Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 HOTS Questions - Contemporary India - I
Q1. What are 'distributaries'?
Ans: The rivers, as they flow towards their lower course, divide into many channels because of the deposition of silt. These channels are called distributaries.
Q2. How 'Punjab Plains' formed?
Ans: The Punjab Plains are located in the western part of the Northern Plains and are primarily formed by the Indus River and its tributaries such as the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Satluj. A major portion lies in Pakistan. These plains are rich in fertile soil and are marked by doabs—tracts of land between two rivers.
Q3. What does 'doab' mean?
Ans: Doab is derived from two words:
- "Do" meaning two
- "ab" meaning water
It refers to a fertile tract of land situated between two converging rivers.
Q4. To which parts Ganga Plains extended?
Ans: The Ganga Plain extends between the Ghaggar and Teesta rivers. It covers several states in North India, including:
- Haryana
- Delhi
- Uttar Pradesh
- Bihar
- Partly Jharkhand
- West Bengal
This region is known for its fertile alluvial soil, making it agriculturally productive.
Q5. What is 'Bhabar'?
Ans: Bhabar is a narrow belt of coarse pebbles and sediments deposited by rivers as they descend from the mountains. It lies parallel to the foothills of the Shiwaliks and is about 8–16 km wide. In this region, streams often disappear due to the porous nature of the soil.
Q6. Which region is called 'Terai Region'?
Ans: South of the bhabar region, streams and rivers reappear, forming a wet, swampy, and marshy area known as the Terai.
- This region is characterised by its rich biodiversity and was once densely forested.
- Much of the forest has been cleared for agriculture and to accommodate migrants from Pakistan after the partition.
- Notable locations in the Terai include Dudhwa National Park.
Q7. What does 'Bhangar' mean?
Ans: The largest part of the northern plains is made up of older alluvium. It is situated above the floodplains of rivers and has a terrace-like appearance. This area is referred to as Bhangar.
Q8. What is 'Khadar'?
Ans: Khadar is the newer, younger alluvial soil found in the floodplains. It is deposited annually by rivers and is more fertile than Bhangar, making it ideal for intensive agriculture.
Q9. How was the Peninsular Plateau of India formed?
Ans: The Peninsular Plateau was formed through the breaking and drifting of the Gondwana land. This process made it part of one of the oldest landmasses on Earth.
- It consists of crystalline, igneous, and metamorphic rocks.
- The plateau features broad, shallow valleys and rounded hills.
- It is divided into two main areas: the Central Highlands and the Deccan Plateau.
- The Central Highlands lie north of the Narmada River and include the Malwa Plateau.
- The Vindhyan range is bordered by the Satpura range to the south and the Aravalis to the northwest.
Q10. Name the two major divisions of the Peninsular Plateau.
Ans: The two major divisions of the Peninsular Plateau are:
- Central Highlands
- Deccan Plateau
Q11. Where are The Central Highlands located?
Ans: The Central Highlands lie north of the Narmada River and include the Malwa Plateau. They are bordered by:
- The Vindhyan Range in the south
- The Aravallis in the northwest
- The Satpura Range to the southwest
They extend eastward into Bundelkhand, Baghelkhand, and further to the Chotanagpur Plateau.
Q12. Which rivers drain Central Highlands?
Ans: The rivers that drain the Central Highlands include:
- Chambal
- Sind
- Betwa
- Ken
Q13. What is the eastward extension of the Central Plateau known as?
Ans: The eastward extensions of the Central Plateau are known as:
- Bundelkhand
- Baghelkhand
- Chotanagpur Plateau
Q14. Which hill ranges form the Deccan Plateau?
Ans: The Deccan Plateau is bordered by several hill ranges:
- The Satpura range lies to the north.
- The Mahadev hills extend to the east.
- The Kaimur hills also form part of the eastern extensions.
- The Maikal range is another eastern extension.
Q15. What is the northeast extension of the Deccan Plateau called?
Ans: The northeast extension of the Deccan Plateau is known as:
- Meghalaya
- Karbi Anglong Plateau
- North Cachar Hills
Q16. What is the average elevation of the Western Ghats?
Ans: The average elevation of the Western Ghats ranges from 900 to 1600 metres.
Q17. Name the highest peak of Western Ghats.
Ans: The highest peak of the Western Ghats is Anai Mudi, standing at an impressive height of 2,695 metres.
Q18. Name the highest peak of Eastern Ghats.
Ans: The highest peak of the Eastern Ghats is Mahendra Giri, which stands at an elevation of 1,501 metres.
Q19. What is the role of the Western Ghats in the southwest Monsoon?
Ans: The Western Ghats play a crucial role in the southwest monsoon by:
- They cause orographic rain as they force moist winds to rise along their western slopes.
- Creating a barrier that enhances rainfall on the western side.
- Influencing the climate and biodiversity of the region.
Q20. Name the famous hill stations of the Western Ghats.
Ans: The famous hill stations in the Western Ghats include:
- Udagamandalam, commonly known as Ooty
- Kodaikanal
Q21. What is Deccan Trap?
Ans: The Deccan Trap refers to the black soil region of the Peninsular Plateau. Key points include:
- It is of volcanic origin, meaning the rocks are igneous.
- Over time, these rocks have weathered and contributed to the formation of black soil.
Q22. Where are Aravali Hills located?
Ans: The Aravali Hills lie along the western and northwestern margins of the Peninsular Plateau. They extend from Gujarat to Delhi in a southwest to northeast direction and are among the oldest mountain ranges in India.
Q23. Which is the only large river of the Indian Desert of Rajasthan?
Ans: The Luni River is the only large river in the Indian Desert. It flows through an arid region with scanty rainfall and disappears into the sand during dry months.
Q24. What are Barchans?
Ans: Barchans are unique sand formations found in desert regions.
- They are shaped like a crescent, resembling a crescent moon.
- These dunes are typically formed by the action of wind.
- Barchans can cover large areas, particularly in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan.
Q25. What are the local names of the Western Coastal Plains?
Ans: The western coastal plains of India are divided into three main sections:
- Konkan: This is the northern part, stretching from Mumbai to Goa.
- Kannad Plain: This central stretch is located in Karnataka.
- Malabar Coast: The southern stretch, which is in Kerala.
Q26. By what names are the Eastern Coastal Plains called?
Ans: The Eastern Coastal Plains are known by two main names:
- The northern part is called the Northern Circar.
- The southern part is referred to as the Coromandel Coast.
These regions are characterised by their wide and level plains along the Bay of Bengal.
Q27. Where is Chilka Lake located?
Ans: The Chilka Lake is the largest saltwater lake in India. It is located in the state of Odisha, south of the Mahanadi Delta.
Q28. How are Lakshadweep Islands formed?
Ans: The Lakshadweep Islands are made up of small coral islands. They are arranged in a horseshoe or ring shape known as atolls.
Q29. Name the capital of Lakshadweep.
Ans: Kavaratti is the capital of Lakshadweep.
Q30. How are Andaman & Nicobar Islands formed?
Ans: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are formed primarily through volcanic eruptions in the sea, specifically in the Bay of Bengal.
- These islands are part of an elevated portion of submarine mountains.
- They consist of various islands, with the Andaman Islands in the north and the Nicobar Islands in the south.
- The region is known for its rich biodiversity and strategic importance.
Q31. What is the contribution of the northern chain of mountain blocks?
Ans: The northern chain of mountains plays a vital role in India's geography and ecology. Their contributions include:
- Water Sources: They are major sources of water, feeding rivers that support agriculture and drinking needs.
- Forest Wealth: These mountains are rich in forests, providing timber and habitat for diverse wildlife.
- Natural Barriers: They act as natural barriers, protecting the country from harsh weather and external threats.
Q32. What is the importance of plateaus in India?
Ans: The plateaus in India are significant for several reasons:
- They serve as storehouses of minerals.
- These minerals have been vital for the country's industrialisation.
- Plateaus support various economic activities, contributing to regional development.
Q33. Name the major physiographic divisions of India.
Ans: The major physiographic divisions of India include:
- The Himalayan Mountains
- The Northern Plains
- The Peninsular Plateau
- The Indian Desert
- The Coastal Plains
- The Islands
Q34. Give a brief description of the Himalayan Mountains.
Ans: The Himalayan Mountains are a young and rugged mountain range located along the northern borders of India. They extend in a west-east direction from the Indus River to the Brahmaputra River.
- They are known for their high peaks, deep valleys, and fast-flowing rivers.
- The Himalayas form an unstable geological zone, representing a youthful topography.
- This mountain system includes the loftiest peaks in the world.
Q35. Describe the three parallel ranges of the Himalayas.
Ans: The three parallel ranges of the Himalayas are:
Great Himalayas (Himadri):
- Highest peaks, with an average height of 6,000 metres.
- Contains famous mountains and is snow-covered.
Lesser Himalayas (Himachal):
- Altitude ranges from 3,700 to 4,500 metres.
- Composed of compressed rocks; includes the Pir Panjal range.
Shiwaliks:
- Lowest range, with altitudes between 900 and 1,100 metres.
- Made of sediments from rivers; features valleys known as Duns.
Q36. Name the highest peaks of the Himalayas with their heights.
Ans:
- Mt. Everest – 8,848 metres, Nepal
- Kanchenjunga – 8,598 metres, India
- Dhaulagiri – 8,172 metres, Nepal
- Nanga Parbat – 8,126 metres, India
- Annapurna – 8,078 metres, Nepal
- Nanda Devi – 7,817 metres, India
- Kamet – 7,756 metres, India
- Namcha Barwa – 7,756 metres, India
- Guria Mandhata – 7,728 metres, Nepal
Q37. Why are the Shiwalik ranges prone to earthquakes?
Ans: The Shiwalik ranges are particularly vulnerable to earthquakes due to several factors:
- They are still undergoing folding, indicating geological activity.
- This range is the youngest part of the Himalayas.
- It consists of unconsolidated rock material, which is less stable.
As a result, these ranges frequently experience earthquakes and landslides.
Q38. Classify the Himalayas on the basis of regions from the West to East.
Ans: The Himalayas can be classified into distinct regions based on river valleys from west to east:
- Punjab Himalayas – Located between the Indus and Satluj rivers. This region is also known as Kashmir and Himachal Himalayas.
- Kumaon Himalayas – Found between the Satluj and Kali rivers.
- Nepal Himalayas – Situated between the Kali and Teesta rivers.
- Assam Himalayas – Lies between the Teesta and Dihang rivers.
- Purvachal – The easternmost part, extending beyond the Dihang gorge.
The eastern boundary of the Himalayas is marked by the Brahmaputra river.
Q39. What do you know about 'Purvanchal'?
Ans:Purvanchal refers to the eastern hills located in northeastern India. Features include:
Composed of sandstone and covered with dense forests
Includes Patkai Bum, Naga Hills, Manipur Hills, Mizo Hills, Garo, Khasi, and Jaintia Hills
Formed by the extension of the Himalayas beyond the Dihang gorge
Q40. Why are the Northern Plains the agriculturally productive parts of India?
Ans: The Northern Plains of India are highly productive for agriculture due to several key factors:
- They are nourished by three major river systems: the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra, along with their tributaries.
- These rivers deposit alluvial soil in vast basins at the foothills of the Himalayas, creating fertile land.
- The region benefits from a rich soil cover, ensuring high fertility.
- There is an adequate water supply from the rivers, which supports irrigation.
- The climate in this area is favourable for various crops, enhancing agricultural productivity.
Q41. How are riverine islands formed?
Ans: Riverine islands are formed through a natural process involving rivers. Here’s how it happens:
- Rivers originating from the northern mountains carry and deposit alluvium as they flow.
- In the lower course of the river, the slope is gentle.
- This gentle slope causes the river's velocity to decrease.
- As a result, sediment builds up, leading to the formation of riverine islands.
Q42. Classify the Northern Plains on the basis of location.
Ans: The Northern Plains can be classified into three main sections:
- Punjab Plains – Located in the western part, formed by the Indus River and its tributaries.
- Ganga Plains – Extends between the Ghaggar and Teesta rivers, covering regions such as Delhi, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- Brahmaputra Plains – Situated east of the Ganga Plains, encompassing Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
Q43. Write any three characteristics of the Central Highlands.
Ans: The Central Highlands are a significant part of the Peninsular Plateau, located north of the Narmada River and primarily covering the Malwa Plateau. Here are three key characteristics:
- Geographical Extent: They extend from the northwest, merging with the sandy and rocky desert of Rajasthan.
- Width Variation: The region is wider in the west and narrows towards the east.
- Eastern Extensions: The eastern parts are known as Bundelkhand and Baghelkhand, with the Chota Nagpur Plateau being the easternmost area, drained by the Damodar River.
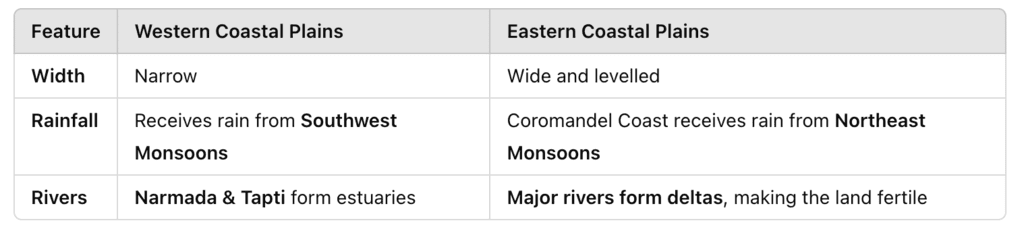
Q44. Differentiate between the Western Coastal Plains and the Eastern Coastal Plains.
Ans: The Western Coastal Plains and the Eastern Coastal Plains of India differ in several key aspects:
Q45. Where are the famous passes of the Himalayas located?
Ans:
- Shipkila Pass – Situated on the Tibet-Himalaya Road in the Satluj Valley, Himachal Pradesh.
- Nathula Pass – Located in Sikkim, connecting India to Lhasa in the Chumbi Valley.
- Bomdila Pass – Found in Arunachal Pradesh, leading to the Arunachal-China border.
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 HOTS Questions - Contemporary India - I
| 1. What are the major physical features of India? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Himalayan mountain range in India? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of the Thar Desert in India? |  |
| 4. How do the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats impact India? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the Deccan Plateau in India? |  |






















