizations should take care of it.
(2) It is the responsibility of community not to dispose garbage waste in water. Time by time water pollution should be checked. Water contamination should be regularly supervised for e.g., project of Ganga cleaning.
(3) Haryali is the water shed development stated by the government of India follow their guidelines.
(4) Industries which are located on the river banks should be monitored for the waste disposals. They should not be throwing the waste in the river.
Ques 14: Mention any four major objectives of the New Industrial Policy, 1991 of India. Describe the role of globalization in achieving these objectives.
Ans: Major objectives of India's New Industrial Policy 1991 are as follows:
(1) The New Industrial Policy, 1991 seeks to liberate the industry from the shackeles of licensing system.
(2) Drastically reduce the role of public sector.
(3) Encourage foreign participation in India's industrial development.
(4) Liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation in industries.
The process of globalization includes opening up of world trade, development of advanced means of communication, internationalization of financial markets, growing importance of MNCs, population migrations and increased mobility of persons, goods, capital, data and ideas but also infections, diseases and pollution. It refers to the integration of economies of the world through uninhibited trade and financial flows, as also through mutual exchange of technology and knowledge.
It also contains free inter-country movement of labour. This implies opening up the economy to foreign direct investment by providing facilities to foreign companies to invest in different fields of economic activity in India, removing constraints and obstacles to the entry of MNCs, allowing Indian companies to enter into foreign collaborations and also encouraging them to set up joint ventures abroad; carrying out massive import liberalization programs by switching over from quantitative restrictions to tariffs and import duties, therefore globalization has been identified with the policy reforms of 1991 in India.
Ques 15: 'The size of a territory and per capita income are not directly related to human development.' Support the statement with examples.
Ans: The size of territory and per capita income are not directly related to human development. Yes, it is true.
(1) Growth of economy and productivity is generally assessed with the help of gross national product and per capital income.
(2) There are few rich and developed states like Maharashtra, Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat and Delhi have per capita income more than Rs. 4,000/month.
(3) Some states have larger area as UP, Bihar, Odisha, MP, Assam and J & K but capital income of these states are 2,000/month.
(4) Poverty is reflected in poor quality of life. Hundreds of malnutrition, deprivation, illiteracy and consequent low level of human development. It does not depend upon the size of territory.
(5) Some large states like Odisha, Bihar, MR UP and Tamil Nadu have more than 50% population below poverty line while Delhi is much smaller area-wise but is a prosperous state.
Ques 16: How is migration a response to the uneven distribution of opportunities over a space? Explain the economic consequences of migration in India.
Ans: Migration is a response to the uneven distribution of opportunities because of the following reasons:
(1) In India many people live in rural areas and they migrate to urban areas mainly due to poverty, high population pressure on land, lack of basic infrastructural facilities like health, education, etc. This proves that migration is responsible for the uneven distribution over space.
(2) People tend to move from place of low opportunity and less safety to a place which has more opportunities and safe.
Economic Consequences:
(1) People migrating send remittance to their families at home and add to economic prosperity. Remittance from international migrants is one of the major sources of foreign exchange. India is the top receiver of remittance from abroad.
(2) Remittance are used for food, repayment of debts, treatment, marriages, children education, agricultural development, construction of houses, etc. Thousands of poor villages of many states works as live blood for economy.
(3) With the ushering of green revolution particularly in Punjab, Haryana, UP, poor people migrated to these stated from Eastern part of UP, Bihar, MP and Odisha. However unregulated migration to metropolitan cities has caused overcrowding and growth of slums.
Ques 17: 'In Modern times international trade is the basis of the world economy.' Support the statement with examples.
Ans: Trade is the base of world economy. The exchange of surplus goods between different countries is called International trade. It is the index of economic development of the country. The countries which export the commodities earn foreign exchange. Developed countries are major trading countries. It also helps to raise the standards of living of the people of developing countries. Some densely populated countries have to import of raw material to meet their demands for their economic and industrial development. Such countries are Japan, Sri Lanka and other countries.
The actual tonnage of goods traded makes up the volume. However, services traded cannot be measured in tonnage is considered to be the volume of trade. The total volume decides.
Trade of primary products was dominant in the beginning of the last century. Later manufactured goods gained prominence and currently, though the manufacturing sector which includes travels, transportation and other commercial services have been showing an upward trend.
Ques 18: Review any five measures adopted to solve the problems of Indian agriculture.
Ans: Measures adopted to solve the problems are:
(1) Indian agriculture is totally dependent on monsoon. The crop production in the cultivated land is directly dependent on rainfall. Excessive rainfall causes flood and less rainfall causes drought conditions. For expansion of irrigation dams, rivers and canals have played a crucial role enhancing agriculture output in country.
(2) The yield of the crops in country is low in comparison to international level. Output of most of the crops such as rice, wheat, cotton and oil seeds in India is much lower than that of USA, Russia, Japan. Use of modern agricultural technologies such as high yield variety or seeds, chemical fertilisers, pesticides and farm -machinery are introduced in India.
(3) The inputs of modern agriculture are very expensive for the farmers to afford- So government is supporting - them by introducing the facilities like farmer loans, machinery loans at very low interest rates.
(4) A large number of farmers produce crops for self-consumption. These farmers do not have enough land and resources to produce more than their requirement. Government is encouraging them to use high yield seeds, fertilisers and provide it in competitive rates.
(5) Government is purchasing crops from farmers directly now-a-days. Government has setup a minimum purchase rate for crops. This make sure that farmers are earning good money with any exploitation of other agencies.
Ques 19: Classify intensive subsistence agriculture into two categories practised in the world. How are they different from each other? Explain.
Ans: Basically, there are two types of intensive subsistence agriculture:
Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation: This type of agriculture is characterised by dominance of the rice crop.
Intensive subsidence agriculture dominated by Non Paddy crops. | |
Paddy | Non Paddy |
Rise is the dominant crop. | Wheat, soyabean, Barley and Sorghum are the main crops. |
Land holdings are very small due to high density of population. | Land holdings are big. |
Labour is supplied by the farmer and his family members. | Machinery deployed for cultivation of non-paddy crops. |
Fertility of soil is maintained by using farm manure. | Fertilisers, pesticides are highly used for increasing soil fertility. |
Ques 20: Classify means of communication on the basis of scale and quality into two categories. Explain any two characteristics of each category.
Ans: The means of communication on the basis of scale and quality into two categories are:
Satellite Communication: Communication through satellites have emerged as a new area in communication technology. Artificial satellites are successfully deployed in the earth's orbit to connect even the remote corners of the globe with limited onsite verification. These have rendered the unit cost and time of communication invariant in terms of distance. It costs the same to communicate over 500 km as it does over 5,000 km via satellite India has also made great strides in satellite development. Aryabhatt was launched on 19th April, 1979, Bhaskar-I in 1979 and Rohini in 1980.
Cyber Space: Internet Cyberspace is the world of electronic computerised space. It is encompassed by the Internet such as the World Wide Web. It is the electronic digital world for communicating over computer networks without physical movement of the sender and the receiver. It is also referred to as the Internet. The speed at which this electronic network has spread is unprecedented in human history. There was over one billion internet users in the world in 2005. Now the majority of the world's users are in U.S.A., U.K., Germany, Japan, China and India. Due to increasing numbers of Internet user each year, cyberspace will expand the contemporary economic and social space of humans through e-mail, e-commerce, e-learning and e-governance.
Ques 21: Identify the five geographical features shown on the given political outline map of the World as A, B, C, D and E and write their correct names on the lines marked near them with the help of the following information: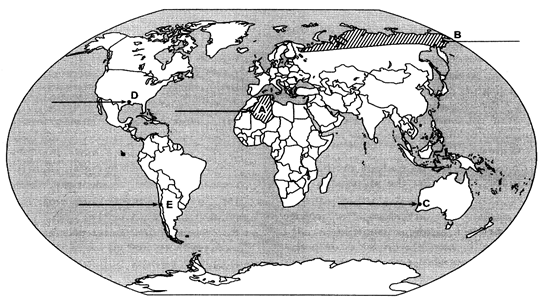 (A) A large country of Africa in terms of area
(A) A large country of Africa in terms of area
(B) A major area of subsistence gathering
(C) The terminal station of a 'Transcontinental Railway'
(D) A major seaport
(E) An international airport
Ans: 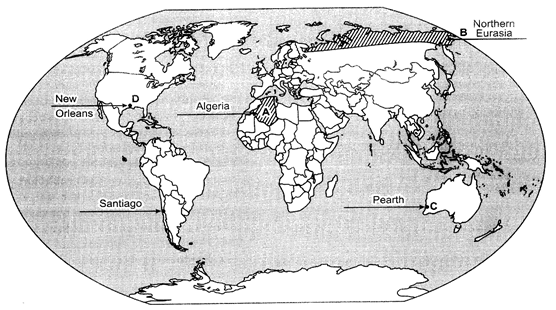
Ques 22: Locate and label the following features with appropriate symbols on the given outline political map of India:
(i) The state having the highest density of population according to Census 2011.
(ii) The leading rice producing state.
(iii) The software technology park located in Gujarat.
(iv) The major coalfield located in Odisha.
(v) An international airport located in Tamil Nadu.
Ans: 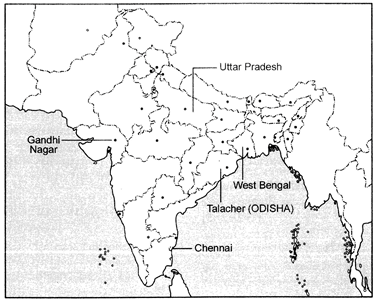
|
168 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Outside Delhi Set-I) - Geography for Grade 12
| 1. What is the importance of solving the Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Outside Delhi Set-I) for Humanities/Arts students? |  |
| 2. How can solving the Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Outside Delhi Set-I) help in exam preparation? |  |
| 3. What are the benefits of solving the Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Outside Delhi Set-I) for Humanities/Arts students? |  |
| 4. How can solving the Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Outside Delhi Set-I) assist in scoring better marks in the final exam? |  |
| 5. Are the questions in the Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Outside Delhi Set-I) representative of the actual exam? |  |





















