Class 9 History Chapter 2 Previous Year Questions - Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. How did Social Democrats disagree with Social Revolutionaries? [2025]
Ans. Social Democrats disagreed with Social Revolutionaries due to following reasons:
- Socialist Revolutionary Party was formed in 1900. They were in favour of peasant's rights. They demanded that land belonging to the nobles be transferred to peasants.
- Disagreed with Socialist Revolutionaries regarding the role of peasants. Lenin felt that peasants were not one united group because there were poor, rich, labourers and capitalists among them. So they could not all be the part of a socialist movement.
Q.2. Explain the consequences of the February Revolution of 1917 in Russia. [2024]
Ans. Consequences of the February Revolution of 1917 in Russia are as mentioned below:
- Tsar abdicated on 2 March.
 Russian Revolution
Russian Revolution
- Soviet leaders and Duma leaders formed a provisional government to run the country.
- It was agreed that Russia’s future would be decided by a constituent assembly, elected on the basis of universal adult suffrage.
- The provisional government removed restrictions on public meetings and associations.
- Soviets, like the Petrograd Soviet, were set up everywhere, though no common system of election was followed.
Q.3. Liberals were not Democrats. Explain.
OR
Why do we say that liberals could not be called ‘democrats’? [2024]
Ans. The liberals could not be called democrats because even though they argued for a representative, elected parliamentary government, subject to laws interpreted by a well-trained judiciary that was independent of rulers and officials, they did not believe in universal adult franchise and also did not want the voting rights for women. They felt that the right to vote should only be given to the propertied men.
Q.4. How did Social Democrats disagree with Socialist-Revolutionaries? [2023]
Ans. Social Democrats disagreed with Socialist Revolutionaries in the following ways:
(i) Social Democrats believed workers to be the main force of revolution whereas Socialist Revolutionaries argued that peasants would be the revolutionary class.
(ii) Social Democrats wanted benefits for the workers and control on the factors of production. Socialist Revolutionaries, on the other hand, demanded land for the peasants.
(iii)Social Democrats felt that peasants were not a united group as they were rich and poor and many owned large tracts of land. Socialist Revolutionaries favoured peasants as natural socialists.
Q.5. What was the difference between Bolshevik and Menshevik group? [2022]
OR
Who were the Bolsheviks and Mensheviks?
Ans. The Bolsheviks were the majority group led by Vladimir Lenin who thought that in a repressive society like Tsarist Russia, the party should be disciplined and control the number and quality of its members.
 Mensheviks Flag and Bolsheviks Flag
Mensheviks Flag and Bolsheviks Flag
The Bolsheviks were the group that led the Russian Revolution. Mensheviks, on the other hand, were the minority group who thought that the party should be open to all. They did not believe in revolution but wanted to bring changes through democratic means.
Q.6. Discuss Lenin’s ‘April Theses’. [2022]
OR
What were the demands referred to in Lenin’s ‘April Theses’?
Ans. The following were the demands referred to in Lenin’s April Theses:
(i) World War I should be brought to an end.
(ii) Land should be transferred to the peasants.
(iii) Banks should be nationalised.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Describe the sequence of events responsible for the Revolution of 1905 in Russia. [2024]
Ans. The sequence of events responsible for the Revolution of 1905 in Russia was as given below:
- Autocracy: There was autocracy in Russia. Liberals, Social Democrats and Socialist Revolutionaries demanded a constitution.
- In the year 1904: Prices rose and wages declined.
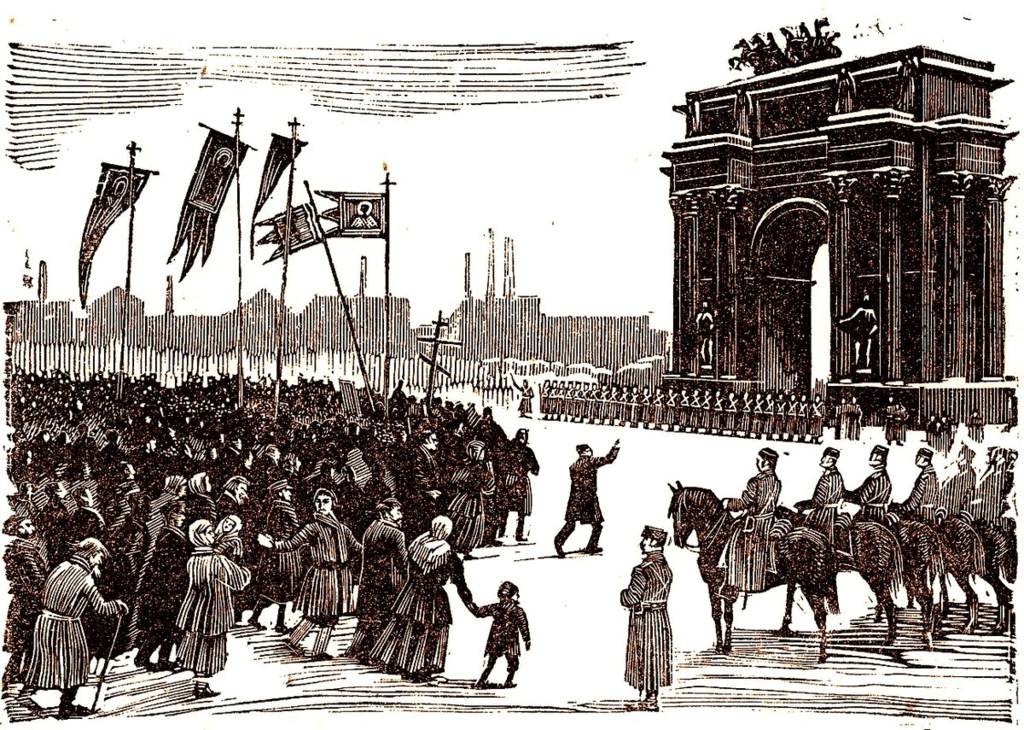 Revolution of 1905 in Russia
Revolution of 1905 in Russia
- Dismissal of four workers of the Assembly of Russian Workers was the immediate cause that led to workers’ strike.
- Demands: They demanded a reduction in the working day to eight hours, an increase in wages and improvement in working conditions.
- Bloody Sunday: A procession of workers led by Father Gapon was attacked by the police killing 100 workers. This led to a series of events that became the 1905 Revolution.
- Results:
(a) The Tsar allowed the creation of an elected consultative Parliament or Duma.
(b) A large number of trade unions and factory committees of factory workers came into existence.
Q.2. Briefly describe the general impact of the First World War on Russia. [2022]
Ans. The general impact of the First World War was as mentioned below:
- Initially, the war was popular and people rallied around Tsar.
- As the war continued, the support became less as Tsar did not consult the main parties in the Duma.
- Defeat of Russian armies in Germany and Austria.
- By 1917 there were 7 million casualties.
 World War I
World War I - As Germany controlled the Baltic Sea, Russian industries could not get supplies. Similarly, there was a breakdown of the railway lines and shortage of labour as most of them were fighting the First World War.
- On their retreat, the Russian army destroyed crops and buildings to prevent the enemy from being able to live off the land. The destruction of crops and buildings led to over 3 million refugees in Russia.
Q.3. Describe the global impact of the Russian Revolution. [2021]
Ans.
- In many countries, communist parties were formed, e.g., the Communist Party of Great Britain.
- The Bolsheviks encouraged colonial people to fight against imperialism.
- Many non-Russians from outside the USSR participated in the Conference of the People of the East (1920). The Bolsheviks founded a committee that served as an international union of pro-Bolshevik socialist parties.
- Some received education in the USSR’s Communist University of the Workers of the East.
- By the time of the outbreak of the Second World War, the USSR had given socialism a global face which eventually led to the rise of the Cold War in Europe.
Q.4. Why did the Bolshevik Party accept the April Theses? Give any five reasons. [2021]
Ans. Bolshevik Party accepted the April Theses because of the following reasons:
(i)The Provisional Government under Kerenskii failed to fulfil the aspirations of the people like land to the tiller, peace, control of industries by the workers, etc. Rather it became more unpopular.
(ii) The government was under the influence of landowners, army officials and industrialists that affected its decisions.
(iii) Lenin felt that time had come to seize power from the government.
(iv) People’s demands were included in the programme along with exit from the war and nationalisation of banks.
(v) Lenin’s view was accepted when the Provisional Government began suppressing the Bolsheviks.
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 History Chapter 2 Previous Year Questions - Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
| 1. What were the main causes of the Russian Revolution? |  |
| 2. What was the impact of World War I on the Russian economy? |  |
| 3. Who were the Bolsheviks and what role did they play in the Russian Revolution? |  |
| 4. How did the ideology of socialism influence the Russian Revolution? |  |
| 5. What were the outcomes of the Russian Revolution for the Russian society? |  |

















