Class 9 Maths Question Answers - Circles
Q1. In the figure, if ∠ ACB = 35°, then find the measure of ∠ OAB.
Ans: ∠AOB = 180° - (∠1 + ∠2)
= 180° - (35° + 35°) [∵ AO = OB ∴ ∠1 = ∠2]
= 110°
∠ACB = (1/2)(∠AOB) = (1/2) (110°) = 55°
Q2. If points A, B and C are such that AB ⊥ BC and AB = 12 cm, BC = 16 cm. Find the radius of the circle passing through the points A, B and C.
Ans: ∵ AB ⊥ BC
∴ ∠B = 90° [Angle in a semicircle]
⇒ AC is a diameter
AC = 20
Radius = 10cm
Q3. The angles subtended by a chord at any two points of a circle are equal. Write true or false for the above statement and justify your answer.
Ans: False. If two points lie in the same segment only, then the angles will be equal otherwise they are not equal.
Q4. Two chords of a circle of length 10 cm and 8 cm are at the distance 8.0 cm and 3.5 cm, respectively from the centre, state true and false for the above statement.
Ans: False. As the larger chord is at a smaller distance from the centre.
Q5. If AB = 12 cm, BC = 16 cm and AB is perpendicular to BC, then the radius of the circle passing through the points A, B and C is
Ans:
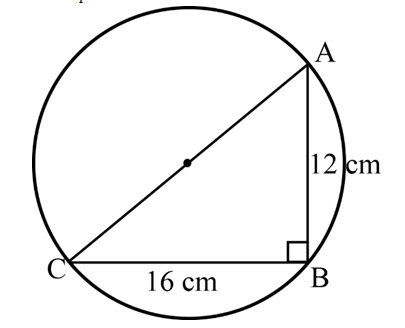
Assuming that AB = 12 cm and BC = 16 cm
If BC and AB are in a circle, then AC will be the circle's diameter.
[circular's diameter forms a right angle to the circle]
Apply the Pythagorean theorem to the ABC right angle.
AC2=AB2+BC2⇒
AC2=(12)2+(16)2⇒
AC2=144+256⇒ AC2=400
⇒ AC2=√400=20 cm
[using the square root of a positive number since the diameter is always positive]
∴ Circle radius = 1/2(AC)=1/220=10 cm
As a result, the circle's radius is 10 cm.
Q6. In Figure, if ∠ABC = 20º, then ∠AOC is equal to:
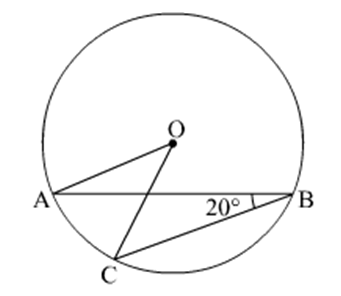 Ans: Assumed: ABC = 20°...(1)
Ans: Assumed: ABC = 20°...(1)
We are aware that an arc's angle at the circle's center is twice as large as its angle at the rest of the circle.
= ∠AOC = 2(20°) (From (1))
= ∠AOC = 40°
∠AOC thus equals 40°
Q7. Two chords AB and AC of a circle with center O are on the opposite sides of OA. Then ∠OAB = ∠OAC.
Write true or false for the above statement and justify your answer.
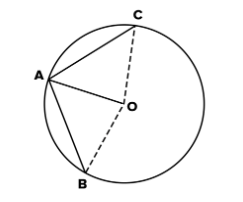
Ans:
Two chords are used: AB and AC.
Join us, OB and OC.
Specifically, triangle OAC and OAB
OA (common side) = OA
Triangles OAB and OAC are not congruent, therefore it is impossible to prove that any third side or angle is equivalent. OC = OB (radius of the circle).
<OAC and <OAB
The claim is untrue as a result.
Ans: Given that ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral with angles of 90°, 70°, 95°, and 105°,
We are aware that the sum of the opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral is 180°.
It can be expressed mathematically as follows: ∠A +∠ C = 90° + 95° = 185° 180°
∠B +∠ D = 70° + 105° = 175°
The sum of the opposing angles in this situation is not 180°.
It is therefore not a cyclic quadrilateral.
The claim is false as a result.
Q9. In Fig, if AOB is the diameter of the circle and AC = BC, then ∠CAB is equal to:
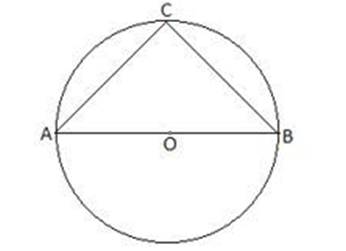
Ans: We are aware that the circle's diameter forms a right angle.
∠BCA = 90∘ ......(i)
AC = BC, and (ii) <ABC=<CAB (the angle opposite to equal sides is equal)
In △ ABC, ∠CBA+∠ABC+∠BCA=180∘ [Triangle's angle-sum attribute]]
∠CAB+∠CAB+90∘=180∘
2 ∠CAB=90∘
∠CAB=45∘.
Q10. Two chords AB and CD of a circle are each at distances 4 cm from the center. Then AB = CD.
Write true or false for the above statement and justify your answer.
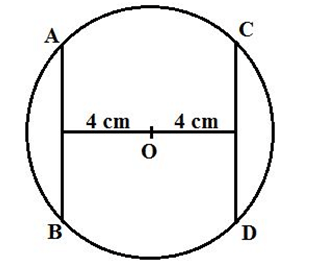 Ans: The right answer is True.
Ans: The right answer is True.
The above assertion is accurate since chords that are equally spaced from a circle's center have equal lengths.
AB=CD
Q11. If A, B, C, and D are four points such that ∠BAC = 30° and ∠BDC = 60°, then D is the center of the circle through A, B and C.
Write true or false for the above statement and justify your answer.
Ans: False
Because there are numerous places D where ∠BDC=60°, none of which can be the center of the circle formed by points A, B, and C.
|
40 videos|560 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Maths Question Answers - Circles
| 1. What are the basic properties of a circle? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the circumference of a circle? |  |
| 3. What is the area of a circle and how is it calculated? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a chord and a diameter in a circle? |  |
| 5. How can a circle be constructed using a compass and straightedge? |  |
















